Which Of The Following Statements Is True Regarding Absorption Costing

Imagine you're running a small bakery, the aroma of freshly baked bread filling the air. You meticulously track the cost of flour, sugar, and butter. But what about the oven's electricity, the baker's salary, or even the rent for the shop? How do you factor those indirect costs into the price of each loaf?
That brings us to a crucial concept in accounting: absorption costing. Understanding absorption costing is essential for anyone involved in manufacturing or production, and its nuances often appear in accounting exams and business decisions. The core question is: Which of the following statements is true regarding absorption costing? The answer lies in how it treats all manufacturing costs, both direct and indirect, as product costs, directly impacting profitability analysis and inventory valuation.
The Fundamentals of Absorption Costing
Absorption costing, sometimes referred to as full costing, is an accounting method used to determine the total cost of a product. It adheres to the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) for external reporting, including financial statements.
Unlike variable costing, which only includes variable manufacturing costs in the product cost, absorption costing encompasses all manufacturing costs, both variable and fixed. This includes direct materials, direct labor, variable manufacturing overhead, and fixed manufacturing overhead.
Key Components of Absorption Costing
Let's break down these components: Direct materials are the raw materials that go directly into the product. Direct labor is the cost of labor directly involved in the production process.
Variable manufacturing overhead includes indirect costs that fluctuate with production volume, like utilities for the factory. Fixed manufacturing overhead represents the indirect costs that remain constant regardless of production levels, such as rent on the factory building or depreciation on equipment.
The total product cost under absorption costing is the sum of all four components: direct materials, direct labor, variable manufacturing overhead, and fixed manufacturing overhead.
How Absorption Costing Works
The magic of absorption costing lies in allocating fixed manufacturing overhead to each unit produced. This allocation is typically based on a predetermined overhead rate.
This rate is calculated by dividing the total estimated fixed manufacturing overhead costs by the estimated level of production activity. Common activity bases include direct labor hours, machine hours, or units produced.
For example, imagine a furniture company estimates $100,000 in fixed manufacturing overhead and expects to produce 10,000 chairs. The predetermined overhead rate would be $10 per chair ($100,000 / 10,000 chairs). This $10 is then added to the other direct costs to arrive at the *total cost* of each chair.
Impact on Financial Statements
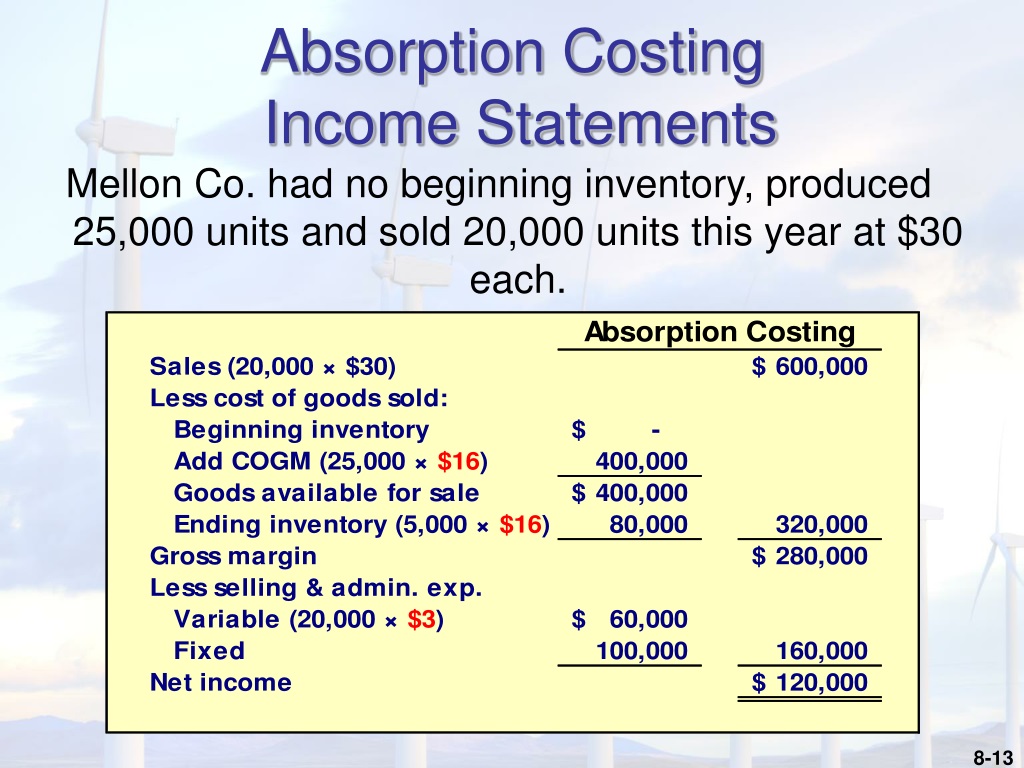
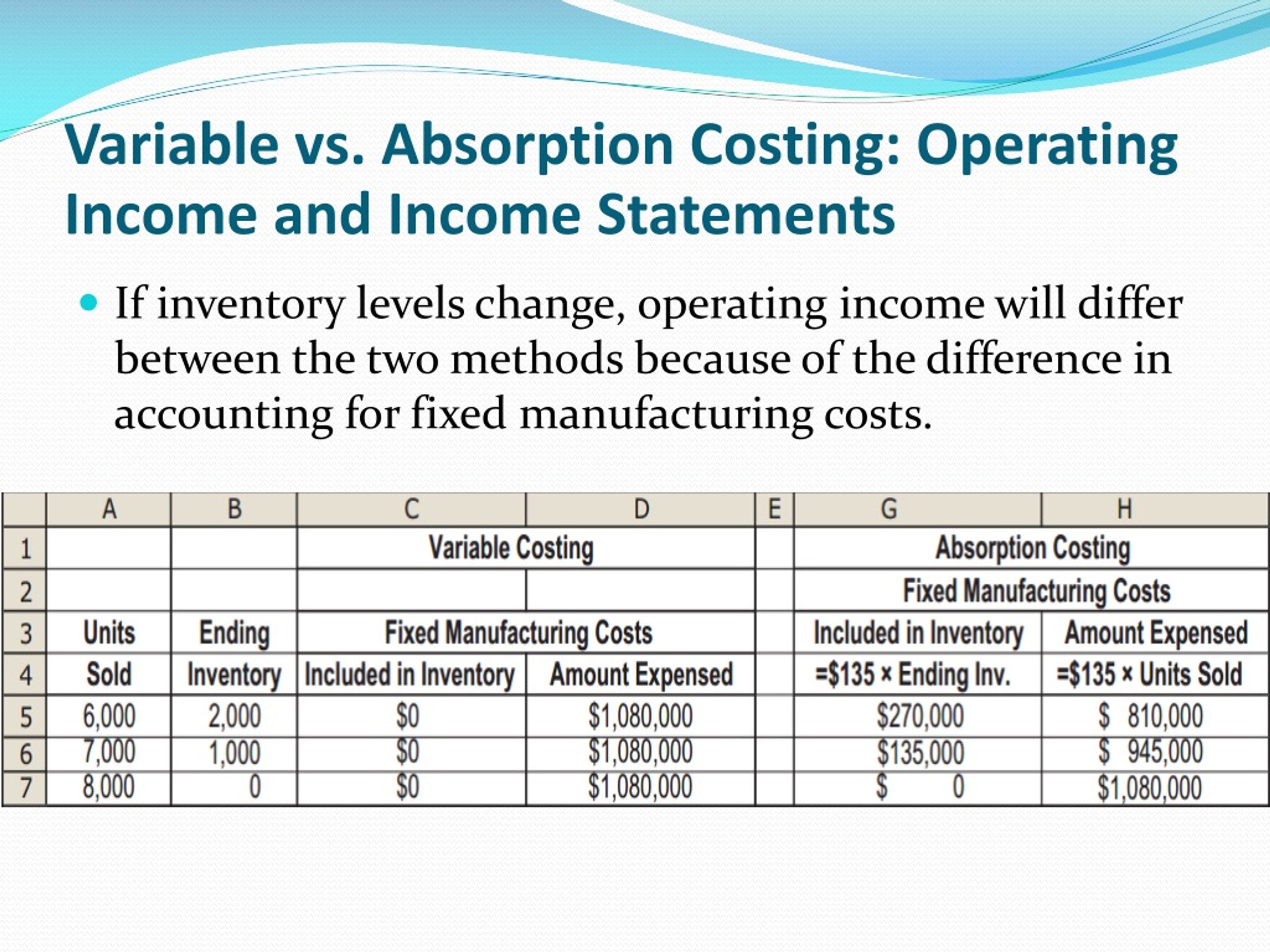
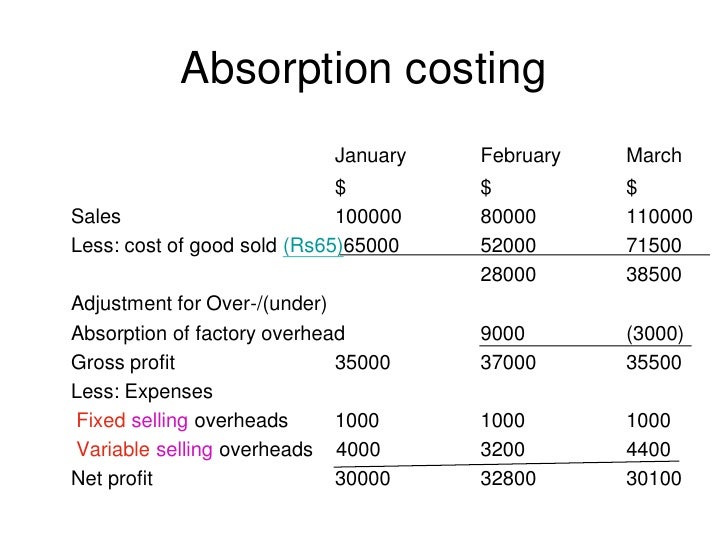
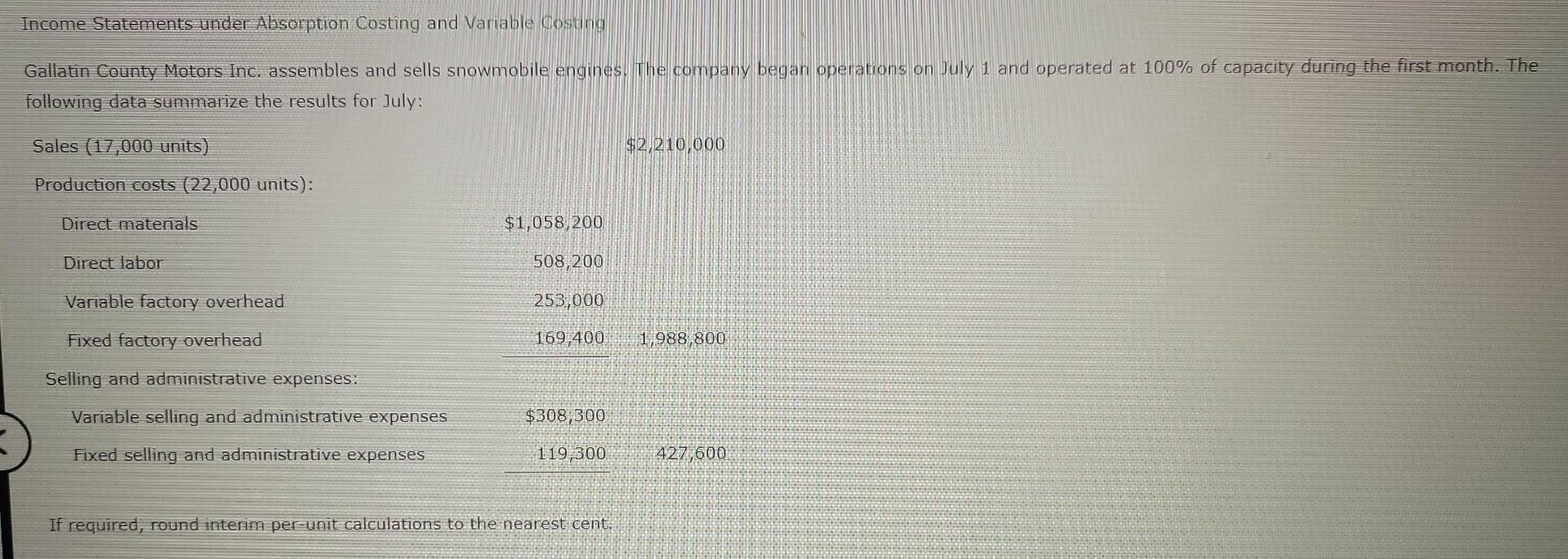
Absorption costing significantly affects a company's financial statements, particularly the income statement and balance sheet. On the income statement, the cost of goods sold includes both variable and fixed manufacturing costs. This can lead to higher reported profits in periods when production exceeds sales, as some of the fixed manufacturing overhead is deferred in inventory.
On the balance sheet, inventory is valued at its full cost, including all manufacturing costs. This can result in a higher inventory valuation compared to variable costing.
"Absorption costing is required for external reporting under GAAP, making it the standard for publicly traded companies," explains Dr. Anya Sharma, a professor of accounting at the University of Business.
Advantages of Absorption Costing
One of the primary advantages of absorption costing is its compliance with GAAP. This is crucial for external reporting and allows for easier comparison of financial statements across different companies.
It also provides a more complete picture of the cost of a product by including all manufacturing costs, which is helpful for long-term pricing decisions.
Moreover, it can discourage managers from focusing solely on short-term profitability by incentivizing production levels to absorb fixed overhead costs.
Disadvantages of Absorption Costing
Despite its advantages, absorption costing has some drawbacks. It can be more complex to implement and requires careful allocation of fixed overhead costs.
It can also lead to inaccurate product costing if the predetermined overhead rate is not accurately calculated. Furthermore, it can mask the true profitability of products, especially when production levels fluctuate.
Professor David Lee, an expert in managerial accounting, emphasizes that "Absorption costing can distort decision-making, especially in the short-term, as it can make it difficult to identify truly profitable products."
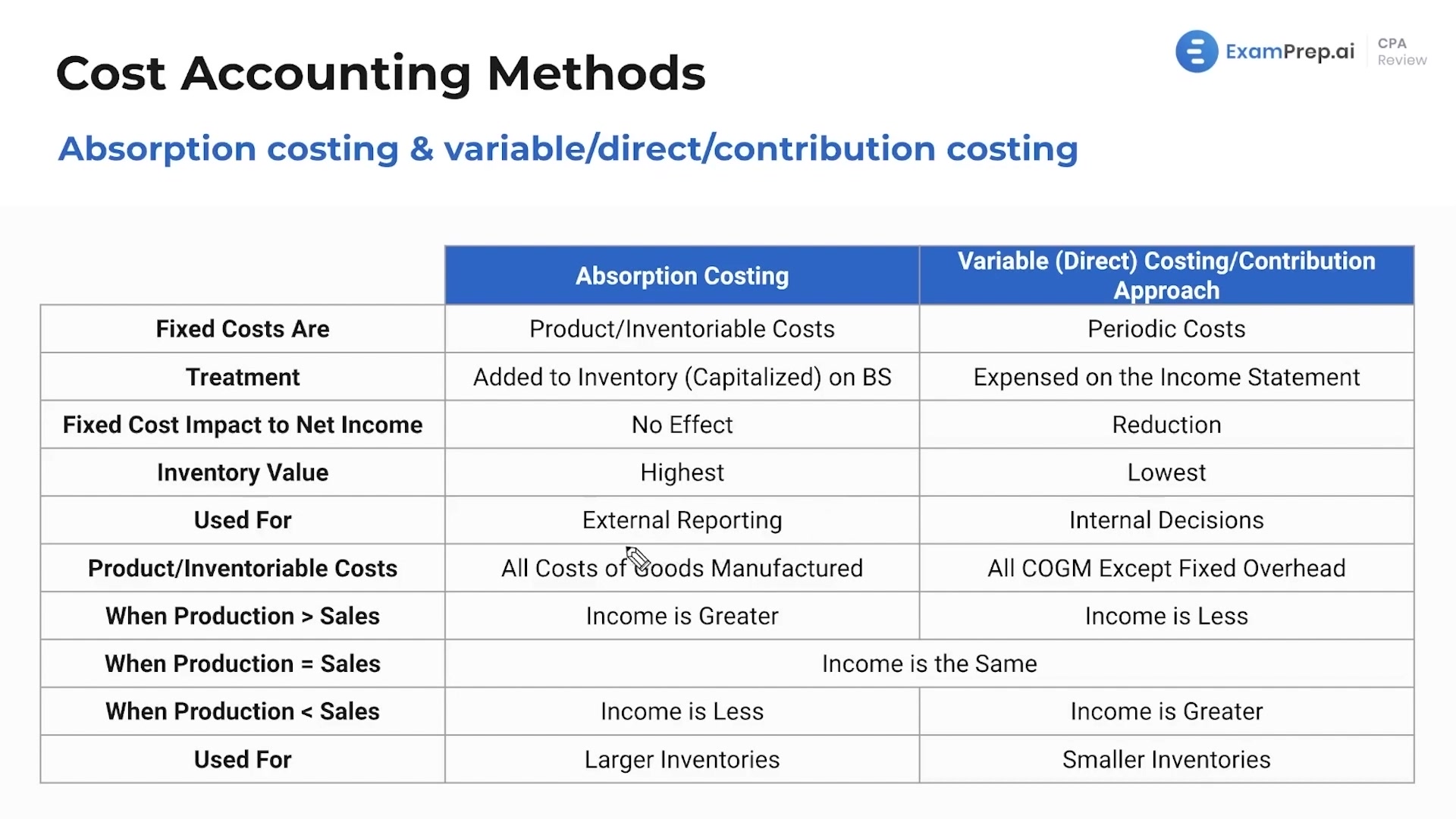
Variable Costing vs. Absorption Costing
It's crucial to understand the difference between absorption costing and variable costing. Variable costing, also known as direct costing, only includes variable manufacturing costs in the product cost. Fixed manufacturing overhead is treated as a period cost and expensed in the period it is incurred.
Under variable costing, the cost of goods sold only includes direct materials, direct labor, and variable manufacturing overhead. This method provides a clearer picture of the incremental cost of producing one more unit.
The key difference lies in the treatment of fixed manufacturing overhead. Absorption costing includes it in product cost, while variable costing treats it as a period cost. This difference can lead to significant variations in reported profits, especially when production and sales levels differ.
The Right Answer: Understanding the True Statement
Now, back to our original question: Which of the following statements is true regarding absorption costing? Given our discussion, the accurate statement is that absorption costing includes all manufacturing costs—both direct and indirect, variable and fixed—in the product cost.
This is the defining characteristic of absorption costing, differentiating it from other costing methods like variable costing.
Therefore, understanding this central tenet is critical for accurate financial reporting and sound business decision-making.
Real-World Implications
The implications of choosing absorption costing extend beyond financial statements. For example, a manufacturing company using absorption costing might decide to increase production, even if sales are stagnant, simply to absorb more fixed overhead costs and improve short-term profitability.
However, this could lead to excess inventory and increased storage costs in the long run. Conversely, a company using variable costing might make different production decisions based on the true incremental cost of production.
Ultimately, the choice between absorption costing and variable costing depends on the specific needs of the business and the purpose of the costing information.
Conclusion: A Holistic View
In conclusion, absorption costing is a comprehensive costing method that plays a vital role in financial reporting and managerial decision-making. While it offers several advantages, including GAAP compliance and a complete picture of product costs, it's essential to be aware of its limitations.
By understanding the principles and implications of absorption costing, businesses can make more informed decisions about pricing, production, and profitability.
It's about more than just numbers; it's about understanding the true cost of bringing that loaf of bread, that chair, or any product to the market. And that, ultimately, is what makes all the difference.