Which Of The Following Is A Chronic Sign Of Overtraining

For athletes and fitness enthusiasts alike, pushing the limits is often seen as the key to progress. However, the line between dedicated training and detrimental overtraining can be blurry, and understanding the chronic signs of pushing too hard is crucial for maintaining health and performance. One of the most telling indicators of chronic overtraining is persistent fatigue that doesn't improve with rest.
Overtraining syndrome (OTS) is a complex condition that results from an imbalance between training stress and recovery. Recognizing the chronic signs of OTS can help individuals adjust their training regimen and prevent long-term negative health consequences. But understanding the chronic signs of OTS can be challenging and often misdiagnosed.
This article will delve into the key chronic signs of overtraining. We'll explore how these symptoms manifest, and strategies for prevention and management.
Understanding Overtraining Syndrome
Overtraining syndrome (OTS) occurs when an athlete consistently trains beyond their body's capacity to recover. This imbalance leads to a cascade of physiological and psychological effects. OTS is not merely excessive fatigue; it represents a deeper systemic disruption.
It's important to distinguish OTS from simply being tired after a hard workout. OTS is characterized by prolonged symptoms that persist even after adequate rest and recovery periods.
The Insidious Onset of Chronic Symptoms
One of the most challenging aspects of OTS is its gradual onset. Athletes often attribute early symptoms, such as minor sleep disturbances or mood swings, to other factors like stress or dietary changes.
However, as the imbalance between training and recovery continues, these seemingly minor symptoms can escalate into more serious and persistent issues. This gradual progression is what makes early detection and intervention so crucial.
Key Chronic Signs of Overtraining
Several key chronic signs can indicate that an individual is experiencing overtraining. These signs span physical, psychological, and performance-related domains, requiring a holistic assessment.
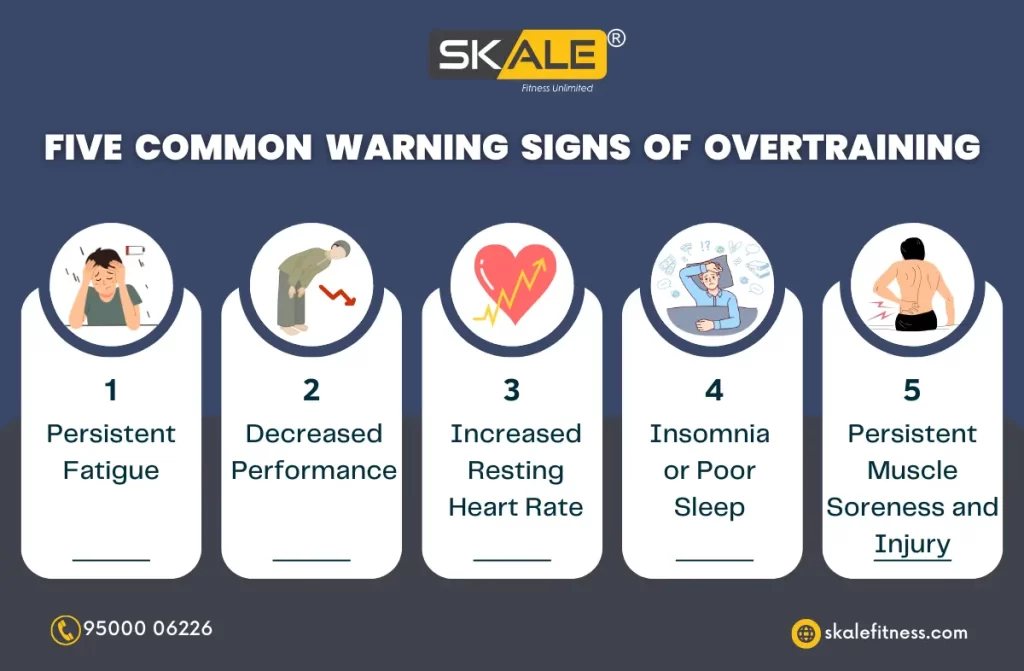
- Persistent Fatigue: This is often the most prominent and debilitating symptom. It's characterized by a deep, unremitting tiredness that isn't alleviated by sleep or rest.
- Decreased Performance: A noticeable decline in athletic performance despite continued training efforts. This could manifest as slower times, reduced strength, or diminished endurance.
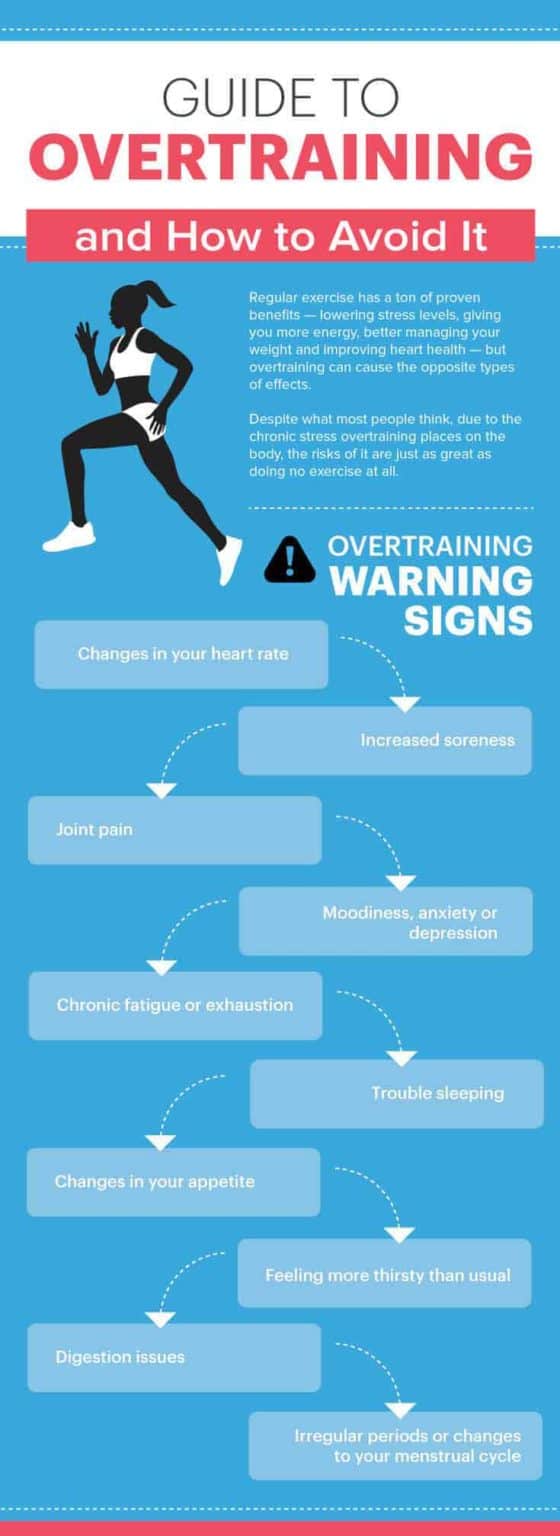
- Sleep Disturbances: Insomnia, difficulty falling asleep, or restless sleep are common. This can be exacerbated by elevated cortisol levels associated with overtraining.
- Mood Changes: Increased irritability, anxiety, depression, or a general loss of enthusiasm. These psychological changes can significantly impact an athlete's overall well-being.
- Increased Susceptibility to Illness: A weakened immune system leading to more frequent colds, infections, or other illnesses. Overtraining can suppress immune function.
- Loss of Appetite: Decreased appetite and unintentional weight loss. This can further exacerbate fatigue and hinder recovery.
- Elevated Resting Heart Rate: A higher than normal resting heart rate, even after days of rest. This reflects the body's constant state of stress.
It's important to note that the presentation of OTS can vary significantly from person to person. Not everyone will experience all of these symptoms, and the severity of each symptom can also differ.
The Role of Heart Rate Variability (HRV)
Heart Rate Variability (HRV) is a measure of the time interval between consecutive heartbeats. It has emerged as a valuable tool for monitoring training load and recovery status. Decreased HRV, particularly in the morning, can be an early warning sign of overtraining.
HRV reflects the balance between the sympathetic (fight-or-flight) and parasympathetic (rest-and-digest) nervous systems. When the body is stressed, the sympathetic nervous system dominates, leading to reduced HRV. Monitoring HRV can provide athletes with objective data to guide their training decisions.
Prevention and Management
Preventing overtraining requires a proactive approach that prioritizes recovery and individualizes training plans. Adequate rest, proper nutrition, and stress management are all essential components.
Individualized training plans should consider an athlete's experience level, training history, and individual recovery capabilities. Gradual increases in training volume and intensity are generally safer than sudden spikes.
If overtraining is suspected, the first step is to reduce training volume and intensity. In severe cases, complete rest may be necessary.
Consulting with a sports medicine physician or qualified healthcare professional is crucial for proper diagnosis and management. They can help identify underlying issues and develop a personalized recovery plan. This plan may include nutritional interventions, stress management techniques, and a gradual return to training.
The Significance of Early Detection
Early detection is paramount in preventing the long-term consequences of OTS. The sooner an athlete recognizes the warning signs and takes corrective action, the faster they can recover and return to peak performance.
Ignoring the chronic signs of overtraining can lead to prolonged periods of underperformance, increased risk of injury, and even burnout. Prioritizing recovery and listening to the body's signals are key to long-term success and well-being.
By understanding the chronic signs of overtraining, athletes and fitness enthusiasts can make informed decisions about their training and recovery strategies. Ultimately, preventing overtraining is not about avoiding hard work, but about ensuring that hard work translates into sustainable progress and optimal health.