Which Of The Following Devices Measures Air Pressure

Time is of the essence. Determining the correct device for measuring air pressure is crucial for various applications, ranging from weather forecasting to aviation safety.
Understanding which instrument accurately gauges atmospheric pressure is no longer optional, it's a necessity. This article cuts through the confusion and delivers a clear, definitive answer.
The Answer: The Barometer
The device that measures air pressure is the barometer. This instrument is fundamental in meteorology and other fields concerned with atmospheric conditions.
What is a Barometer?
A barometer measures atmospheric pressure, the force exerted by the weight of air above a given point. This pressure is often reported in units like inches of mercury (inHg), millimeters of mercury (mmHg), or Pascals (Pa).
Types of Barometers
There are two main types of barometers: mercury barometers and aneroid barometers. Each uses a different mechanism to gauge air pressure.
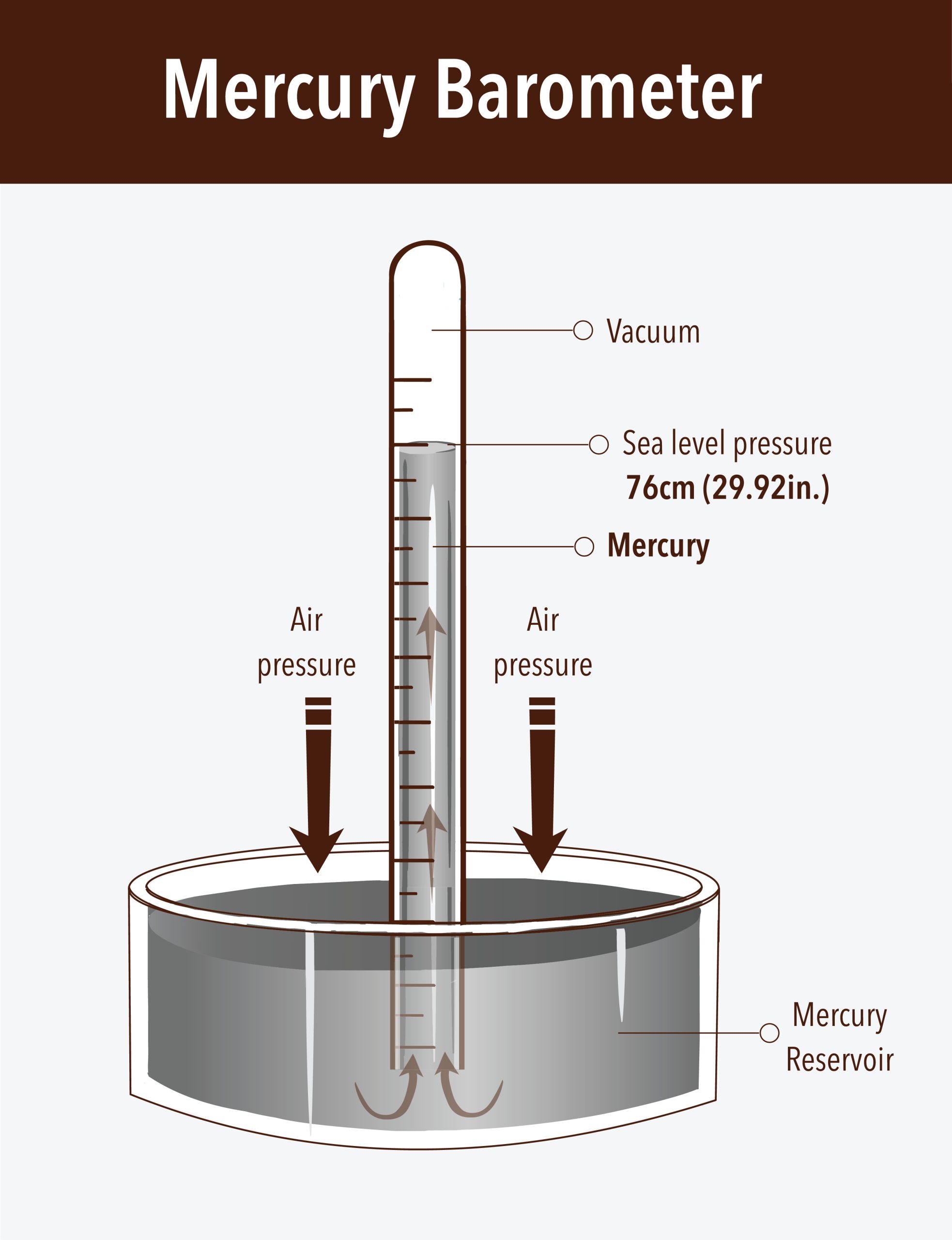
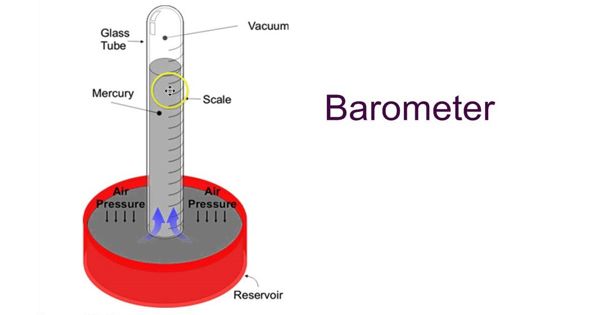
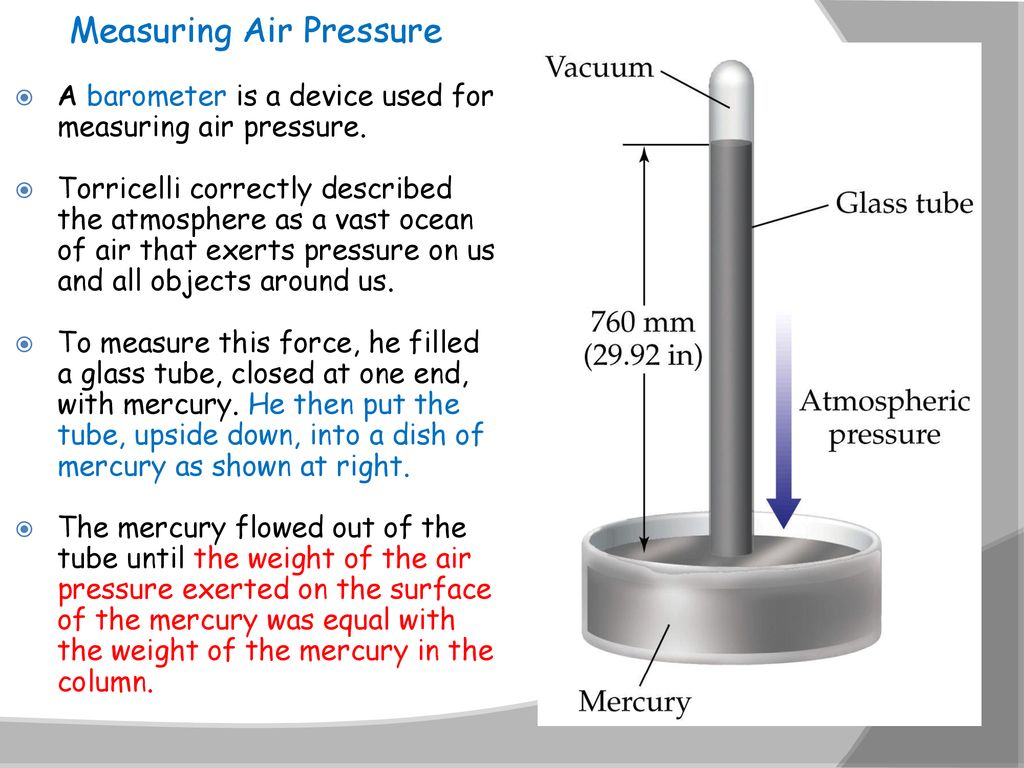
Mercury Barometers
Mercury barometers, invented by Evangelista Torricelli in the 17th century, use a column of mercury in a glass tube. Changes in atmospheric pressure cause the mercury level to rise or fall, indicating pressure fluctuations.
"The mercury barometer is the original standard for measuring atmospheric pressure."
Aneroid Barometers
Aneroid barometers use a small, flexible metal box called an aneroid cell. This cell is partially evacuated of air, and changes in air pressure cause it to expand or contract.
These movements are mechanically amplified to move a needle on a dial, providing a pressure reading. Aneroid barometers are generally more portable and less fragile than mercury barometers.
Why is Measuring Air Pressure Important?
Air pressure measurements are vital for weather forecasting. Lowering air pressure often indicates approaching storms, while rising pressure suggests improving weather conditions.
Pilots rely on barometric altimeters (a type of barometer) to determine altitude. Accurate pressure readings are essential for safe navigation.
Industries such as manufacturing and HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) also depend on precise air pressure measurements for system control and efficiency.
Where are Barometers Used?
Barometers are found in a variety of settings. Weather stations use them for continuous monitoring of atmospheric conditions.
Aviation relies heavily on barometers integrated into aircraft instrumentation. Even home weather stations often include a barometer for personal monitoring.
How Barometers Work: A Deeper Dive
The core principle behind all barometers is to measure the force exerted by the atmosphere. Mercury barometers directly measure this force against a column of mercury.
Aneroid barometers translate pressure changes into mechanical movement. This movement is then calibrated to provide an accurate pressure reading.
Other Devices and Air Pressure
While the barometer is specifically designed for measuring air pressure, other devices may indirectly use pressure sensors. For example, some weather balloons carry sensors that measure temperature, humidity, and air pressure at different altitudes.
These sensors relay data back to ground stations, providing valuable information for weather models.
The Future of Air Pressure Measurement
Digital barometers and pressure sensors are becoming increasingly common. These devices offer high accuracy and can be easily integrated into electronic systems.
The development of smaller, more robust pressure sensors is expanding the applications of air pressure measurement in fields like wearable technology and environmental monitoring.
Data from these sensors are used to create detailed atmospheric models. These models help improve weather forecasting accuracy.
Next Steps
For accurate air pressure readings, ensure that your barometer is properly calibrated. Consult a qualified technician if you suspect your instrument is not functioning correctly.
Continue to monitor weather reports that include barometric pressure data to stay informed about changing atmospheric conditions. Stay safe, stay informed.