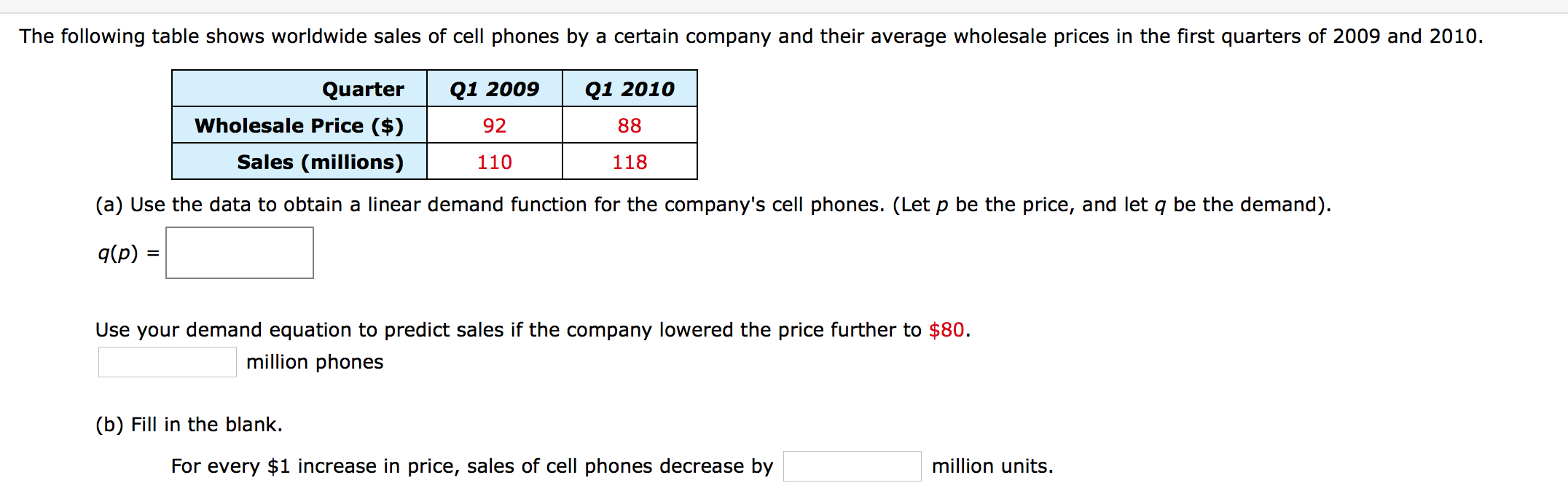
Which Of The Following Statements About The Average Wholesale Price

Imagine walking into a bustling farmer's market, the air thick with the aroma of freshly picked apples and the vibrant colors of locally grown produce. Vendors proudly display their wares, each price tag reflecting not just the cost of cultivation but also the intricate dance of supply, demand, and the myriad factors that shape the market. Understanding how these prices are determined, especially at the wholesale level, is crucial for everyone from farmers to consumers, and ultimately impacts the economic heartbeat of our communities.
This article delves into the often-misunderstood world of average wholesale prices, clarifying key statements and shedding light on what truly influences the costs that retailers pay before marking up goods for consumers. We'll explore the factors that drive these prices, the common misconceptions, and why accurate understanding is essential for making informed economic decisions.
The Fundamentals of Average Wholesale Price
The average wholesale price represents the typical cost a retailer pays to purchase goods directly from a manufacturer, distributor, or other supplier in bulk.
It's a critical figure that sits between the raw production costs and the final retail price consumers see.
Understanding its intricacies is key to grasping the broader economic landscape.
Defining Averages: More Than Meets The Eye
One common misconception is that the average wholesale price is a fixed, static number.
In reality, it's a dynamic metric that fluctuates based on a variety of market conditions.
A statement suggesting a single, unchanging average wholesale price across all regions and time periods is therefore inaccurate.
Consider the example of avocados. During peak season, when supply is abundant, the average wholesale price is likely to be lower. Conversely, during the off-season, when supply is limited, the price will rise.
Geographical location also plays a significant role.
Transportation costs, regional demand, and local regulations can all influence the price.
The Supply and Demand Equation
The most fundamental principle influencing average wholesale price is the law of supply and demand.
When demand for a product is high and supply is limited, prices tend to increase.
Conversely, when supply exceeds demand, prices tend to decrease.
For example, if a sudden frost damages a large portion of the orange crop, the supply of oranges will decrease.
This scarcity will drive up the average wholesale price for orange juice, and ultimately, the price consumers pay at the grocery store.
Statements ignoring this interplay are fundamentally flawed.
Production Costs: The Foundation of Price
The cost of production is a crucial component of the average wholesale price.
These costs encompass everything from raw materials and labor to manufacturing overhead and transportation.
Increases in production costs inevitably lead to higher wholesale prices.
Consider the impact of rising energy prices on the production of plastic goods.
Higher energy costs translate directly into increased manufacturing expenses, which in turn push up the average wholesale price of plastic products.
Therefore, a statement claiming that production costs have no bearing on the average wholesale price is demonstrably false.
Market Competition: A Balancing Act
The level of competition within a particular market also influences the average wholesale price.
In highly competitive markets, suppliers are often forced to lower their prices to attract customers, driving down the overall average.
Conversely, in markets with limited competition, suppliers have more leverage to set higher prices.
Imagine a scenario where several companies are vying to supply a particular type of electronic component to a major manufacturer.
To win the contract, each supplier will likely offer a competitive price, leading to a lower average wholesale price for that component.
A statement that disregards the impact of market competition provides an incomplete and potentially misleading picture.
Government Regulations and Tariffs
Government policies, such as regulations and tariffs, can significantly impact the average wholesale price.
Regulations related to environmental protection, labor standards, or product safety can increase production costs, leading to higher prices.
Tariffs, which are taxes on imported goods, directly increase the cost of those goods, pushing up the average wholesale price.
For instance, if a government imposes a tariff on imported steel, the average wholesale price of steel products will inevitably rise.
Similarly, stricter environmental regulations requiring manufacturers to invest in cleaner production technologies can increase their operating costs and subsequently impact wholesale prices.
Statements that ignore the impact of government policies on pricing are incomplete and inaccurate.
The Role of Distributors and Intermediaries
Distributors and other intermediaries play a crucial role in the wholesale market.
They connect manufacturers with retailers, handling logistics, warehousing, and often providing financing.
The fees and margins charged by these intermediaries are factored into the average wholesale price.
If a distributor adds a significant markup to cover their expenses and profit margin, the average wholesale price will reflect this increase.
The more complex the distribution chain, the more likely the price is to be affected by these intermediary costs.
Therefore, statements that exclude the role of distributors present a skewed view of price determination.
The Impact of Technology
Technological advancements can have a mixed impact on the average wholesale price.
Automation and improved efficiency in production can lower costs, potentially leading to lower prices.
However, the cost of implementing new technologies can also be substantial, potentially offsetting some of the savings.
For instance, the adoption of automated farming techniques can reduce labor costs and increase crop yields, potentially lowering the average wholesale price of agricultural products.
However, the initial investment in this technology can be significant, and these costs must be recouped over time.
A comprehensive analysis must consider both the cost and benefit aspects of technology's role in determining prices.
Conclusion
Understanding the average wholesale price requires a nuanced perspective that considers the interplay of various factors, including supply and demand, production costs, market competition, government regulations, the role of distributors, and technological advancements. Oversimplifying this complex equation with blanket statements can lead to a flawed understanding of the economic forces at play. By recognizing the dynamic nature of wholesale prices, we empower ourselves to make more informed decisions as businesses, consumers, and citizens, ultimately contributing to a more transparent and equitable marketplace.
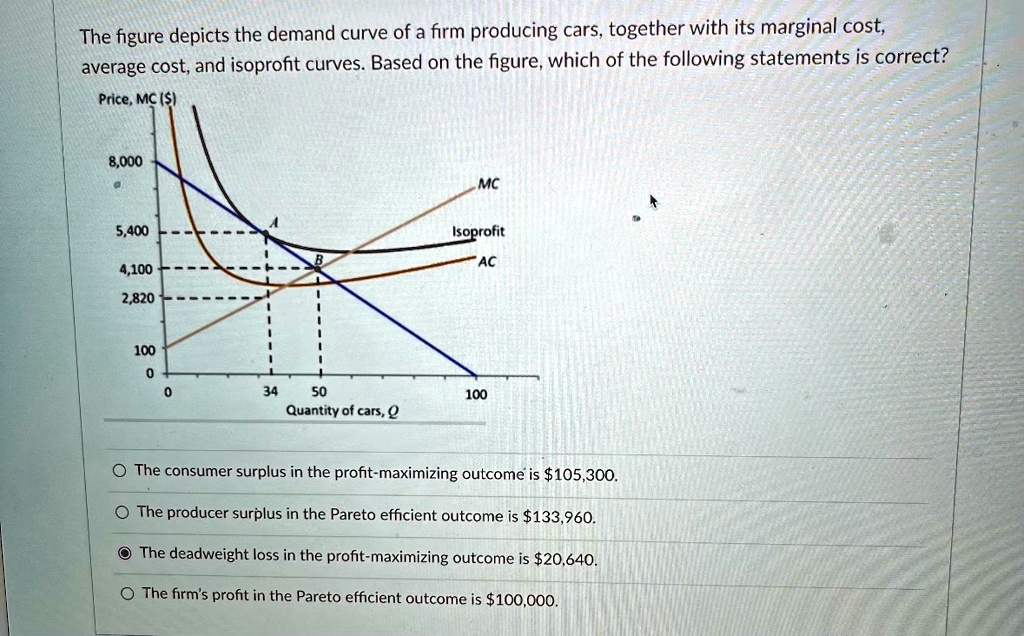

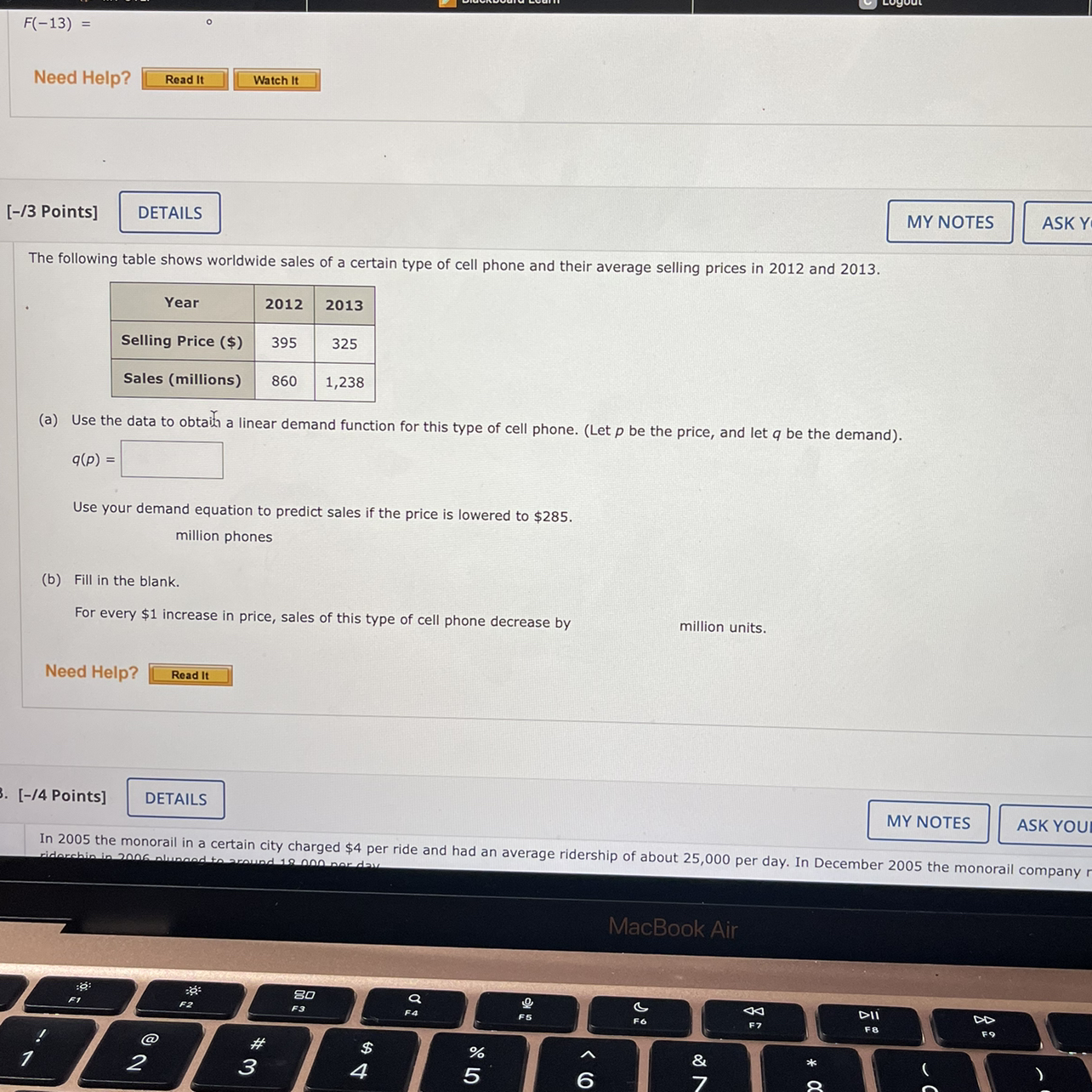

+-+Discounted+Average+Wholesale+Price+(AWP)+Purchasing+Model.jpg)