Which Of The Following Is True About Primary Aggression

Confusion and misinformation are spreading rapidly regarding the characteristics of primary aggression, potentially impacting legal interpretations and therapeutic interventions. Immediate clarification is needed to dispel inaccuracies and ensure consistent understanding of this critical behavioral concept.
This report provides a definitive answer, based on established psychological and criminological literature, concerning the true nature of primary aggression, also known as proactive aggression. It directly addresses prevalent misconceptions to facilitate accurate identification and management of aggressive behaviors.
Defining Primary Aggression: Fact vs. Fiction
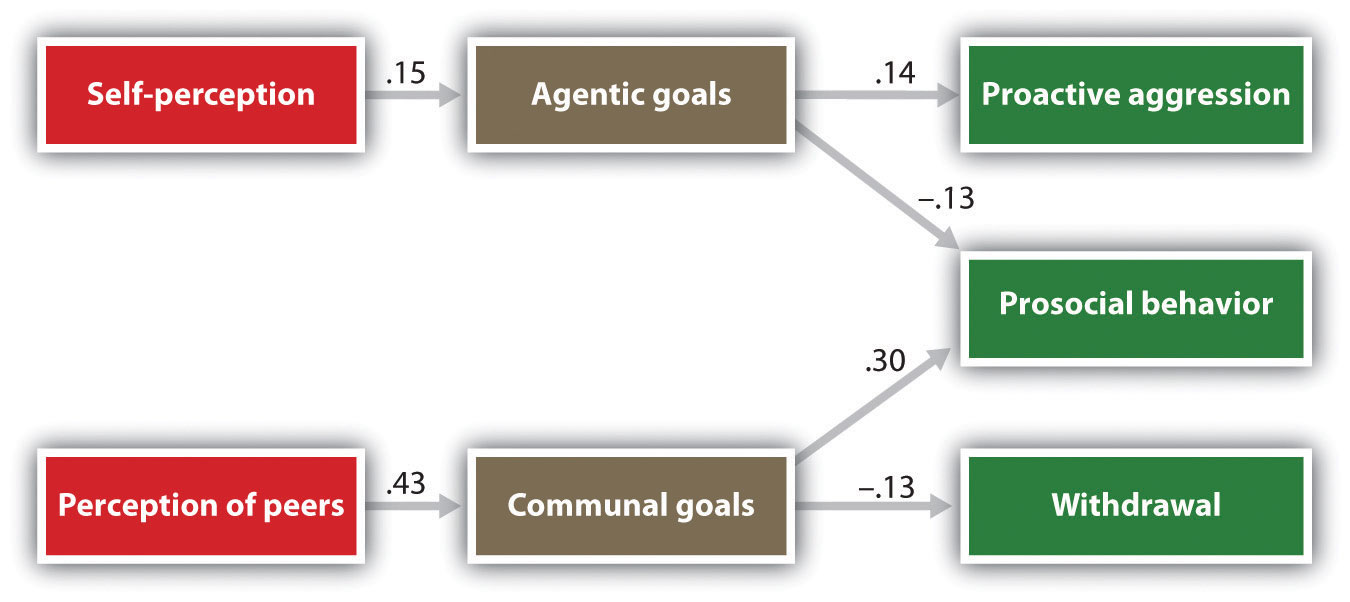
Primary aggression, unlike reactive aggression, is not driven by immediate threat or emotional arousal. It is a planned and purposeful behavior. The aggressor initiates the act to achieve a specific goal, such as dominance, resources, or social status.
One common misconception is that primary aggression is always physical. While physical violence can be a manifestation, it is not a defining characteristic. Primary aggression can manifest in various forms, including verbal abuse, social manipulation, and even cyberbullying, as long as the behavior is premeditated and goal-oriented.
Key Characteristics of Primary Aggression
The essential feature is the absence of an immediate perceived threat. The aggressive act is not a response to provocation. It's carefully chosen and executed.
Individuals exhibiting primary aggression often display a lack of empathy. They use others instrumentally to achieve their objectives. This calculated approach is central to understanding this type of aggression.
Furthermore, those who engage in primary aggression typically show no remorse for their actions. This absence of guilt distinguishes it from reactive aggression, where remorse may occur after the aggressive outburst subsides.
What is NOT True About Primary Aggression
It is absolutely false that primary aggression is solely triggered by fear or frustration. Fear or frustration triggers reactive aggression. Primary aggression stems from a deliberate choice to exert control or gain advantage.
Another falsehood is equating primary aggression with impulsivity. While impulsive acts can be aggressive, primary aggression involves planning and forethought. Impulsivity is a hallmark of reactive, not proactive, aggression.
It is also incorrect to assume that primary aggression is exclusively a male trait. While studies suggest higher prevalence in males, females also exhibit primary aggressive behavior, often manifesting through social manipulation and indirect aggression.
"Primary aggression is a learned behavior, not simply an innate response," states Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in aggression research at the University of California, Berkeley. "Understanding its origins is crucial for effective intervention."
The Implications of Misinformation
Misunderstanding primary aggression can lead to ineffective intervention strategies. Treating proactive aggressors as reactive aggressors can exacerbate the problem. Tailored interventions are essential.
In legal contexts, mischaracterizing the type of aggression can influence sentencing and rehabilitation efforts. Accurate assessment is crucial for justice. Understanding the intent behind the act is key.
Therapeutic approaches must focus on developing empathy and addressing the underlying motivations for using aggression as a tool. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and social skills training are often employed.
Moving Forward: Addressing the Knowledge Gap
Further research is needed to fully understand the neurological and environmental factors contributing to the development of primary aggression. Early identification and intervention are paramount.
Educational initiatives should target professionals in fields such as law enforcement, education, and mental health. This ensures accurate identification and appropriate responses. Collaboration is essential.
Ongoing efforts are underway to develop standardized assessment tools for distinguishing between primary and reactive aggression. These tools will aid in accurate diagnosis and tailored intervention strategies.