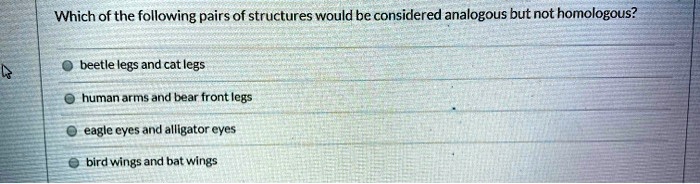
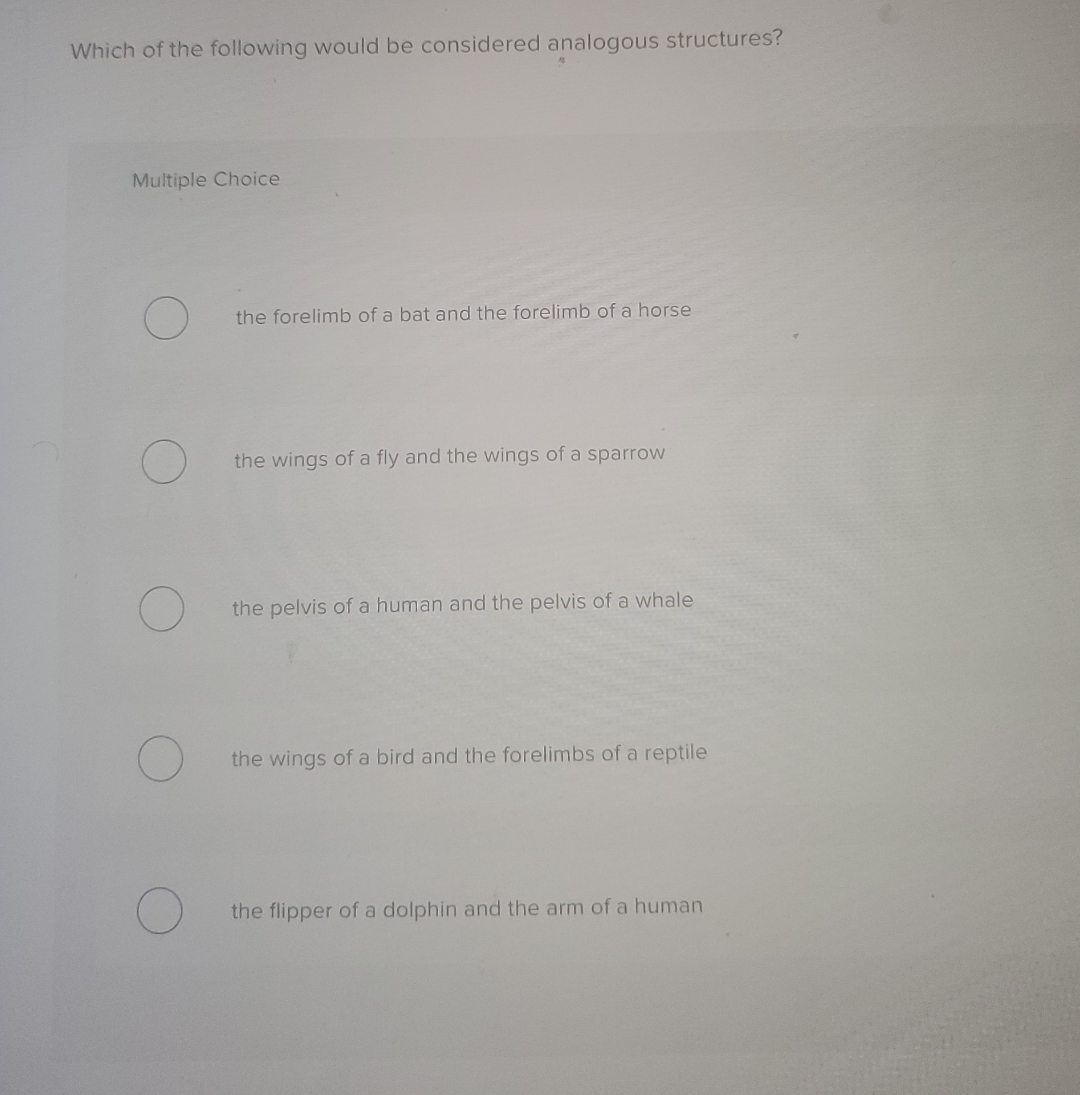
Which Of The Following Would Be Considered Analogous Structures
The natural world, a tapestry woven with intricate designs and surprising convergences, often presents us with structures that bear a striking resemblance despite vastly different origins. Understanding these similarities, particularly when they arise through convergent evolution, is crucial for grasping the mechanisms that shape life on Earth. One key concept in unraveling these patterns is the identification of analogous structures, a cornerstone of evolutionary biology.
Analogous structures, features in different species that perform similar functions but evolved independently, highlight how natural selection can arrive at the same solution through different evolutionary pathways. This article delves into the intricacies of identifying analogous structures, exploring examples, and underscoring their significance in evolutionary studies. We'll examine how these structures differ from homologous structures, and what insights they offer into the power of environmental pressures.
Understanding Analogous Structures
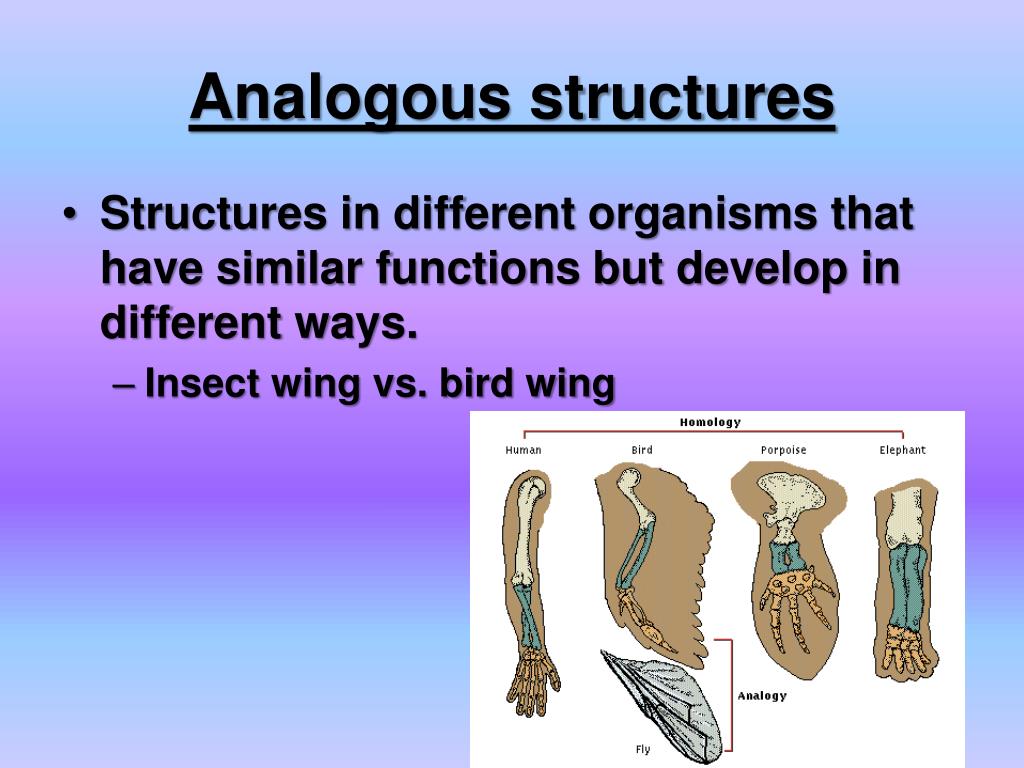
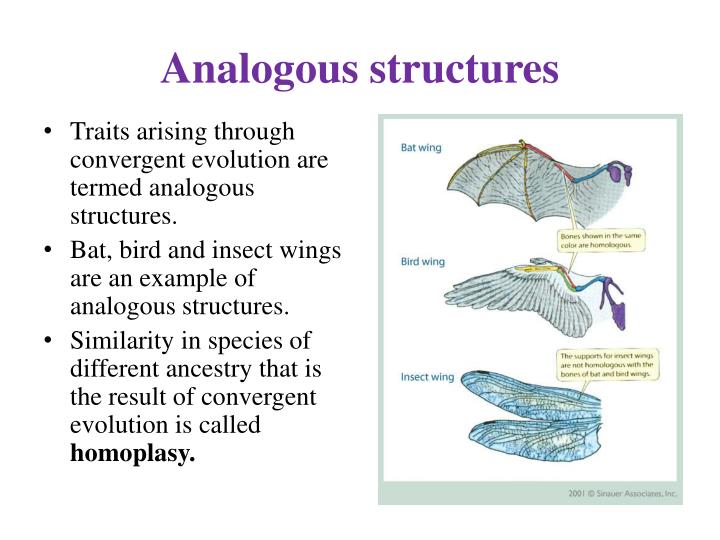
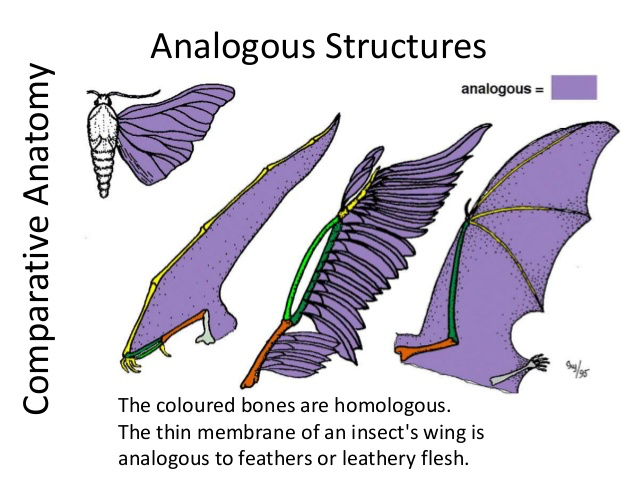
Analogous structures arise through convergent evolution, a process where unrelated organisms independently evolve similar traits as adaptations to similar environments or ecological niches. It's important to distinguish analogous structures from homologous structures, which share a common ancestry even if their function differs.
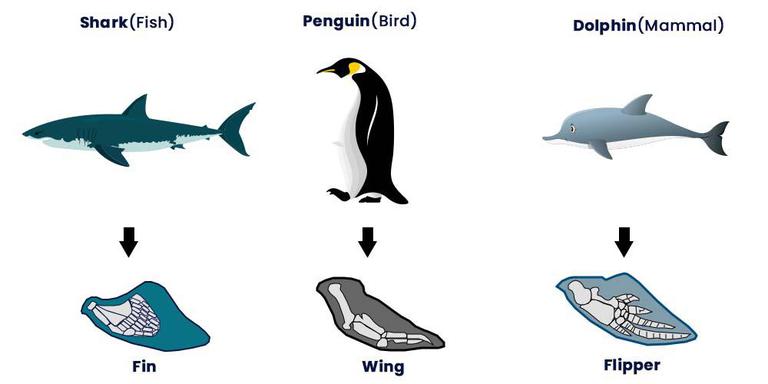
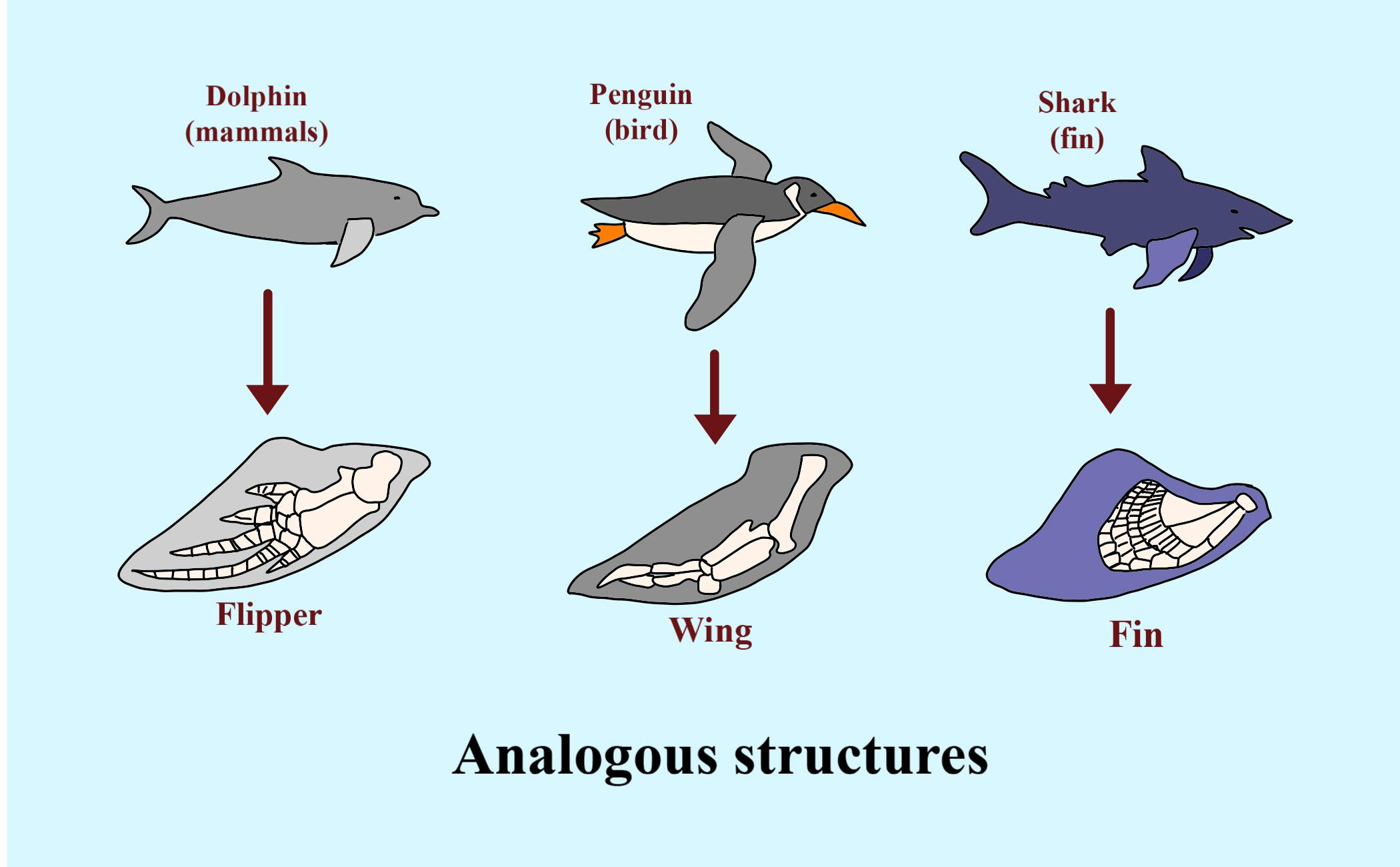
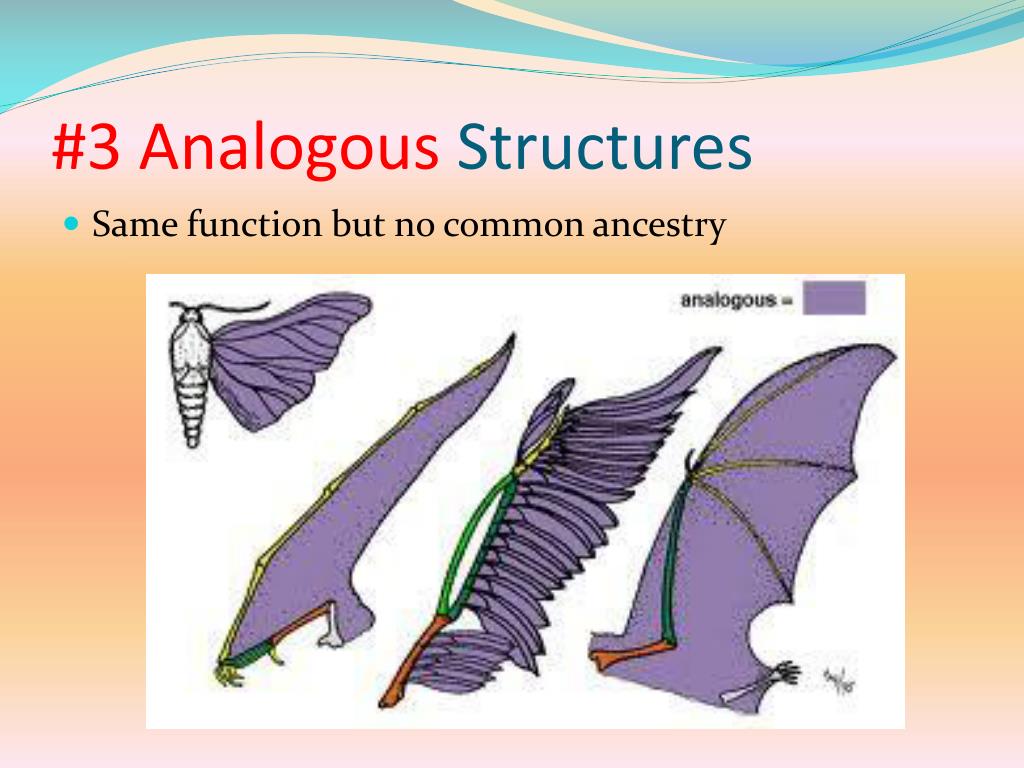
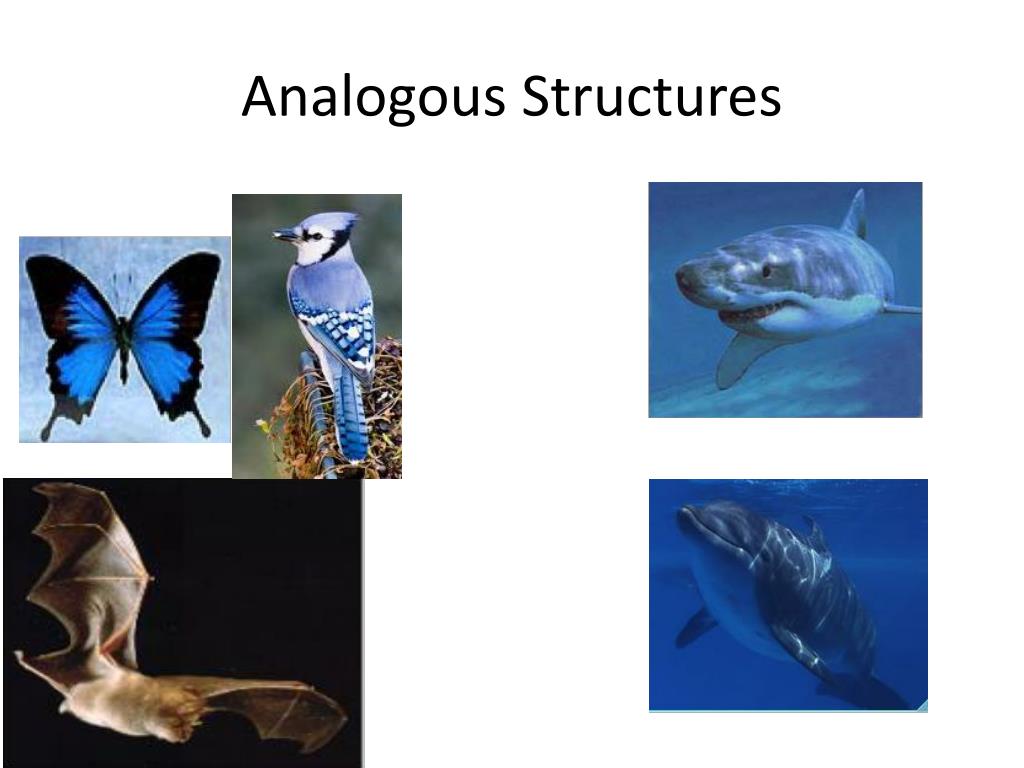
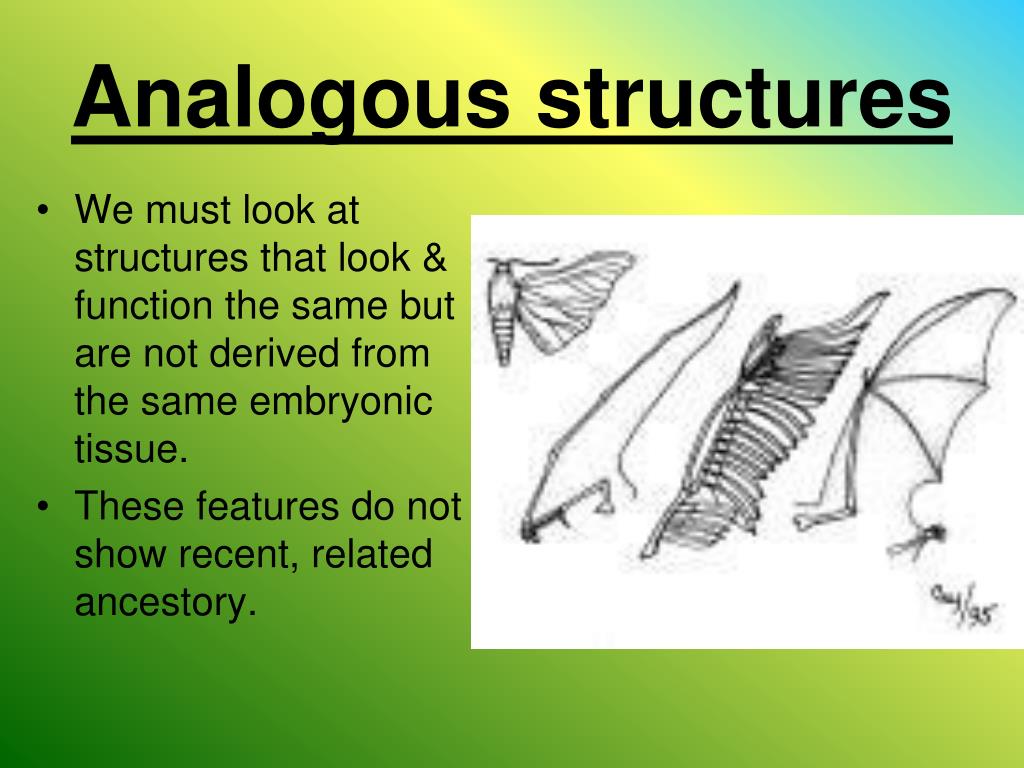
For example, the wing of a bat and the wing of an insect are analogous. Both serve the function of flight. However, their underlying anatomy and developmental origins are completely different.
Key Characteristics of Analogous Structures
Several key characteristics help identify analogous structures. These include similar function, different underlying anatomy, and independent evolutionary origins.
The structure also doesn’t have to be exactly the same, rather, it must serve a similar purpose. Often, the more different species and the more similar the environmental pressures, the more analogous features stand out.
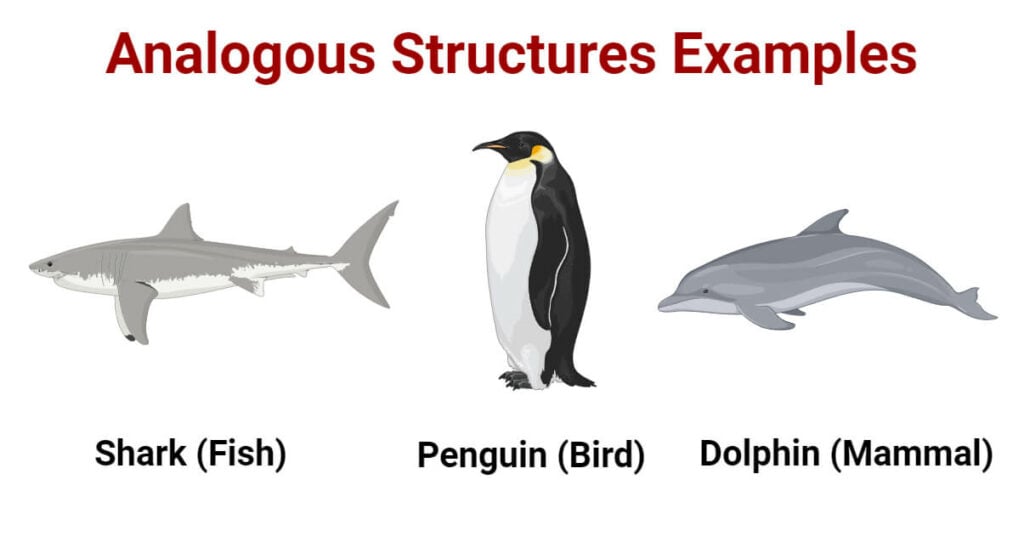
Consider the streamlined body shape of a shark (a fish) and a dolphin (a mammal). Both live in aquatic environments and require efficient movement through water, leading to the evolution of similar body forms. This is another prime example.
Examples of Analogous Structures
Numerous examples of analogous structures exist across the biological spectrum. These examples illustrate the diverse ways in which evolution can converge on similar solutions.
The camera eye of an octopus and the camera eye of a vertebrate represent a classic example. While both structures achieve the same function, image capture, their developmental pathways and underlying anatomy are quite distinct.
Similarly, the thorns of a rose bush and the spines of a cactus serve the same function - protection from herbivores. However, roses are flowering plants and cacti are desert plants. Therefore, these are analogous structures.
Distinguishing Analogy from Homology
The distinction between analogy and homology is fundamental to understanding evolutionary relationships. Homologous structures share a common ancestry, even if their function differs.
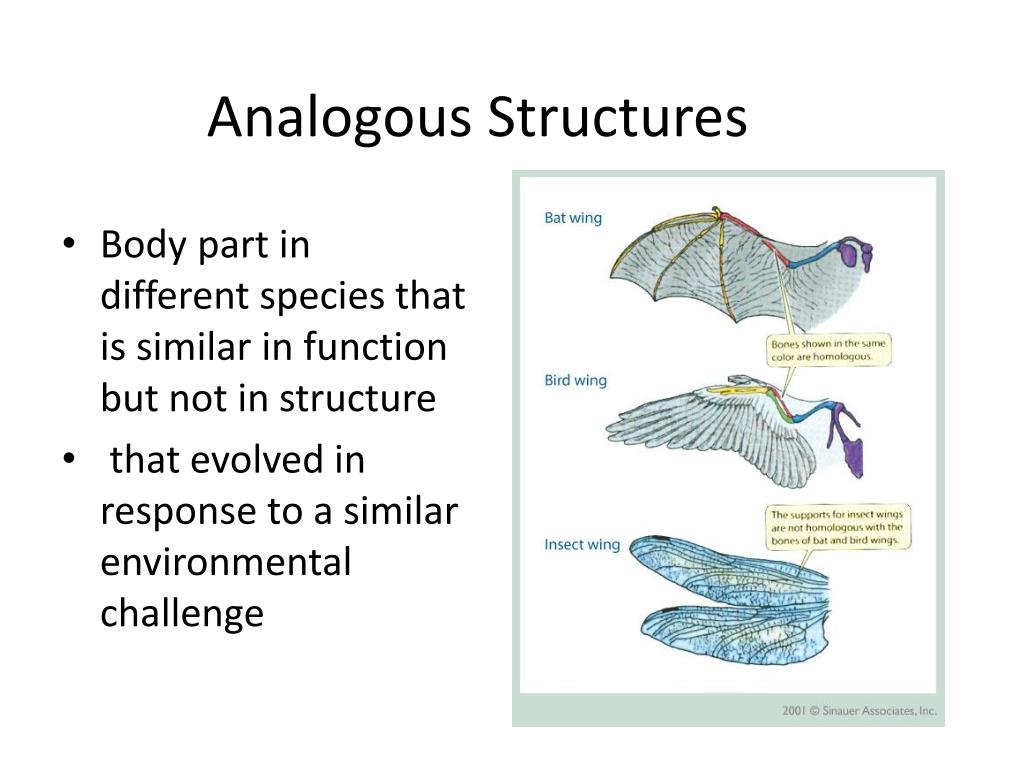
A classic example is the forelimb of a human, a bat, and a whale. While used for different purposes (grasping, flying, and swimming), all share the same basic bone structure, indicating a shared evolutionary origin.
Analogy, on the other hand, arises independently due to similar environmental pressures. This is evident in the wings of birds and insects. They are not from a shared ancestor.
The Significance of Analogous Structures in Evolutionary Studies
Analogous structures provide valuable insights into the power of natural selection and the adaptability of life. They demonstrate that similar environmental pressures can lead to similar evolutionary outcomes, even in distantly related organisms.
By studying analogous structures, evolutionary biologists can better understand the constraints and opportunities that shape the evolution of life on Earth. It allows them to trace the origins of specific adaptions.
Furthermore, the study of analogous structures is crucial for reconstructing phylogenetic trees and understanding the evolutionary relationships between different species. This is critical for biodiversity and conservation efforts.
Challenges in Identifying Analogous Structures
Identifying analogous structures can sometimes be challenging, especially when dealing with complex traits or incomplete fossil records. It requires careful analysis of anatomical, developmental, and genetic data to distinguish between convergent evolution and shared ancestry.
One potential pitfall is mistaking superficially similar structures as analogous when they may actually be homologous. This can lead to incorrect interpretations of evolutionary relationships.
Advanced techniques, such as molecular phylogenetics and comparative genomics, are increasingly being used to resolve these ambiguities and provide more accurate assessments of evolutionary history.
Future Directions in Analogous Structure Research
Future research on analogous structures is likely to focus on integrating multiple lines of evidence, including genomic, developmental, and ecological data. This holistic approach will provide a more comprehensive understanding of the evolutionary processes that drive convergent evolution.
Additionally, researchers are exploring the genetic mechanisms underlying the development of analogous structures. This may reveal common genetic pathways that are activated in response to similar environmental pressures.
Understanding the evolution of analogous structures will continue to be a vital area of research, furthering our appreciation of the remarkable adaptability and diversity of life on Earth. It's a critical step in understanding the history of organisms and their adaptations.