Which Of The Following Conditions Promotes Edema

Imagine your favorite pair of shoes, snug yet comfortable, suddenly feeling tight and restrictive by the end of the day. Or perhaps noticing your fingers appearing a little plumper than usual, rings feeling stubbornly stuck. It’s a common experience many of us have brushed aside, attributing it to a long day or salty meal. But what if these subtle changes are whispers from your body, hinting at something more than just fleeting discomfort?
This article dives into the world of edema, exploring the conditions that can lead to this often-overlooked phenomenon. We'll uncover the various health states that can contribute to fluid retention, helping you understand when it's a minor inconvenience and when it warrants a closer look by a healthcare professional.
What is Edema?
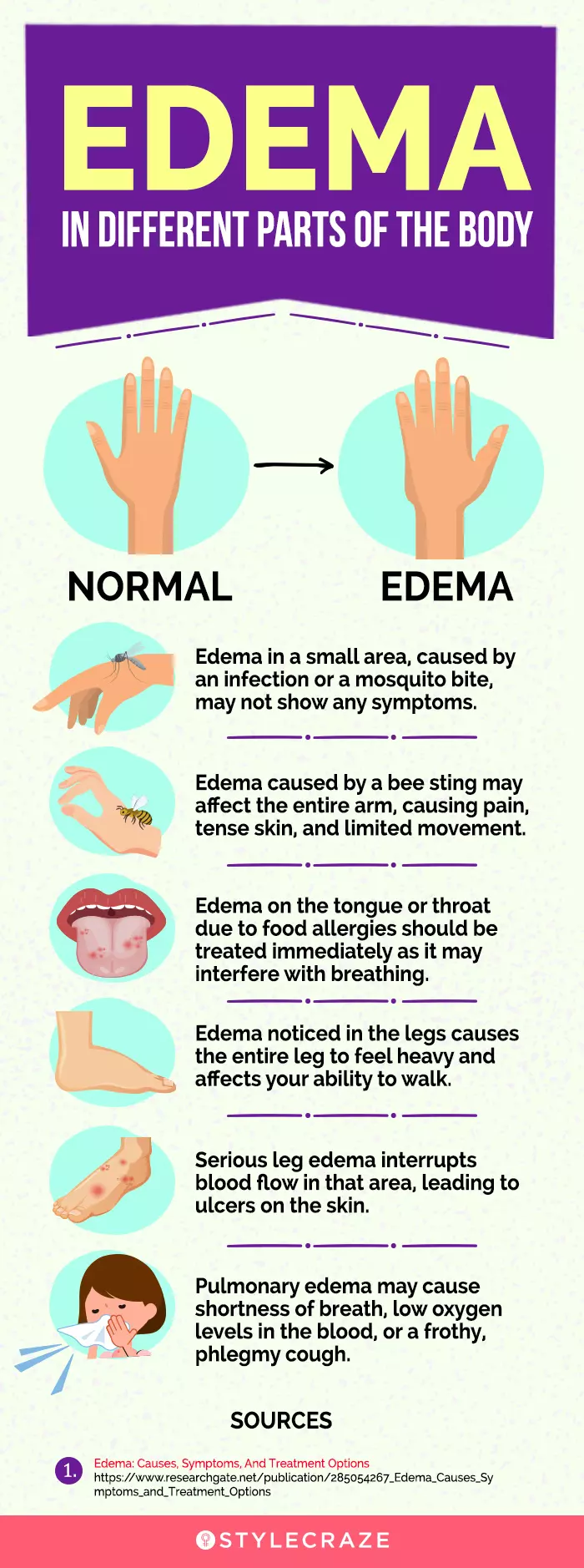
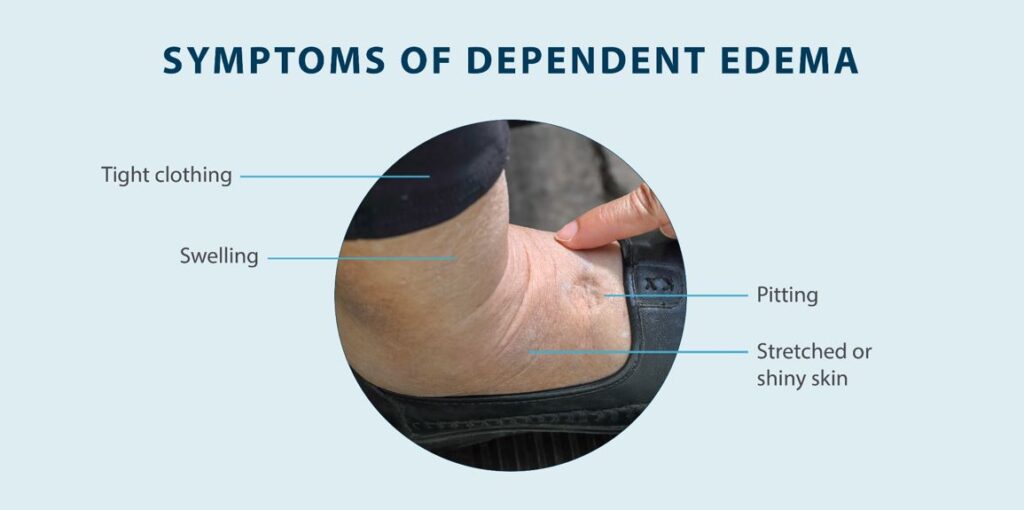
Edema, simply put, is swelling caused by excess fluid trapped in your body's tissues. While it can occur anywhere, it's most noticeable in the hands, arms, feet, ankles, and legs. The underlying causes are varied, ranging from temporary lifestyle factors to more significant underlying medical conditions.
The Body's Fluid Balance
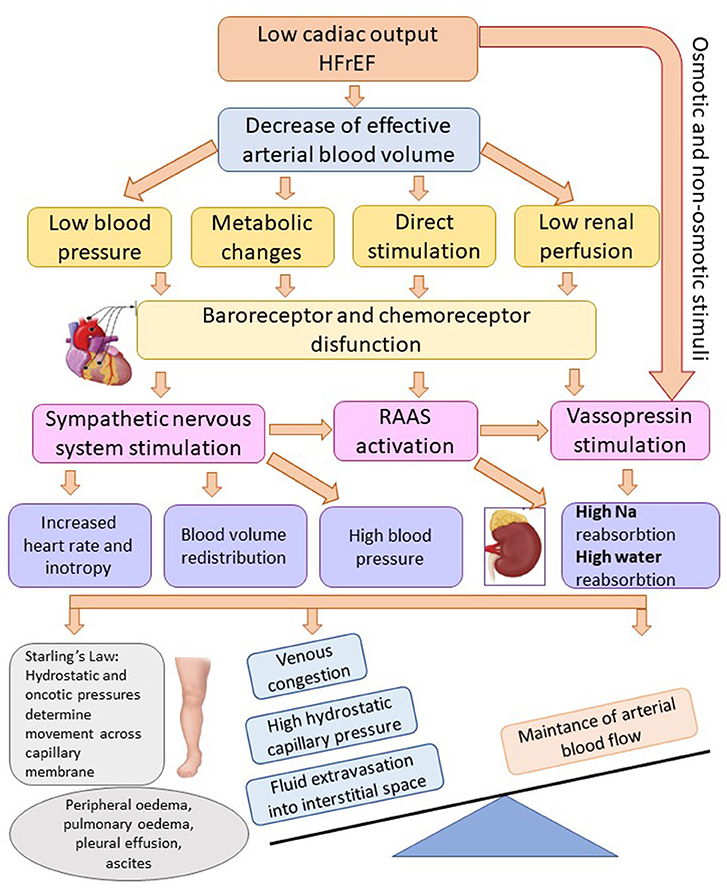
Our bodies are remarkably adept at maintaining a delicate balance of fluids. This balance is maintained by several systems working in harmony, including the circulatory system (heart and blood vessels), the lymphatic system, and the kidneys. When one or more of these systems is compromised, fluid can leak out of the blood vessels and accumulate in the surrounding tissues.
The circulatory system ensures the efficient transport of blood and nutrients to all parts of the body. The lymphatic system helps remove waste and excess fluid from tissues. Finally, the kidneys play a crucial role in regulating fluid levels by filtering waste and excess water from the blood.
Conditions That Promote Edema
Several factors and conditions can disrupt this delicate fluid balance, leading to edema.
Lifestyle Factors
Sometimes, edema is a temporary inconvenience linked to lifestyle choices. Prolonged standing or sitting, especially during long flights, can hinder blood flow back to the heart, leading to fluid buildup in the lower extremities.
A diet high in sodium can also contribute to fluid retention. Sodium causes the body to hold onto more water, leading to swelling, especially if kidney function is slightly impaired.
Medical Conditions
However, edema can also be a symptom of a more serious underlying medical condition, necessitating prompt medical attention.
Heart Failure
Heart failure occurs when the heart cannot pump blood effectively enough to meet the body's needs. This can cause blood to back up in the veins, leading to fluid buildup in the lungs and extremities. This is a classic symptom of heart failure, and often presents as swelling in the ankles and legs.
Kidney Disease
The kidneys are vital for regulating fluid and electrolyte balance. When the kidneys are not functioning properly, they may not be able to remove excess fluid from the body, resulting in edema. Kidney disease can manifest in many ways, so it is important to seek care to get an accurate diagnosis.
Liver Disease
Liver disease, particularly cirrhosis, can lead to a decrease in albumin production. Albumin is a protein in the blood that helps keep fluid in the blood vessels. A shortage of albumin allows fluid to leak into the tissues, particularly in the abdomen (ascites) and legs.
Venous Insufficiency
Venous insufficiency is a condition in which the veins in the legs have difficulty sending blood back to the heart. This can cause blood to pool in the legs, leading to swelling and other complications. This can cause pain, skin changes and ultimately lead to the formation of ulcers.
Lymphedema
Lymphedema occurs when the lymphatic system is blocked or damaged, preventing the proper drainage of lymph fluid. This can result in swelling, most commonly in the arms or legs. Common causes of lymphedema include cancer treatment and surgical removal of lymph nodes.
Pregnancy
Mild edema is common during pregnancy due to hormonal changes and increased blood volume. However, sudden or severe swelling can be a sign of preeclampsia, a serious pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine, and warrants immediate medical attention.
Medications
Certain medications, such as some blood pressure medications, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and steroids, can also contribute to edema. If you suspect your medication is causing swelling, consult your doctor.
Other Potential Causes
Less common causes of edema include allergic reactions, infections, and nutritional deficiencies. It is important to consider all the symptoms presented in order to come to the correct conclusion.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While mild edema can often be managed with simple lifestyle changes, it's important to know when to seek medical attention. You should consult a doctor if you experience:
- Sudden or severe swelling
- Edema accompanied by shortness of breath, chest pain, or difficulty breathing
- Swelling that doesn't improve with elevation or compression
- Edema associated with pain, redness, or warmth in the affected area
These symptoms could indicate a serious underlying medical condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing the cause of edema typically involves a physical exam, a review of your medical history, and potentially some diagnostic tests. These tests may include blood tests to assess kidney and liver function, urine tests, and imaging studies such as ultrasound or X-rays.
Treatment for edema depends on the underlying cause. It may involve lifestyle changes, such as reducing sodium intake and elevating your legs, as well as medications to remove excess fluid (diuretics) or to treat the underlying medical condition. In some cases, compression stockings can help improve blood flow and reduce swelling.
Living with Edema
For those living with chronic edema, managing the condition becomes a daily priority. In some cases, dietary adjustments, such as a low-sodium diet, can make a significant difference. Regular exercise can help improve circulation and reduce fluid buildup.
Compression therapy can also be incredibly beneficial, providing support to the veins and lymphatic system, aiding in fluid drainage. Regular monitoring of weight and swelling is also important for identifying changes and adjusting treatment accordingly.
A Note on Self-Care
It is always a good idea to seek a consult from a medical professional to get an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan. However, there are some steps that can be taken to help manage the symptoms in the meantime.
Remember, self-care is not a substitute for professional medical advice. However, simple measures can provide relief and improve your overall quality of life.
Conclusion
Edema, while often a benign and temporary inconvenience, can sometimes be a sign of a more significant health issue. Understanding the conditions that promote edema empowers us to be more attuned to our bodies and seek appropriate medical attention when needed. By recognizing the warning signs and taking proactive steps, we can work towards maintaining a healthy fluid balance and overall well-being.