Which Of The Statements Correctly Represents The Accounting Equation
The fundamental accounting equation, a cornerstone of financial accounting, ensures the balance between a company's assets, liabilities, and equity. Understanding which statement accurately represents this equation is crucial for anyone involved in financial analysis, business management, or even personal finance.
This article delves into the correct representation of the accounting equation, exploring its components and implications. The equation, in its simplest form, dictates that a company's total assets must always equal the sum of its liabilities and equity. This seemingly straightforward formula underpins the entire double-entry bookkeeping system and provides a snapshot of a company's financial health.
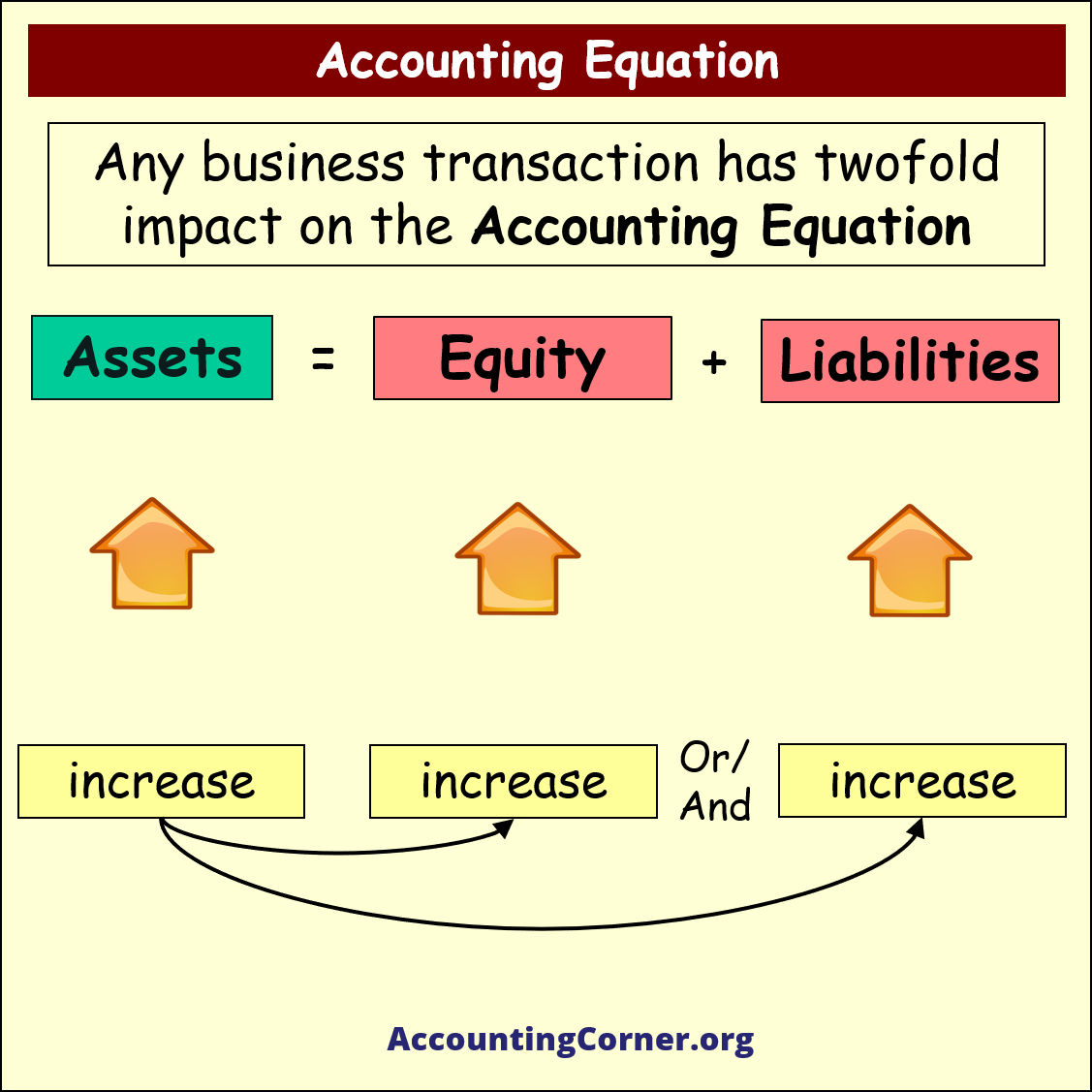
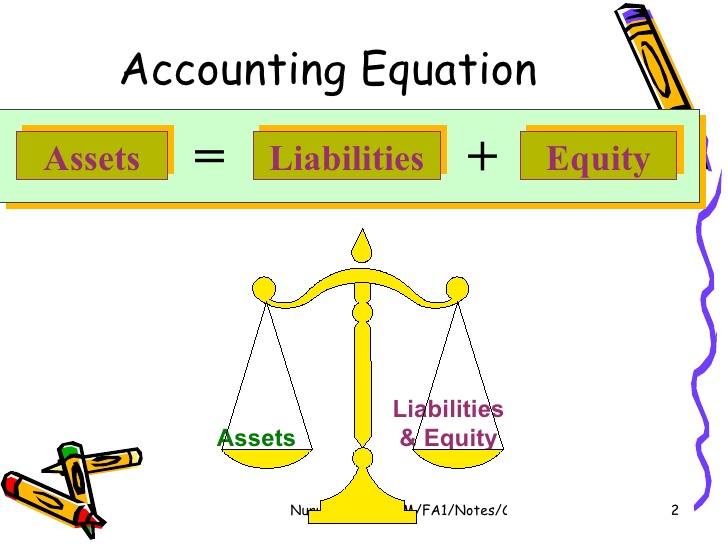
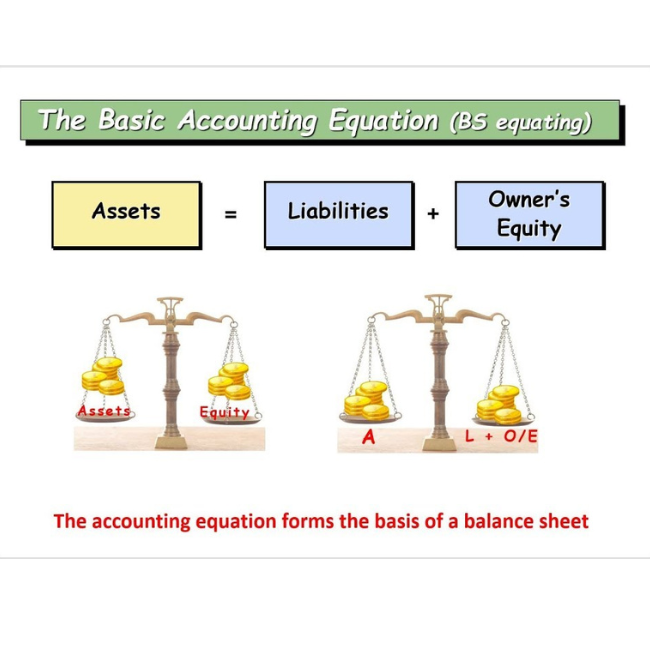
The Accounting Equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity
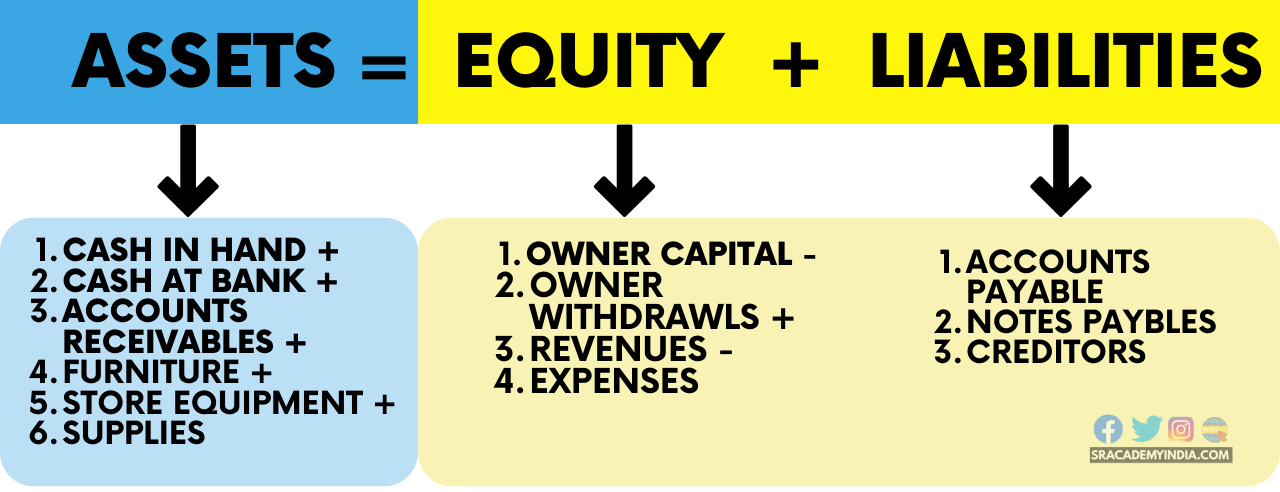
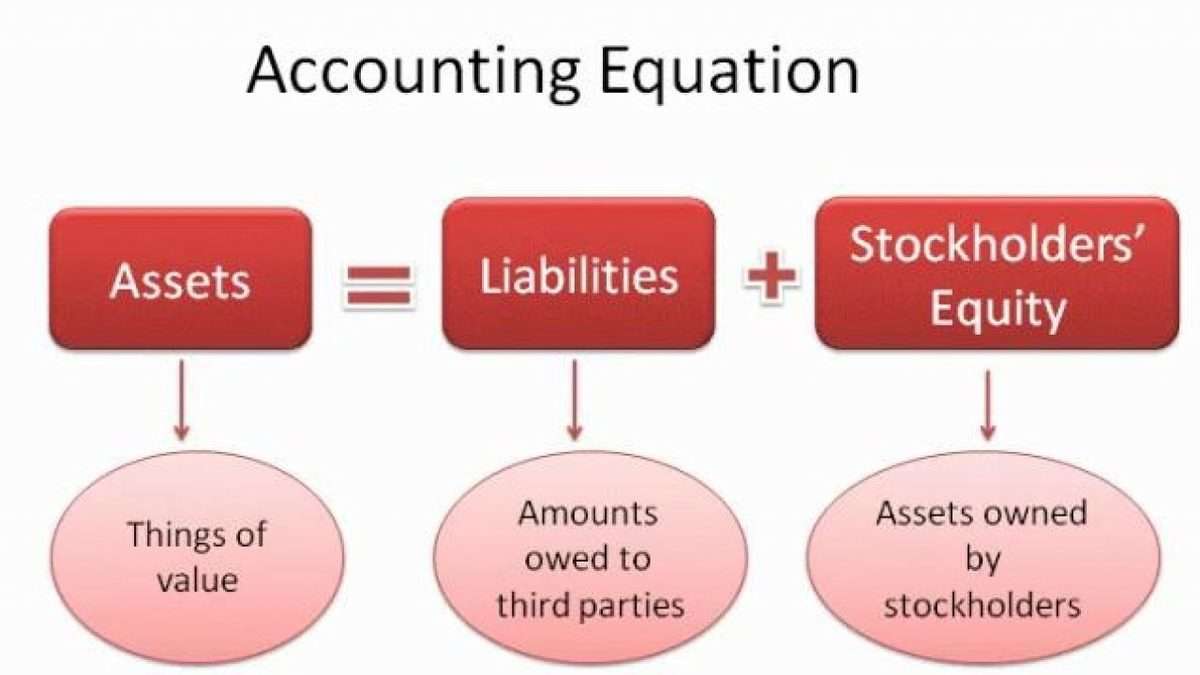
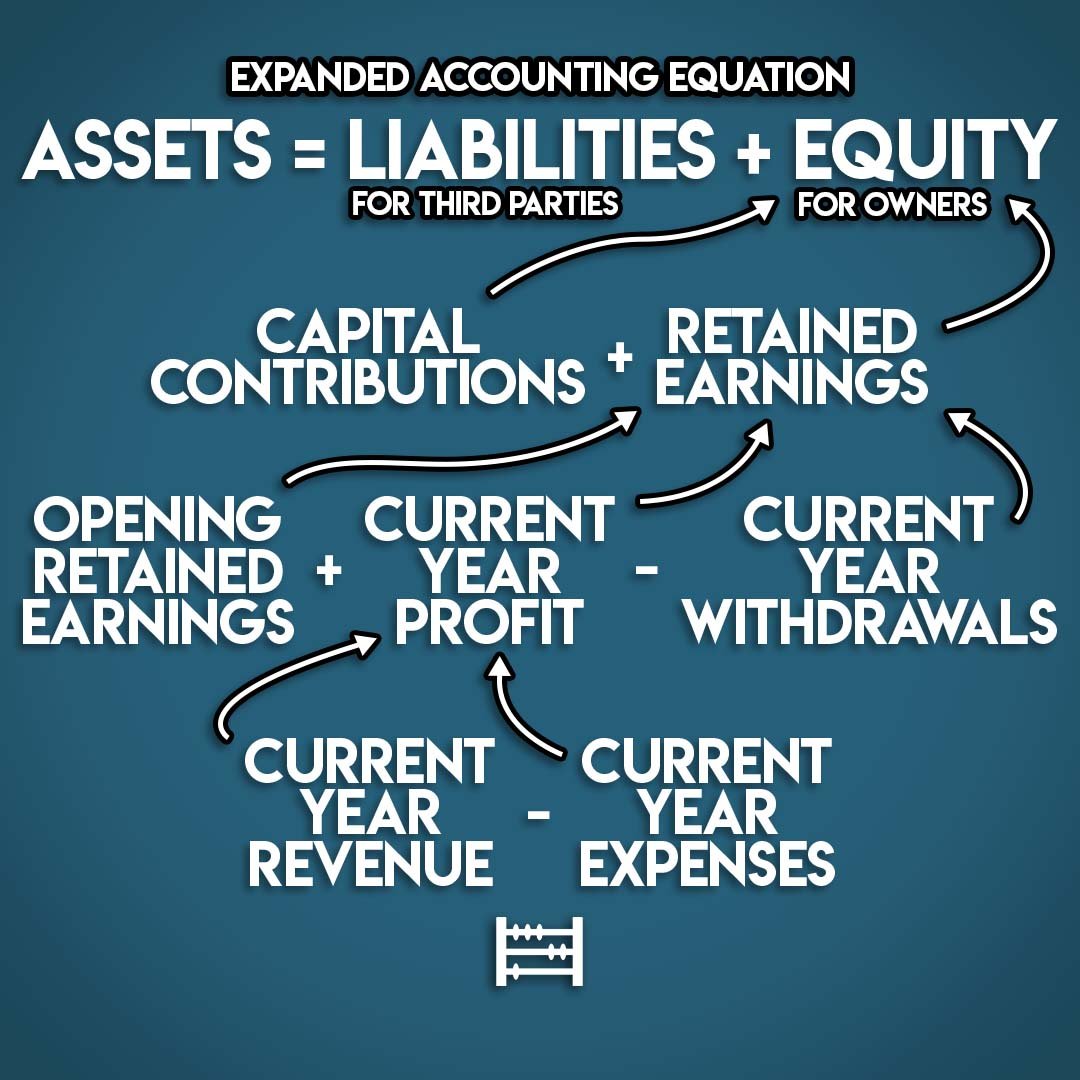
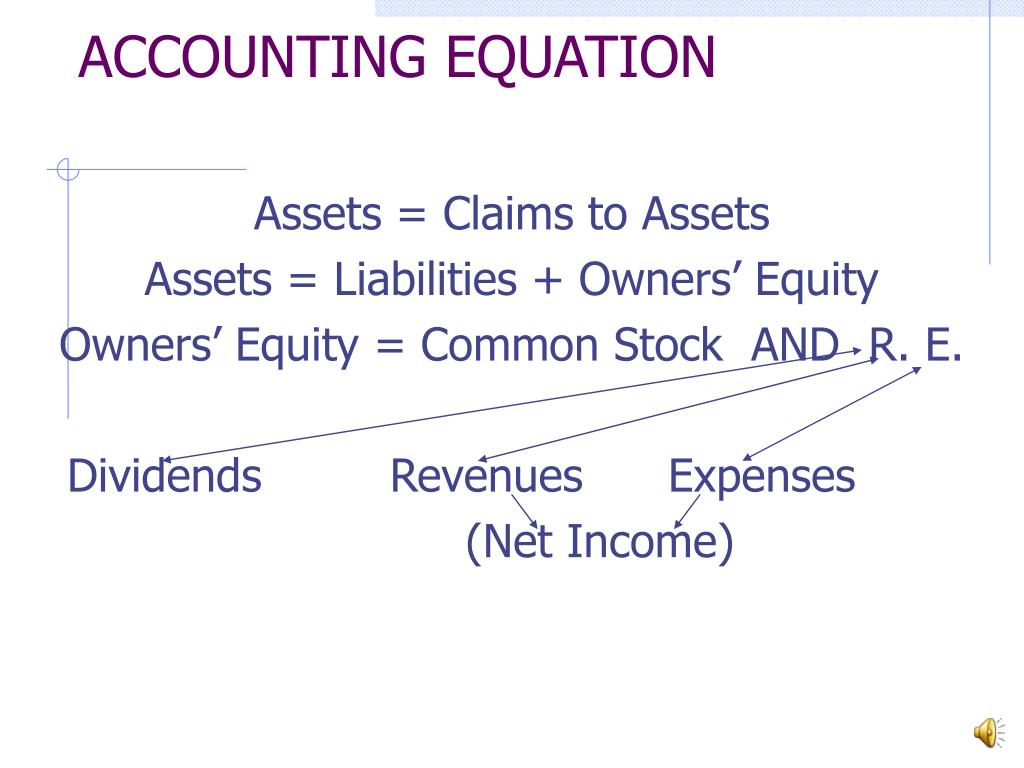
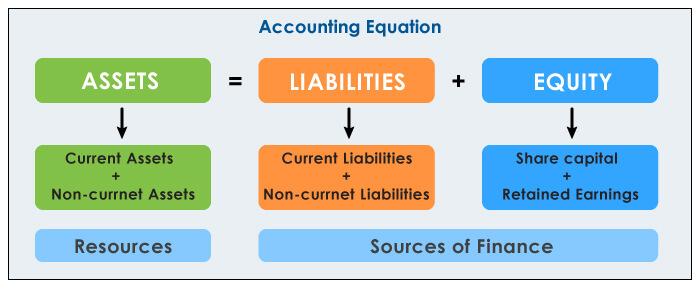
The correct representation of the accounting equation is: Assets = Liabilities + Equity. This equation highlights the fundamental relationship between what a company owns (assets), what it owes to others (liabilities), and the owner's stake in the company (equity).
Assets represent everything a company owns that has monetary value. This includes cash, accounts receivable, inventory, equipment, and real estate. Assets are resources that the company uses to generate revenue.
Liabilities, on the other hand, represent the company's obligations to external parties. These include accounts payable, salaries payable, loans, and deferred revenue. Liabilities are essentially debts that the company must repay.
Equity, also known as owner's equity or shareholders' equity, represents the residual interest in the assets of the company after deducting liabilities. It is the owner's stake in the business and reflects the net worth of the company.
Understanding the Components
To further clarify the equation, let's consider a simple example. Suppose a business has $100,000 in assets, $30,000 in liabilities, and $70,000 in equity. This means the business owns resources worth $100,000, owes $30,000 to creditors, and the owners have a $70,000 stake in the business.
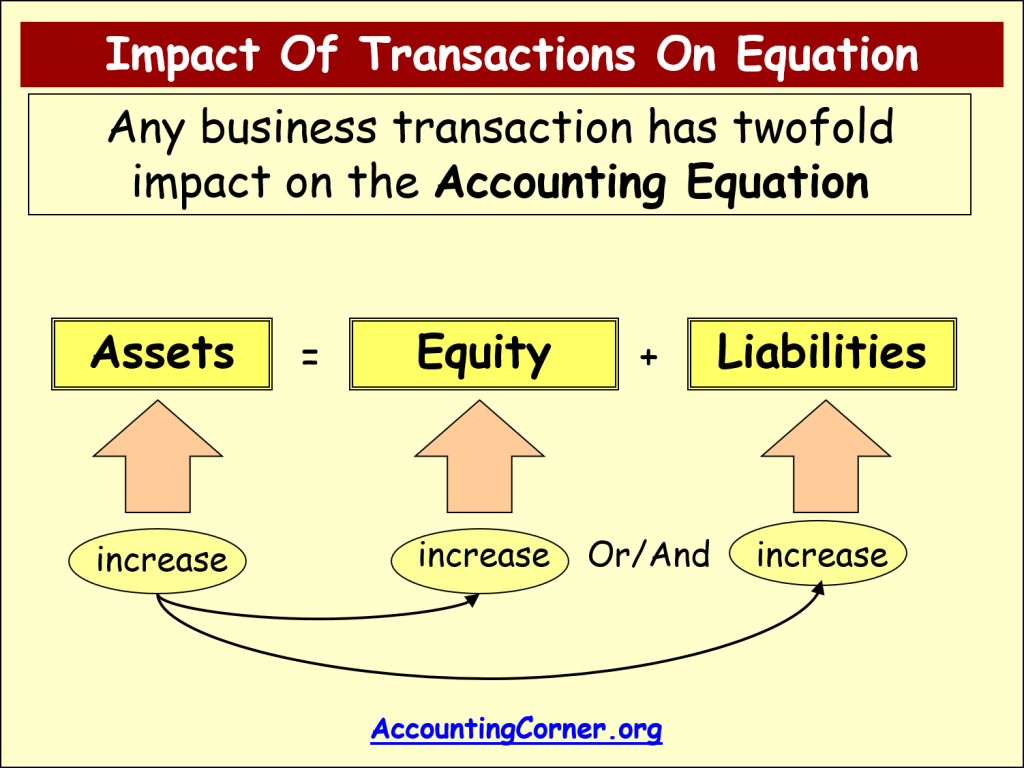
The equation remains balanced because $100,000 (Assets) = $30,000 (Liabilities) + $70,000 (Equity). Any transaction that affects one side of the equation must have an equal and opposite effect on the other side to maintain balance.
For instance, if the company takes out a $10,000 loan (increasing liabilities), the cash account (an asset) will also increase by $10,000. This ensures that the equation remains in balance.
Why is the Accounting Equation Important?
The accounting equation is the foundation upon which the entire accounting system is built. It ensures that every transaction is recorded in a way that maintains the balance between assets, liabilities, and equity.
This balance is critical for several reasons. First, it provides a clear picture of a company's financial position at any given time. Second, it helps prevent errors in accounting records, as any imbalance in the equation indicates a mistake.
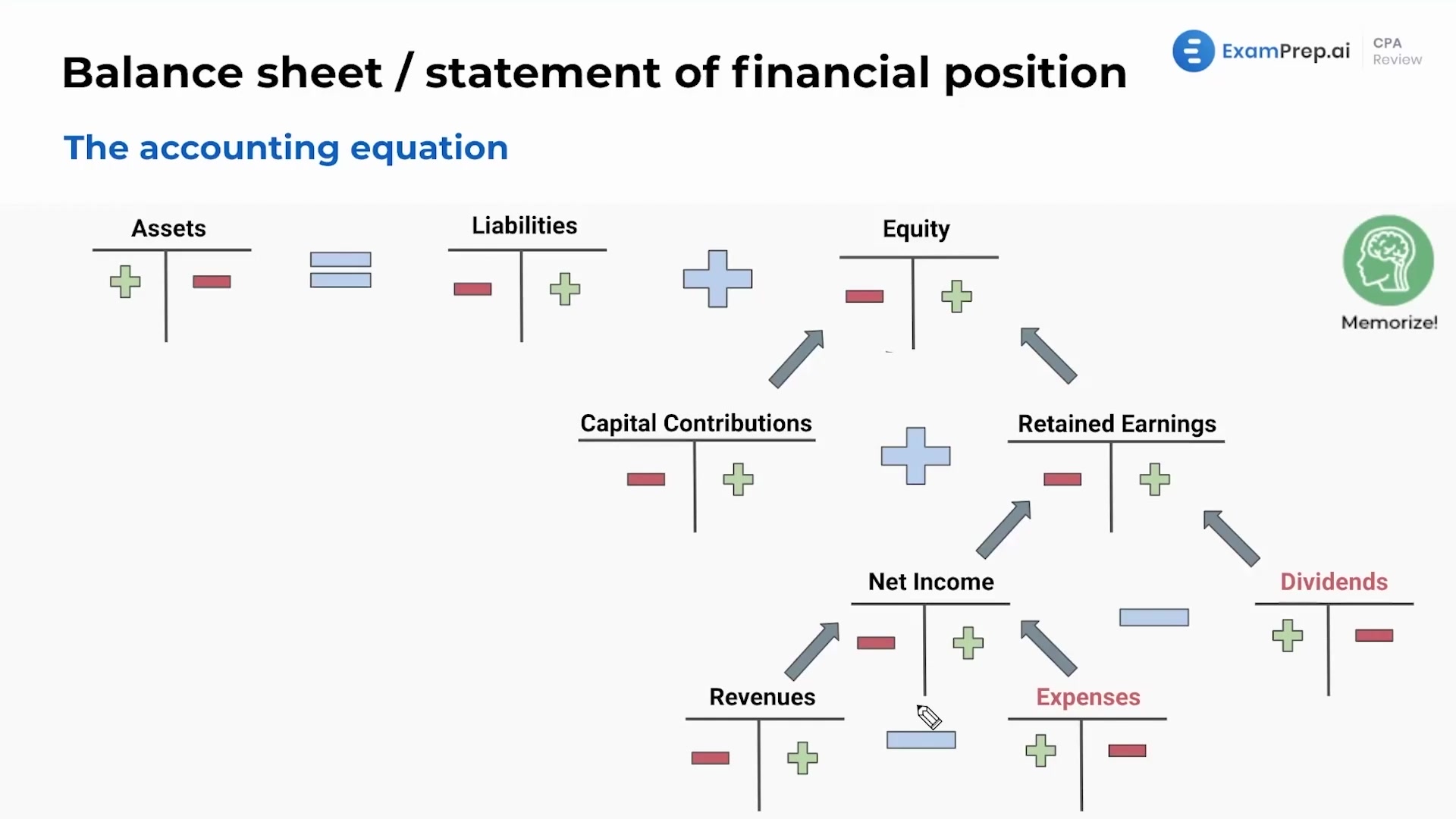
Furthermore, the accounting equation is used to prepare key financial statements, such as the balance sheet. The balance sheet is a snapshot of a company's assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time, derived directly from the accounting equation.
The importance of the accounting equation extends beyond internal accounting practices. Investors and creditors rely on this equation to assess the financial health of a company before making investment or lending decisions.
A company with a healthy balance sheet, reflected in a balanced accounting equation, is generally considered a safer investment. It indicates that the company has sufficient assets to cover its liabilities and a solid equity base.
Common Misconceptions
One common misconception is that the accounting equation is just a theoretical concept. In reality, it is a practical tool used daily by accountants and financial professionals to record and analyze financial transactions.
Another misconception is that it only applies to large corporations. The accounting equation is equally relevant to small businesses, non-profit organizations, and even individuals managing their personal finances.
Understanding and applying the accounting equation is essential for making informed financial decisions. For example, understanding how taking out a loan (increasing liabilities) affects your assets and equity can help you manage your debt responsibly.
In conclusion, the statement that correctly represents the accounting equation is: Assets = Liabilities + Equity. This equation is the bedrock of accounting principles and a vital tool for understanding and managing financial resources. It is used to track and record economic activity and provides a simple, yet powerful, model for understanding the financial health of any organization or individual.
Mastering the accounting equation is a fundamental step towards financial literacy and success in the business world.
By understanding how assets, liabilities, and equity interact, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions to achieve their financial goals.

/balancesheet.asp-V1-5c897eae46e0fb0001336607.jpg)
/balancesheet.asp-V1-5c897eae46e0fb0001336607.jpg)




/dotdash_Final_Accounting_Equation_Aug_2020-01-5991871f007444398dea7856b442af55.jpg)