1.5 Micrometers Squared To Meters Squared

Imagine holding a speck of dust in your hand, so tiny it’s almost invisible. Now picture that speck not as a random particle, but as a precisely measured square. That’s the kind of scale we’re talking about, a world of micrometers where even the smallest differences matter.
This article explores the journey from understanding a minute area of 1.5 micrometers squared to grasping its equivalent in the more familiar scale of meters squared. It delves into the significance of this conversion across various scientific and technological fields, highlighting how this seemingly simple mathematical exercise bridges the gap between the microscopic and macroscopic worlds.
The World of Micrometers
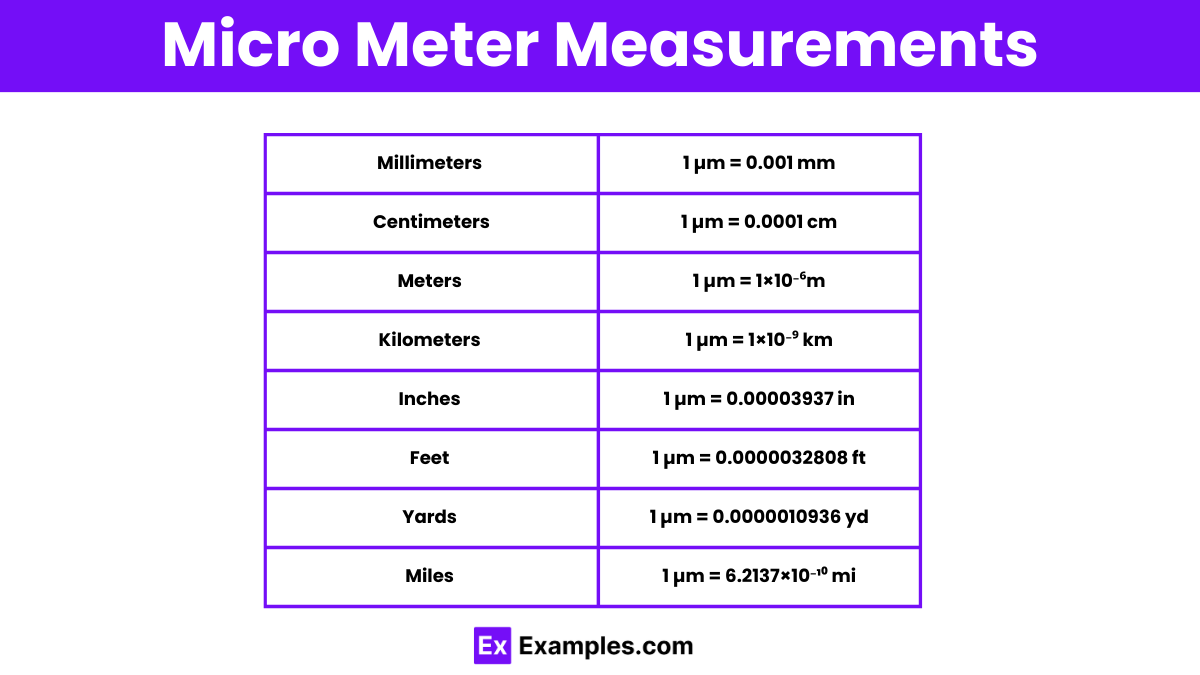
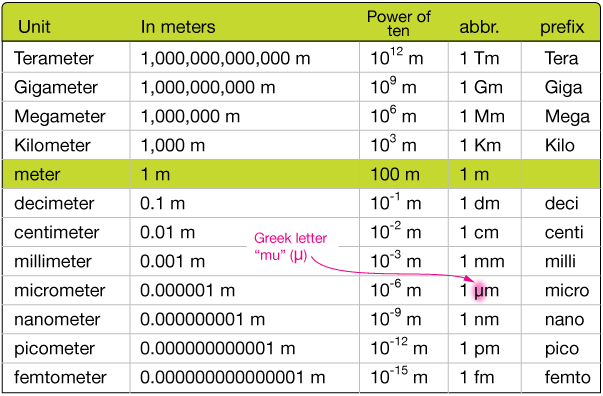
The micrometer, also known as a micron, is a unit of length equal to one millionth of a meter (10-6 m). It's a common unit in fields like microscopy, cell biology, and materials science, where observations and measurements often occur at the cellular or even subcellular level.
To put this in perspective, a human hair is typically between 17 and 180 micrometers in diameter, according to the U.S. National Nanotechnology Initiative. Bacteria are typically 0.5 to 5 micrometers in length. You can find more details on this from sources like the National Institutes of Health.
When we talk about area, we're considering a two-dimensional space. One micrometer squared (μm2) is the area of a square with sides that are each one micrometer long. This unit becomes crucial when quantifying the surface area of cells, microchips, and other minuscule objects.
Bridging the Gap: Converting to Meters Squared
While micrometers squared are essential for nanoscale work, meters squared (m2) are far more practical for everyday applications. Architects, engineers, and even home decorators use meters squared to measure rooms, buildings, and land.
The conversion factor between micrometers and meters is significant: 1 meter is equal to 1,000,000 micrometers. Therefore, 1 meter squared is equal to 1,000,000,000,000 micrometers squared (1012 μm2).
To convert 1.5 micrometers squared to meters squared, we divide 1.5 by 1012. This gives us 1.5 x 10-12 m2, a tremendously small number that highlights the vast difference in scale.
Why Does This Conversion Matter?
The ability to convert between these units is critical in several disciplines. In microelectronics, for example, the size of transistors and other components is often measured in micrometers. Converting these measurements to meters allows engineers to understand how these tiny components contribute to the overall size and function of larger devices.
In cell biology, scientists often study the surface area of cells to understand how they interact with their environment. Understanding the size of individual cells and their surface area is crucial for research related to diseases and cures, as detailed in numerous scientific publications.
Consider the development of new materials. Researchers might design a material with specific properties at the microscale, but need to scale up production to create larger samples. Converting between micrometers squared and meters squared helps them bridge the gap between laboratory experiments and real-world applications.
Examples in Action
Let's look at a practical example. Imagine a researcher is studying the spread of a virus on a cell surface. They measure the infected area as 1.5 μm2.
While this number is useful for analyzing the infection at the microscopic level, converting it to meters squared (1.5 x 10-12 m2) provides a different perspective. It illustrates just how small the infected area is compared to, say, the surface area of a lab dish, or even the skin on your finger.
Another example comes from the field of microfluidics. Engineers designing microfluidic devices, tiny chips that manipulate fluids on a microscopic scale, might need to calculate the cross-sectional area of microchannels. A channel with a cross-sectional area of 1.5 μm2, when converted to meters squared, allows for calculations involving flow rates and fluid dynamics in more conventional units.
Tools and Resources for Conversion
Fortunately, converting between micrometers squared and meters squared doesn't require complex calculations by hand. Many online conversion tools and calculators are available to simplify the process.
Websites like Google's built-in unit converter, or dedicated sites like UnitConverters.net, offer quick and accurate conversions. These tools are invaluable for students, researchers, and anyone working with measurements at different scales.
For more complex scientific calculations, software packages like MATLAB or Python with libraries like NumPy provide robust tools for unit conversions and data analysis.
The Bigger Picture
The simple act of converting 1.5 micrometers squared to meters squared highlights a fundamental concept in science and engineering: scale. The world looks drastically different depending on the units we use to measure it.
Understanding the relationship between these units allows us to connect the microscopic world of atoms and cells to the macroscopic world of everyday objects and human experiences. It's a crucial step in translating scientific discoveries into practical applications.
Ultimately, by mastering these conversions, we gain a more complete and nuanced understanding of the world around us, from the smallest speck of dust to the largest buildings and beyond.