Which Of The Following Statements Is True About The Skin

Imagine a toddler, giggling as they smear sunscreen across their nose, leaving a thick white streak. Think about the comforting warmth of a loving grandparent's hand, the delicate skin revealing stories of a life well-lived. Our skin, that incredible, ever-present organ, is more than just a surface; it's a dynamic shield, a sensory receptor, and a vital player in our overall health. But how much do we truly understand about this remarkable layer that protects us?
The human skin is the body's largest organ, playing a vital role in protection, regulation, and sensation. Understanding its structure and function is key to maintaining overall health. Therefore, let’s explore the truth about our integumentary system.
The Skin: A Multi-Layered Marvel
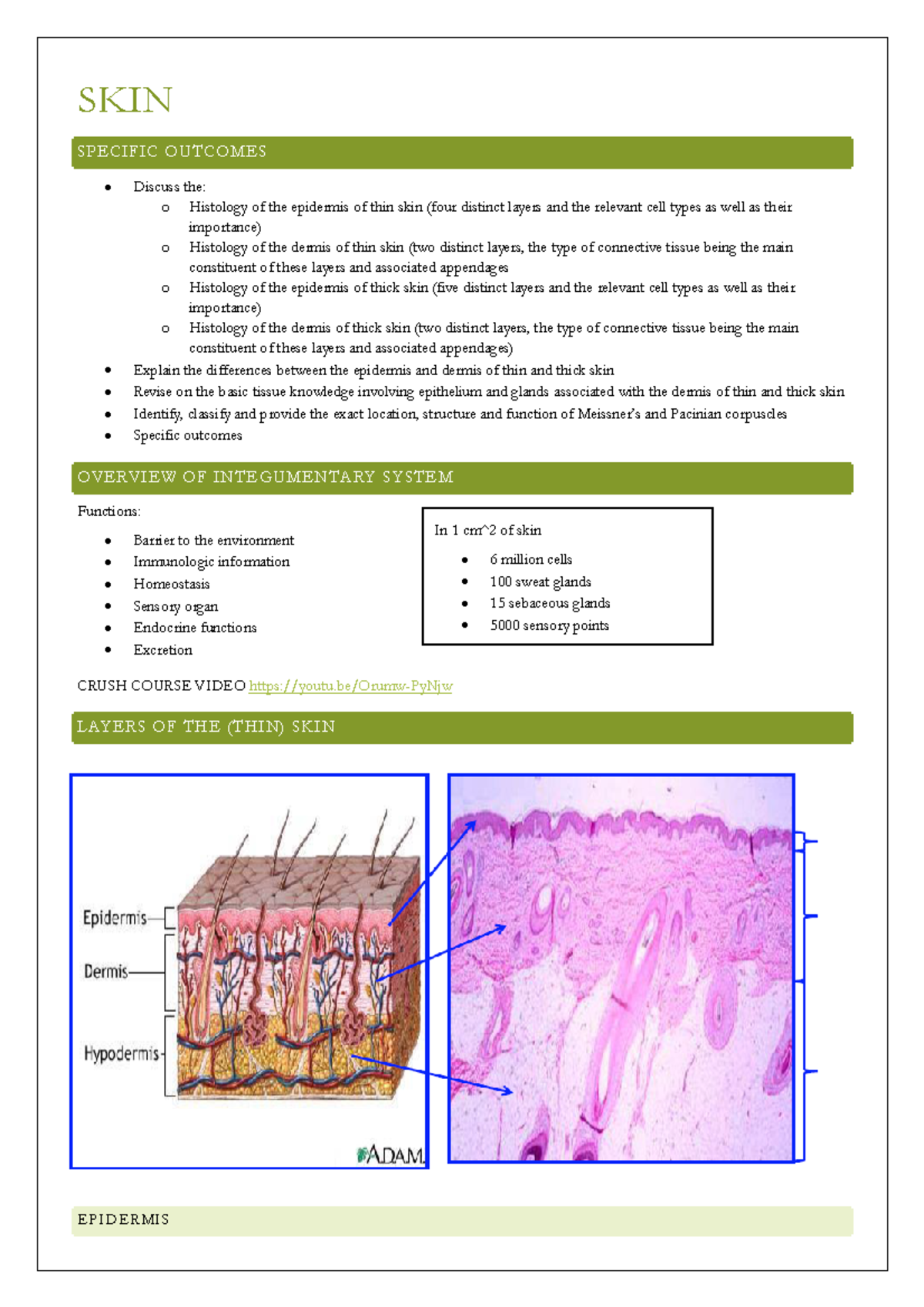
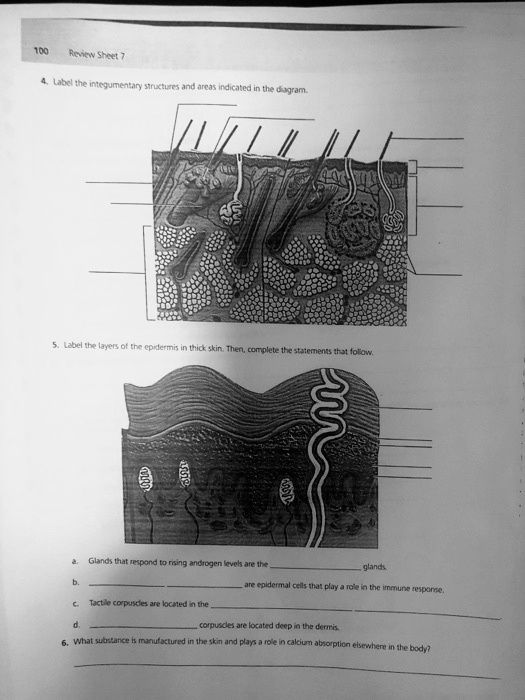
The skin isn't a single entity, but rather a complex structure composed of three primary layers: the epidermis, the dermis, and the hypodermis. Each layer boasts unique characteristics and specialized functions, working in harmony to maintain our well-being.
The Epidermis: Our First Line of Defense
This outermost layer is what we see and touch. It's constantly regenerating, with cells being shed and replaced in a continuous cycle. The epidermis provides a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone.
The outermost layer, the stratum corneum, is comprised of dead skin cells. These cells are filled with keratin, a protein that makes the skin tough and protective.
The epidermis also contains melanocytes, cells that produce melanin. Melanin is the pigment responsible for skin color, and it helps protect the skin from harmful UV radiation. Variations in the amount of melanin determine an individual's skin tone.
The Dermis: Where the Action Happens
Beneath the epidermis lies the dermis, a thicker layer that provides strength and elasticity. The dermis is the heart of our skin.
It houses blood vessels, nerve endings, hair follicles, and sweat glands. Collagen and elastin fibers within the dermis give the skin its structure and ability to stretch and rebound.
Sensory receptors in the dermis allow us to feel touch, pressure, pain, and temperature. Blood vessels help regulate body temperature by constricting or dilating as needed.
The Hypodermis: Insulation and Support
The hypodermis, also known as the subcutaneous layer, is the deepest layer of the skin. It primarily consists of fat tissue (adipose tissue). This layer provides insulation, cushioning, and energy storage.
The hypodermis connects the skin to underlying muscles and bones. It also contains larger blood vessels and nerves that supply the skin.
Key Functions of the Skin: More Than Just a Covering
The skin's role extends far beyond simply holding us together. It is involved in vital processes.
- Protection: Acting as a barrier against pathogens, UV radiation, and physical trauma.
- Regulation: Maintaining body temperature through sweat glands and blood vessel activity.
- Sensation: Detecting touch, pressure, pain, and temperature through nerve endings.
- Vitamin D Synthesis: Producing Vitamin D when exposed to sunlight.
- Excretion: Eliminating waste products through sweat.
Common Misconceptions About Skin
Several misconceptions surround skin and skincare. Let's debunk a few of them.
Myth: Tanning beds are a safe way to tan. Fact: Tanning beds emit harmful UV radiation that increases the risk of skin cancer.
Myth: Darker skin tones don't need sunscreen. Fact: Everyone, regardless of skin tone, is susceptible to sun damage and should use sunscreen.
Myth: Wrinkles are solely caused by aging. Fact: While aging contributes, sun exposure, genetics, and lifestyle factors also play a significant role.
Taking Care of Your Skin: A Lifelong Journey
Caring for your skin is an investment in your overall health. Adopt a routine that suits your skin type and lifestyle.
Sun protection is paramount. Use sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days. Seek shade during peak sun hours and wear protective clothing.
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water. Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants to nourish your skin from the inside out. Choose gentle skincare products appropriate for your skin type and avoid harsh chemicals that can cause irritation.
Regularly examine your skin for any changes in moles or new growths. Consult a dermatologist for professional advice and treatment for any skin concerns.
The Enduring Legacy of Our Skin
The skin, often taken for granted, is a remarkable organ that plays a critical role in our health and well-being. By understanding its structure, functions, and needs, we can make informed choices to protect and nourish it throughout our lives. From the toddler slathering on sunscreen to the grandparent sharing a loving touch, our skin is a constant companion, a testament to the beauty and resilience of the human body.
Taking care of your skin is a long-term commitment, not a fleeting trend. By embracing healthy habits and seeking professional guidance when needed, you can ensure your skin remains healthy and radiant for years to come.