Which Is Most Secure Radius Pki

Organizations face a critical security dilemma: selecting the most robust authentication method to protect their networks. The debate centers on RADIUS coupled with PKI, but pinpointing the definitively "most secure" configuration demands careful analysis.
This article cuts through the complexity to identify key considerations and best practices for achieving optimal security with RADIUS and PKI, focusing on real-world implementations and vulnerabilities.
Understanding the Fundamentals
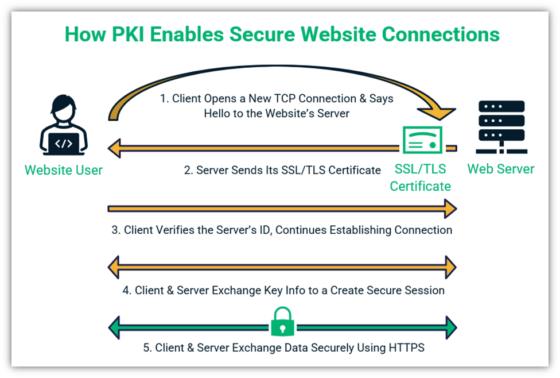
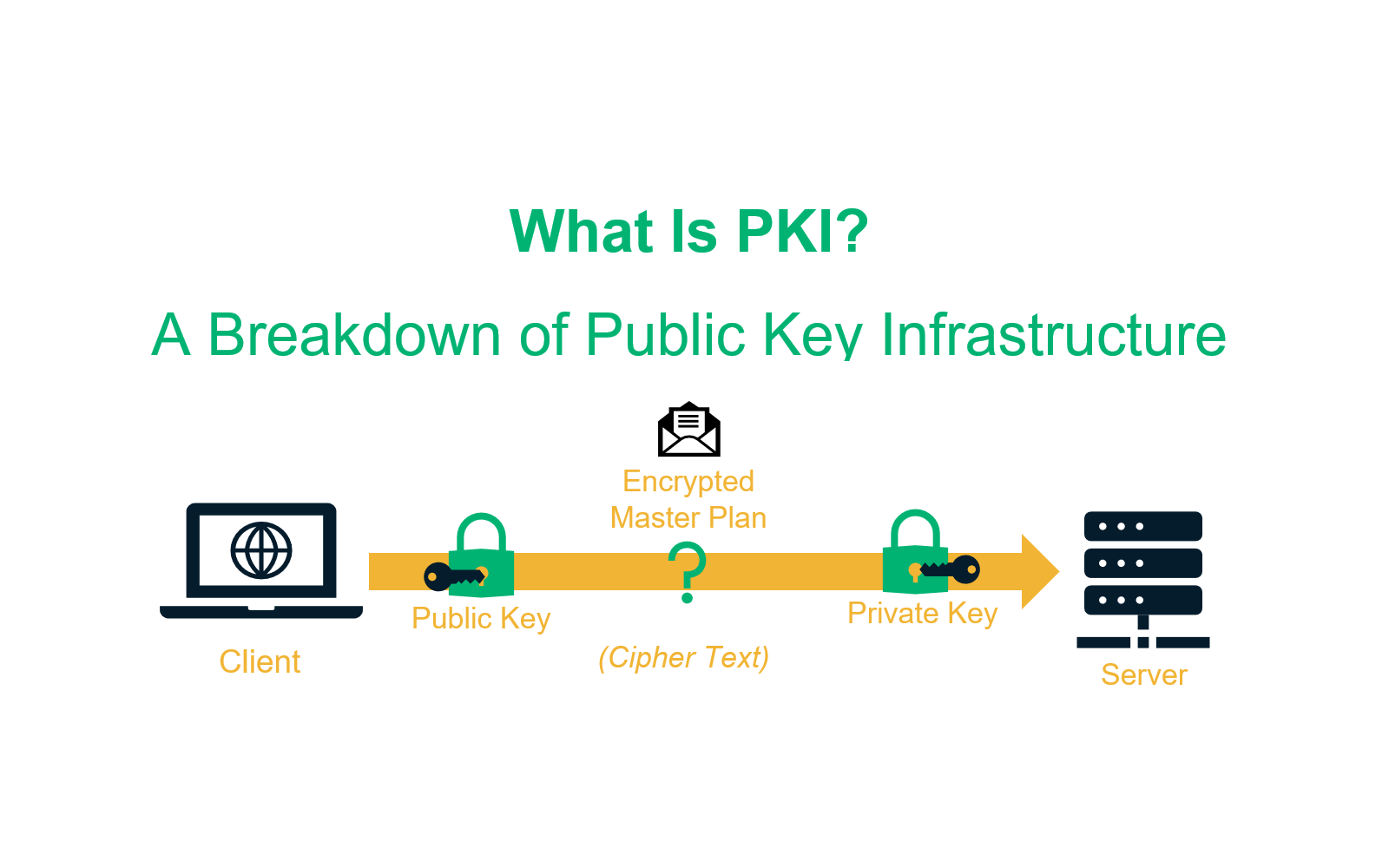
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) is a networking protocol that provides centralized Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) management for users who connect to a network service. PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) uses digital certificates to verify the identity of users and devices.
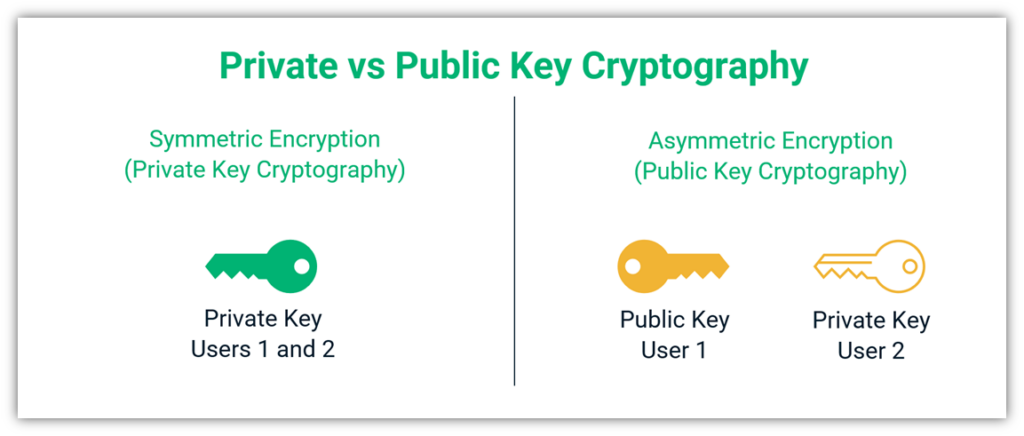
The combination of RADIUS and PKI enhances security by replacing weaker authentication methods like passwords with certificate-based authentication. Certificate-based authentication is much harder to compromise than password-based systems.
Key Considerations for Secure RADIUS PKI Implementations
The strength of a RADIUS PKI setup hinges on several critical components. Improper configuration in any of these areas can significantly weaken security.
Certificate Authority (CA) Management
The CA issuing the certificates is paramount. A compromised CA instantly invalidates the entire security model.
Organizations should use reputable, well-audited CAs or establish their own internal CAs with strict security controls.
Certificate Revocation
A robust certificate revocation process is essential. Compromised or lost certificates must be revoked immediately to prevent unauthorized access.
Implementing Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) or Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) responders is crucial for real-time revocation checks.
RADIUS Server Configuration
The RADIUS server must be hardened against attacks. This includes regularly patching the server software and disabling unnecessary services.
Strong encryption protocols, like TLS 1.2 or higher, should be enforced for all communication between the RADIUS server and clients.
Client Configuration
Clients, whether they are Wi-Fi access points, VPN gateways, or individual workstations, must be configured to properly validate certificates. Mutual authentication, where both the client and the server authenticate each other, is highly recommended.
Clients should also be configured to check the CRL or OCSP responder to ensure that certificates have not been revoked.
Addressing Common Vulnerabilities
Several vulnerabilities can undermine the security of RADIUS PKI implementations.
Weak Certificate Validation
Failure to properly validate certificates on the client side is a common mistake. Clients may accept certificates from untrusted CAs or fail to check for revocation.
Careful configuration and monitoring are necessary to prevent this type of vulnerability.
Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
While PKI provides strong authentication, it is still susceptible to Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks if not properly configured. This attack involves intercepting communication between the client and the server.
Mutual authentication and strong encryption can mitigate the risk of MITM attacks.
Compromised Private Keys
If the private key associated with a certificate is compromised, an attacker can impersonate the legitimate user or device.
Protecting private keys with strong encryption and storing them securely is paramount.
Best Practices for Maximizing Security
To achieve the highest level of security with RADIUS PKI, organizations should adhere to the following best practices:
- Use strong encryption algorithms for certificate generation and communication.
- Implement a robust certificate revocation process.
- Harden RADIUS servers and clients against attacks.
- Regularly audit and monitor the RADIUS PKI infrastructure.
- Train users on security awareness and best practices.
Organizations should also conduct regular penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities and assess the effectiveness of their security controls.
Conclusion: Ongoing Vigilance is Key
While no single RADIUS PKI configuration can be definitively declared "most secure" in all contexts, adhering to the above best practices and continuously monitoring for vulnerabilities is crucial. The security landscape is constantly evolving, so organizations must remain vigilant and adapt their security measures accordingly.
Immediate next steps include reviewing existing RADIUS PKI configurations for weaknesses and implementing necessary security enhancements. Continuous monitoring and regular security audits are essential for maintaining a strong security posture.