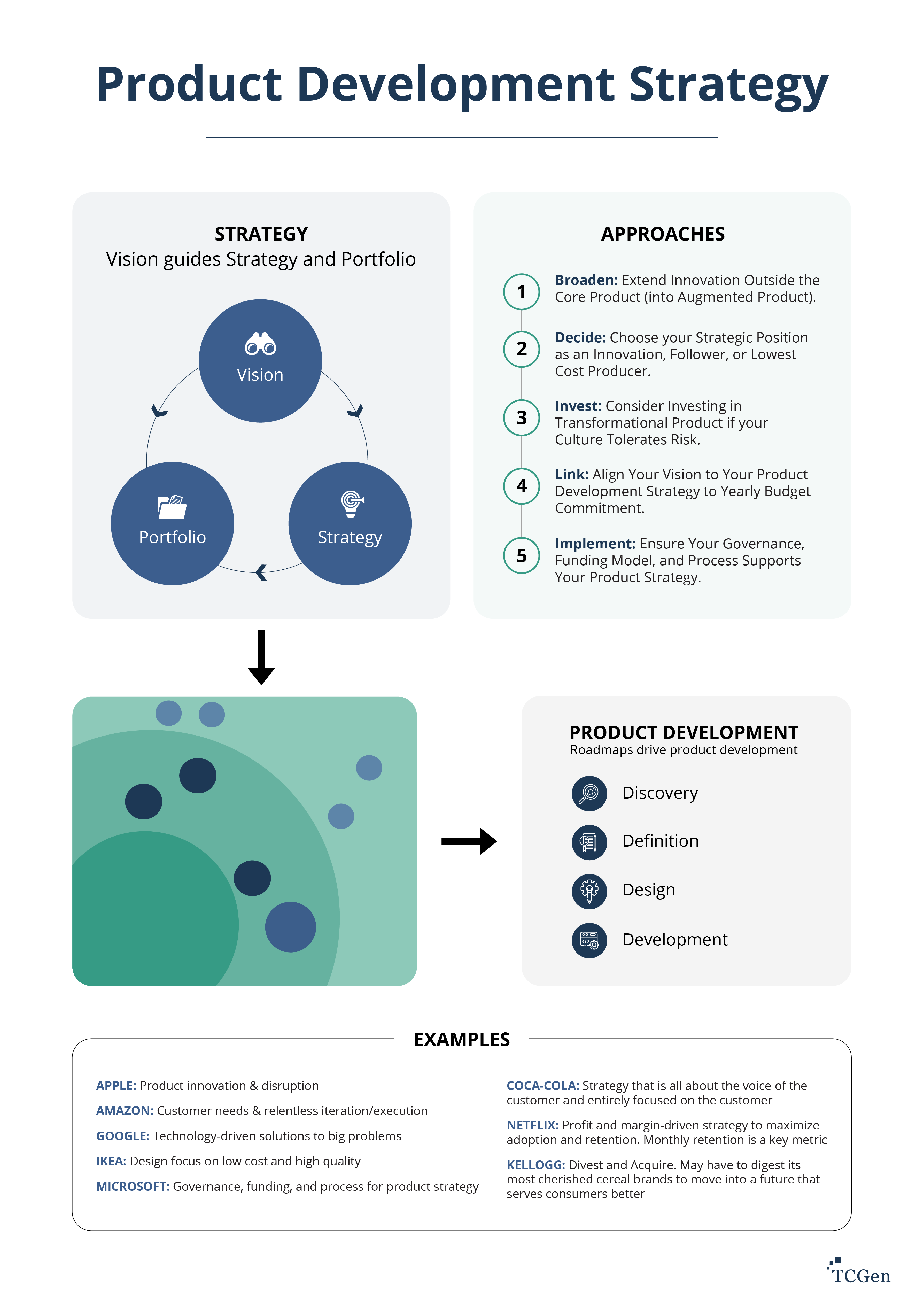
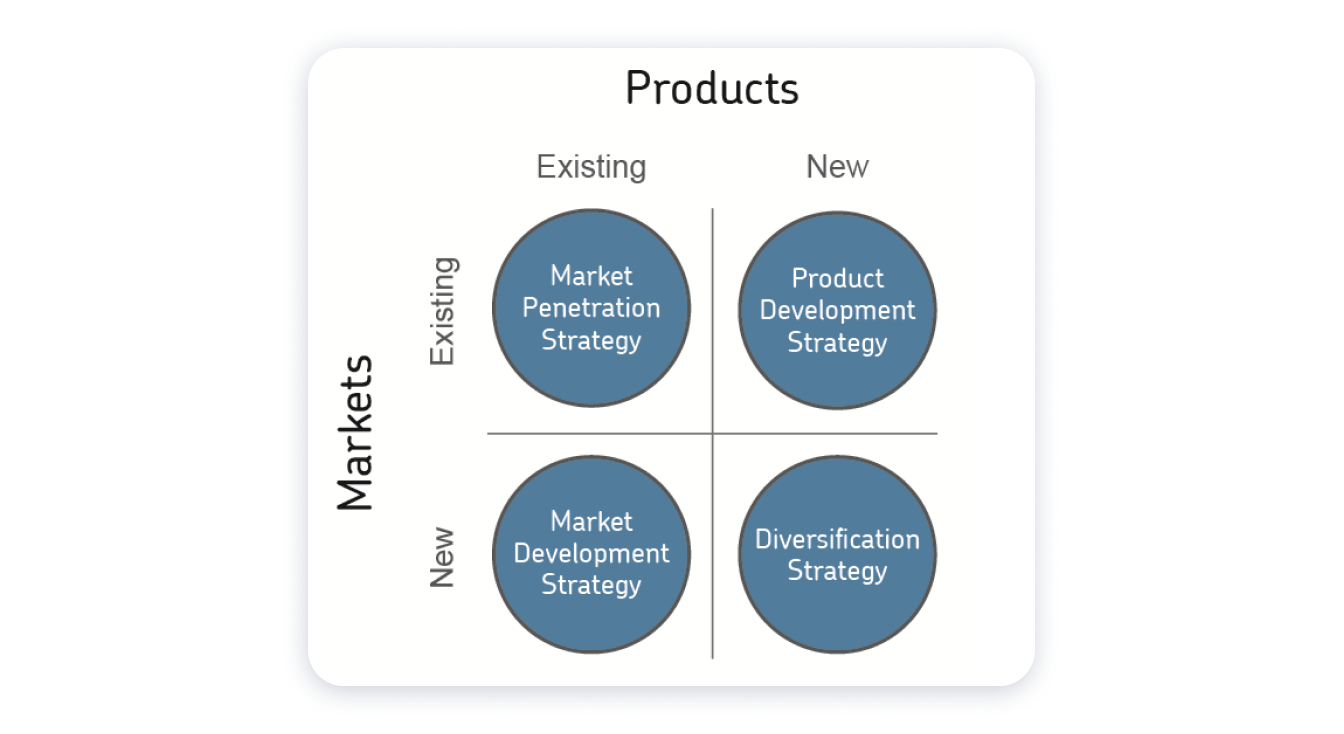
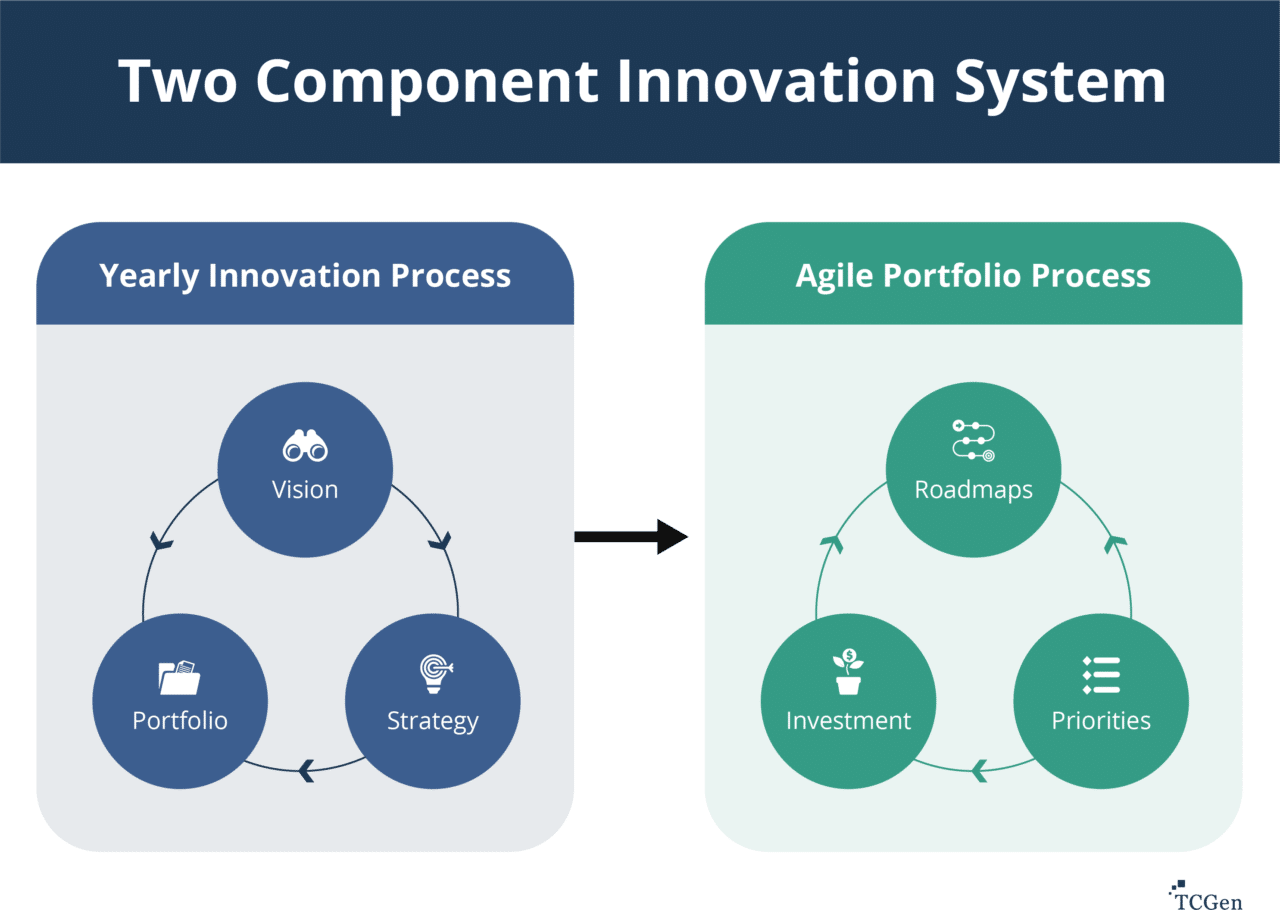
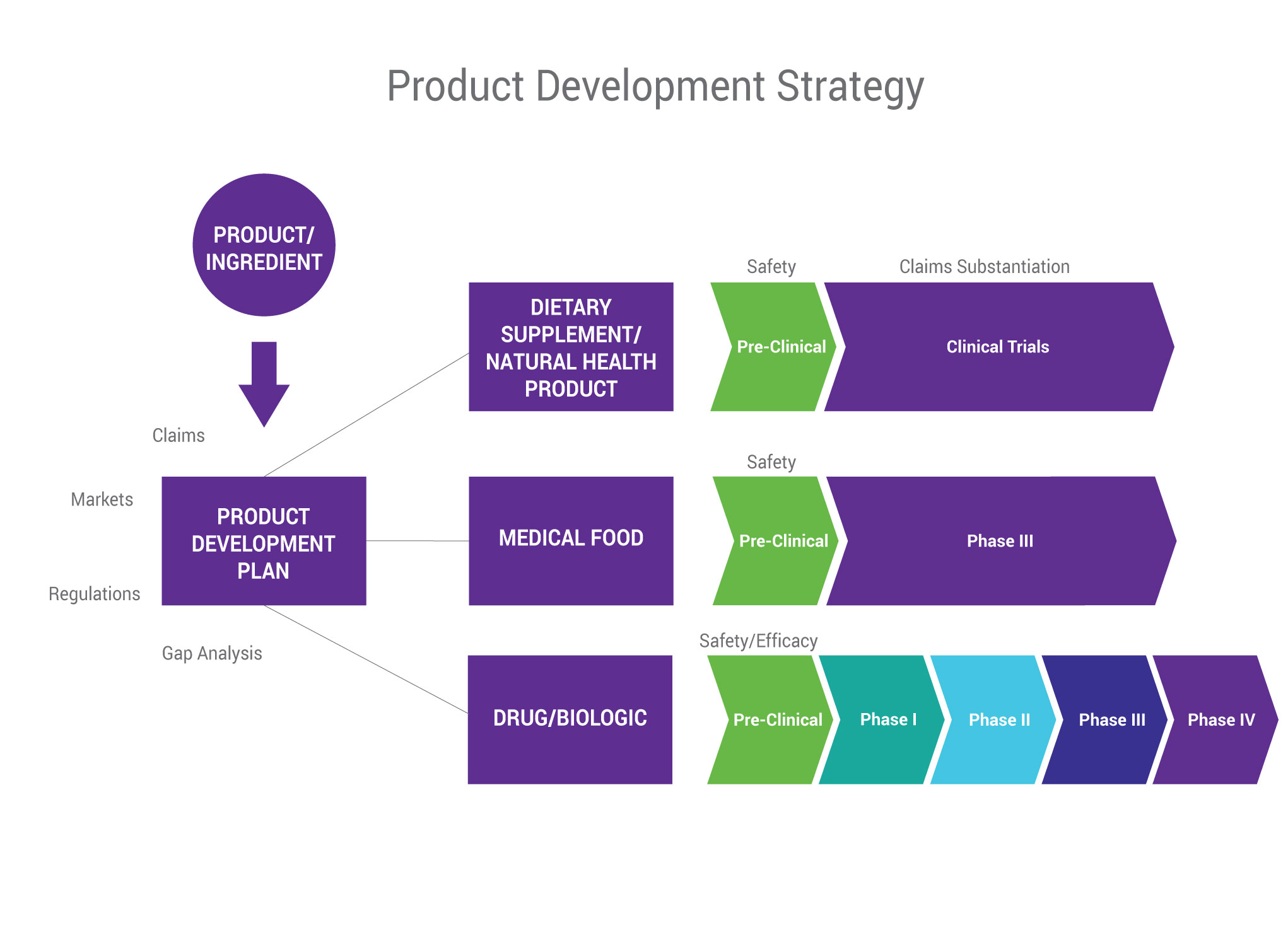
Which Of The Following Represents An Internal Product Development Strategy

The question of whether a company should build its products internally or outsource their development is a perennial debate in the business world. Recently, discussions have intensified around which strategies truly represent an *internal* product development approach, particularly as companies navigate increasingly complex technological landscapes.
This article aims to clarify what constitutes an internal product development strategy, exploring its key characteristics, benefits, and potential drawbacks. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions about their product development processes and ultimately, their competitive advantage.
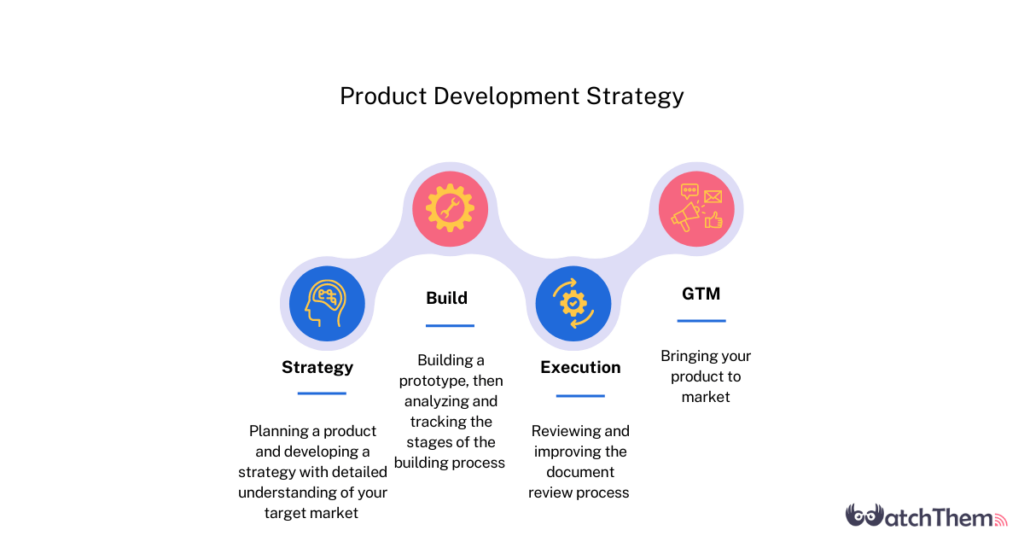
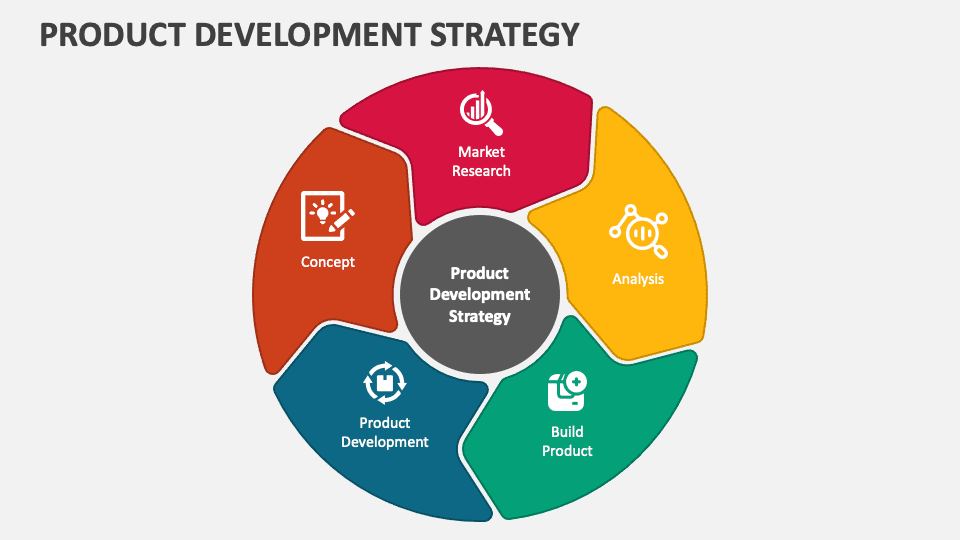
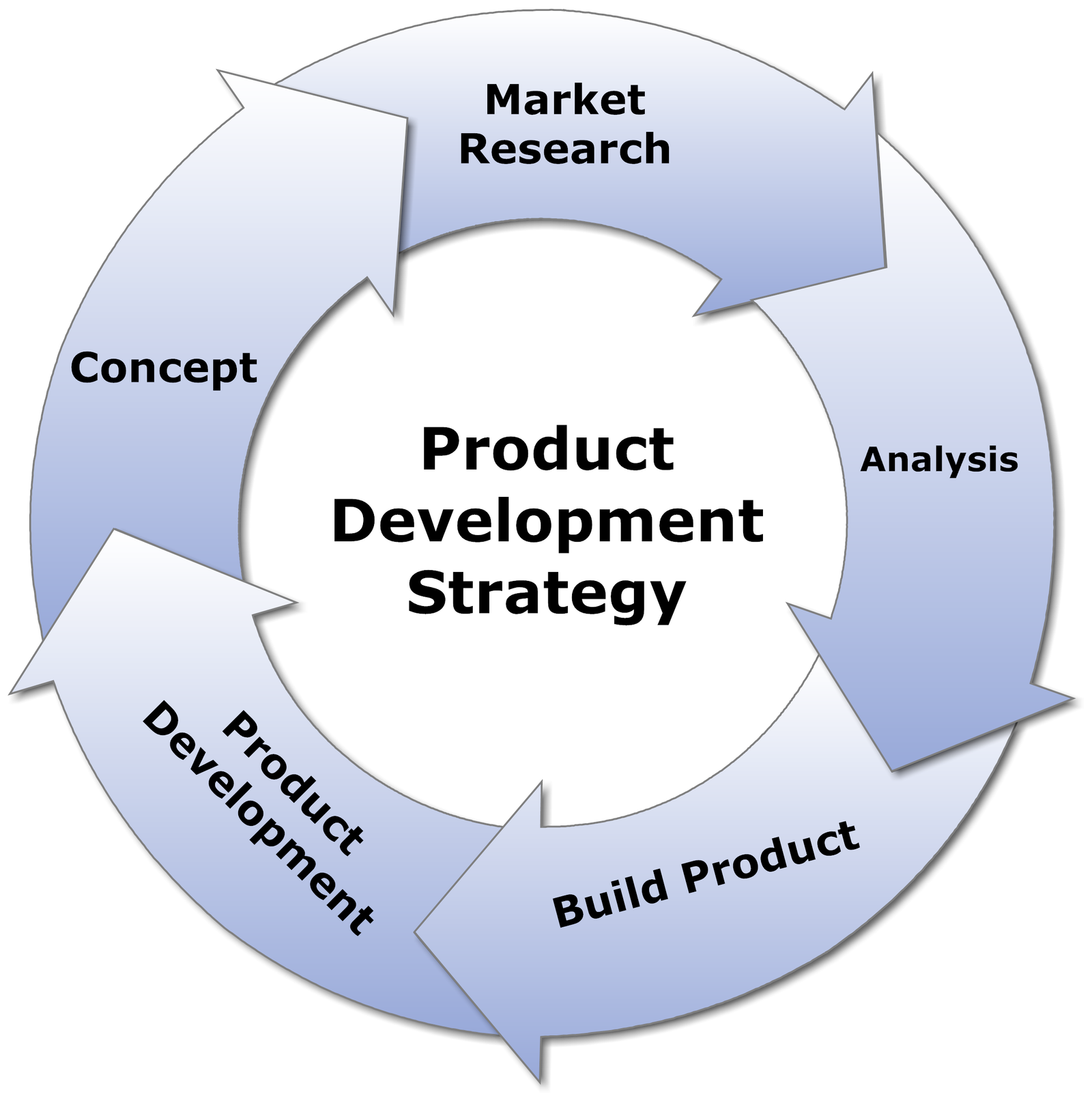
Defining Internal Product Development
An internal product development strategy, at its core, refers to a process where a company uses its own resources – employees, technology, and infrastructure – to create and refine new products or services. This is in direct contrast to outsourcing, where these activities are delegated to external partners or vendors.
The decision to pursue an internal strategy often hinges on factors such as the availability of skilled personnel, the desire to maintain control over intellectual property, and the need for deep integration between different parts of the organization.
Key Characteristics
A key element is the ownership of the development process, which lies entirely within the company. This includes everything from initial ideation and design to coding, testing, and deployment.
Another important feature is the utilization of in-house expertise. The company's own employees, with their specialized skills and knowledge, are the driving force behind the development effort. Maintaining intellectual property is also a significant factor; the company retains full control over its innovations.
Examples of Internal Strategies
Consider a software company that develops a new mobile application entirely using its own team of engineers, designers, and product managers. All aspects of the project, from conception to launch, are handled internally, leveraging the company's established infrastructure and expertise.
Similarly, a manufacturing firm might invest in research and development, employing its own scientists and engineers to create a new type of material. The investment in internal research allows the company to innovate beyond existing market offerings.
The Benefits and Drawbacks
There are several potential advantages to adopting an internal product development strategy. Stronger control over the development process is one such advantage.
Internal teams often have a deeper understanding of the company's culture, values, and strategic goals. This can lead to products that are more aligned with the company's overall vision and brand. In-house development can foster innovation by allowing for rapid iteration and experimentation, leading to more creative solutions.
However, internal development also has its limitations. Maintaining a highly skilled internal team can be expensive. There's also a risk of becoming insular, which can stifle creativity and lead to a lack of fresh perspectives.
The "Make vs. Buy" Decision
The choice between internal development and outsourcing is often framed as a "make vs. buy" decision. Companies must carefully weigh the pros and cons of each approach, considering their specific circumstances and strategic objectives.
Factors to consider include the availability of internal resources, the complexity of the project, the desired level of control, and the potential for long-term cost savings.
In some cases, a hybrid approach may be the most effective. This involves combining internal expertise with external resources, leveraging the strengths of both approaches.
Impact and Future Trends
The rise of agile development methodologies has further blurred the lines between internal and external development. These methods emphasize collaboration, iterative development, and continuous improvement, which can be applied to both internal and outsourced projects. The push for digital transformation has placed increased emphasis on speed and agility, which has affected product development.
As technology continues to evolve, companies will need to adapt their product development strategies to remain competitive. This may involve investing in new technologies, upskilling their workforce, or exploring new models of collaboration and partnerships.
Ultimately, the most effective product development strategy will depend on a company's unique circumstances, goals, and capabilities. But a clear understanding of what constitutes an internal development strategy is a crucial starting point for making informed decisions.

![Which Of The Following Represents An Internal Product Development Strategy Product Development Strategy - 8 Company Examples [2022]](https://www.tcgen.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/product-development-strategy.png)