Cancer Rates In China Vs Us

The specter of cancer looms large across the globe, but its manifestation and impact differ significantly between the world's two largest economies, China and the United States. While both nations grapple with rising cancer incidence, their experiences are shaped by distinct demographics, environmental factors, lifestyle choices, and healthcare systems. Understanding these differences is crucial for informing public health strategies and improving cancer outcomes worldwide.
This article delves into a comparative analysis of cancer rates in China and the US, examining the prevalence of various cancer types, the underlying risk factors contributing to these disparities, and the challenges each nation faces in combating this complex disease. By scrutinizing epidemiological data, research findings, and public health initiatives, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of the cancer landscape in these two global powers.
Cancer Incidence and Mortality: A Tale of Two Nations
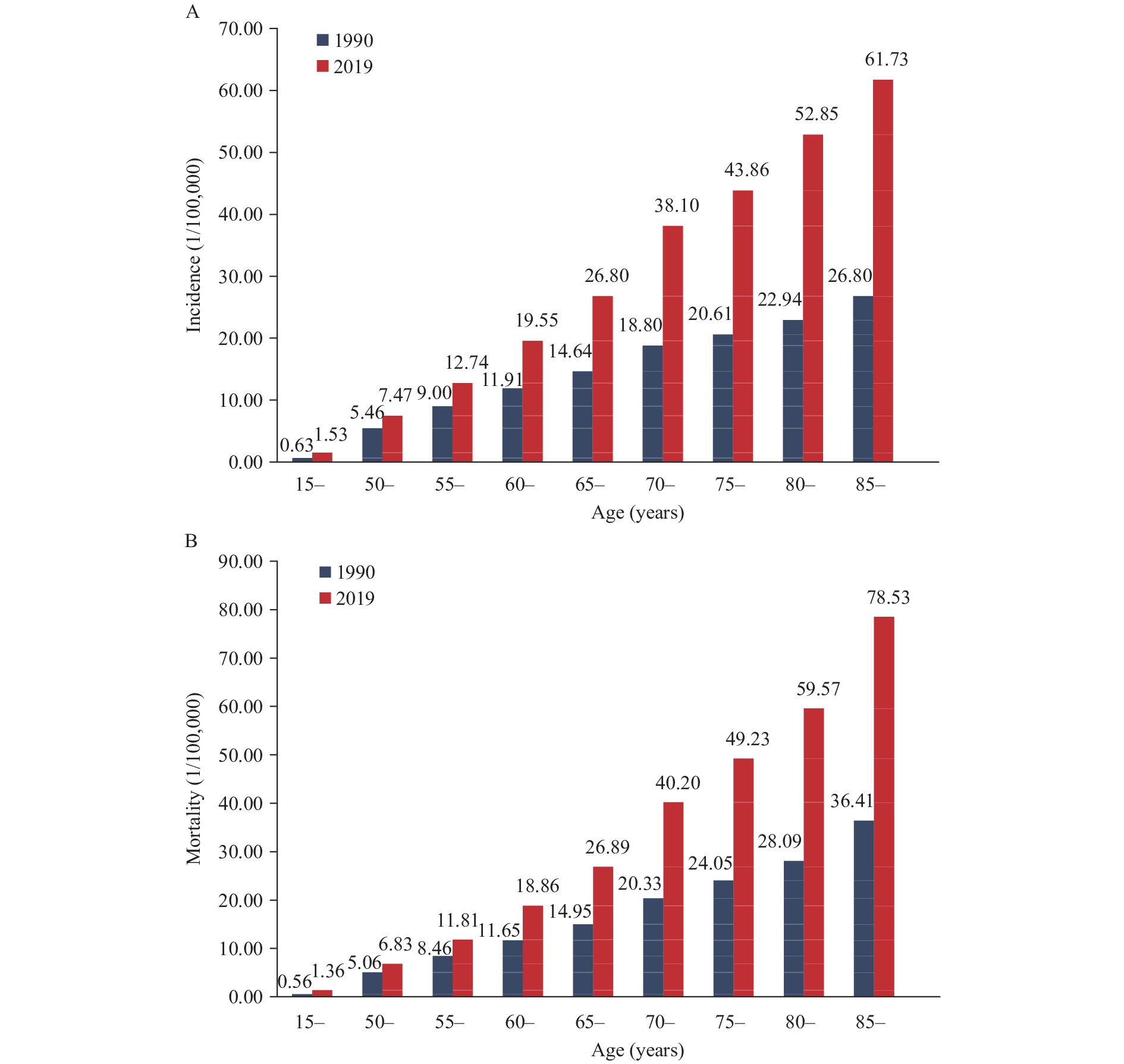
Cancer statistics paint a complex picture. While the US has historically shown higher overall cancer incidence rates, China has witnessed a rapid increase in recent decades.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the US sees a higher number of newly diagnosed cancer cases per capita compared to China, but the gap is narrowing.
Several factors contribute to this trend, including increasing life expectancy in China, changes in lifestyle and dietary habits, and improved cancer detection rates.
Leading Cancer Types: Diverging Patterns
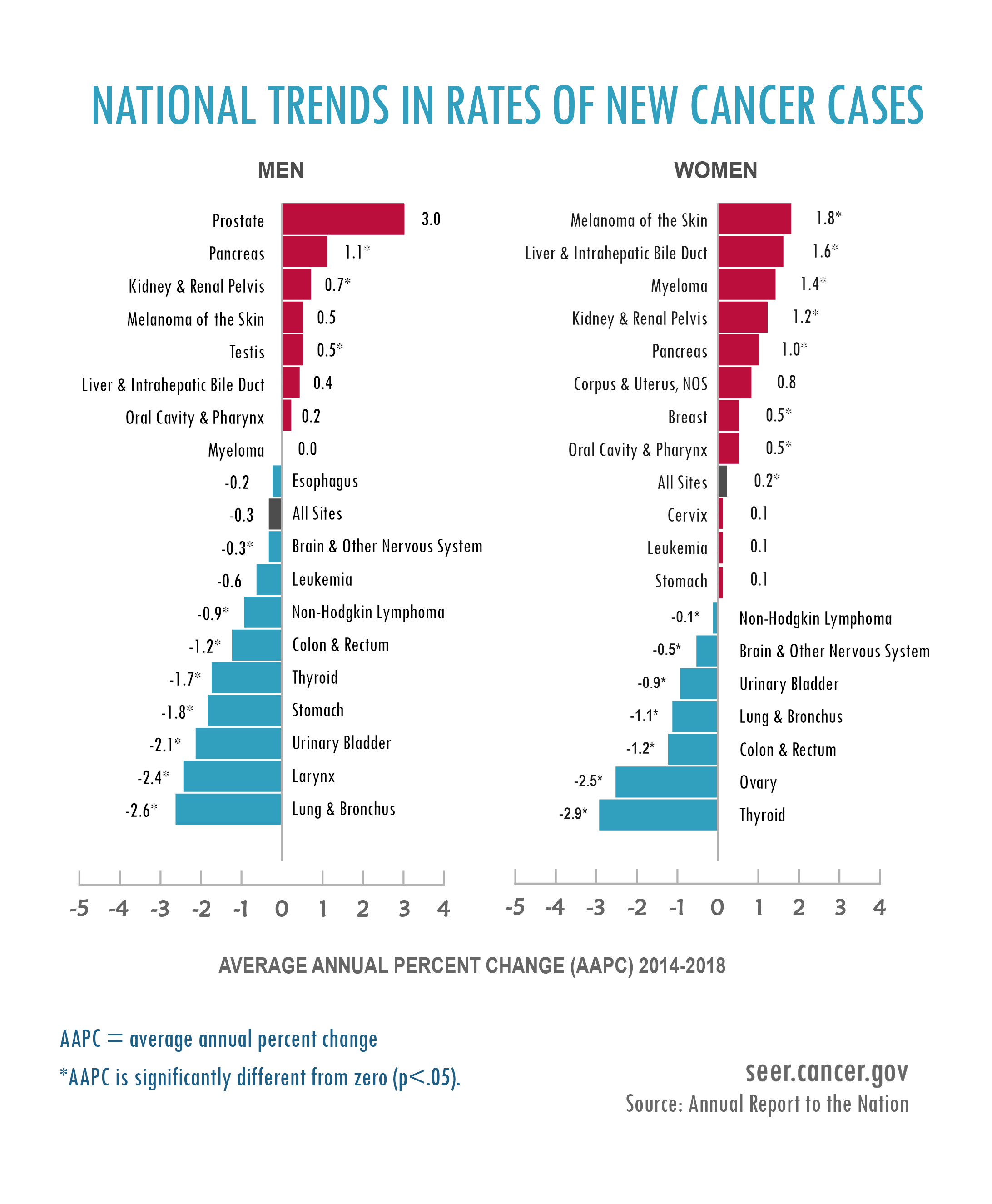
The types of cancer most prevalent in each country also differ. In the US, breast cancer, prostate cancer, and lung cancer are among the most commonly diagnosed, while in China, lung cancer, stomach cancer, and liver cancer take the lead.
This divergence is influenced by a combination of genetic predispositions, environmental exposures, and cultural practices. For example, higher smoking rates in China contribute to the elevated incidence of lung cancer.
Similarly, dietary habits, such as the consumption of preserved foods, have been linked to the higher prevalence of stomach cancer in certain regions of China.
Risk Factors and Environmental Influences
Environmental factors play a significant role in cancer development. Air pollution, particularly in urban areas of China, is a major concern.
Exposure to pollutants like particulate matter (PM2.5) and industrial emissions increases the risk of lung cancer and other respiratory illnesses.
In the US, while air quality has improved in recent decades, exposure to environmental toxins and occupational hazards remains a concern for specific populations.
Lifestyle choices, such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and diet, are also significant contributors to cancer risk in both countries.
The prevalence of obesity and a sedentary lifestyle in the US has been linked to an increased risk of several types of cancer, including breast, colon, and endometrial cancer.
In China, the adoption of Westernized diets, characterized by high-fat and processed foods, is contributing to a similar trend.
Healthcare Systems and Access to Treatment
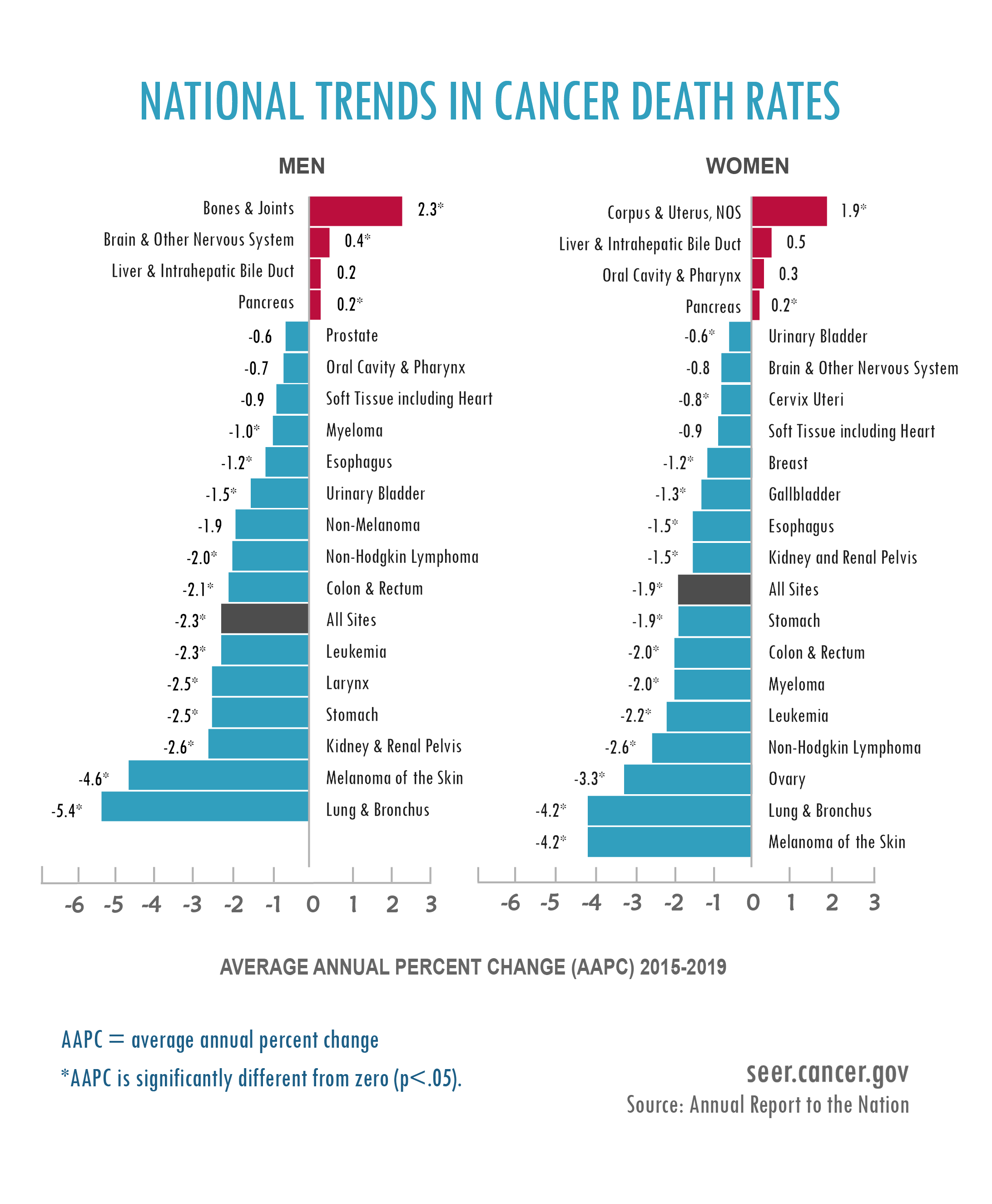
Access to quality healthcare is a critical determinant of cancer outcomes. The US boasts a sophisticated healthcare system with advanced diagnostic and treatment options.
However, disparities in access to care based on socioeconomic status and insurance coverage remain a significant challenge.
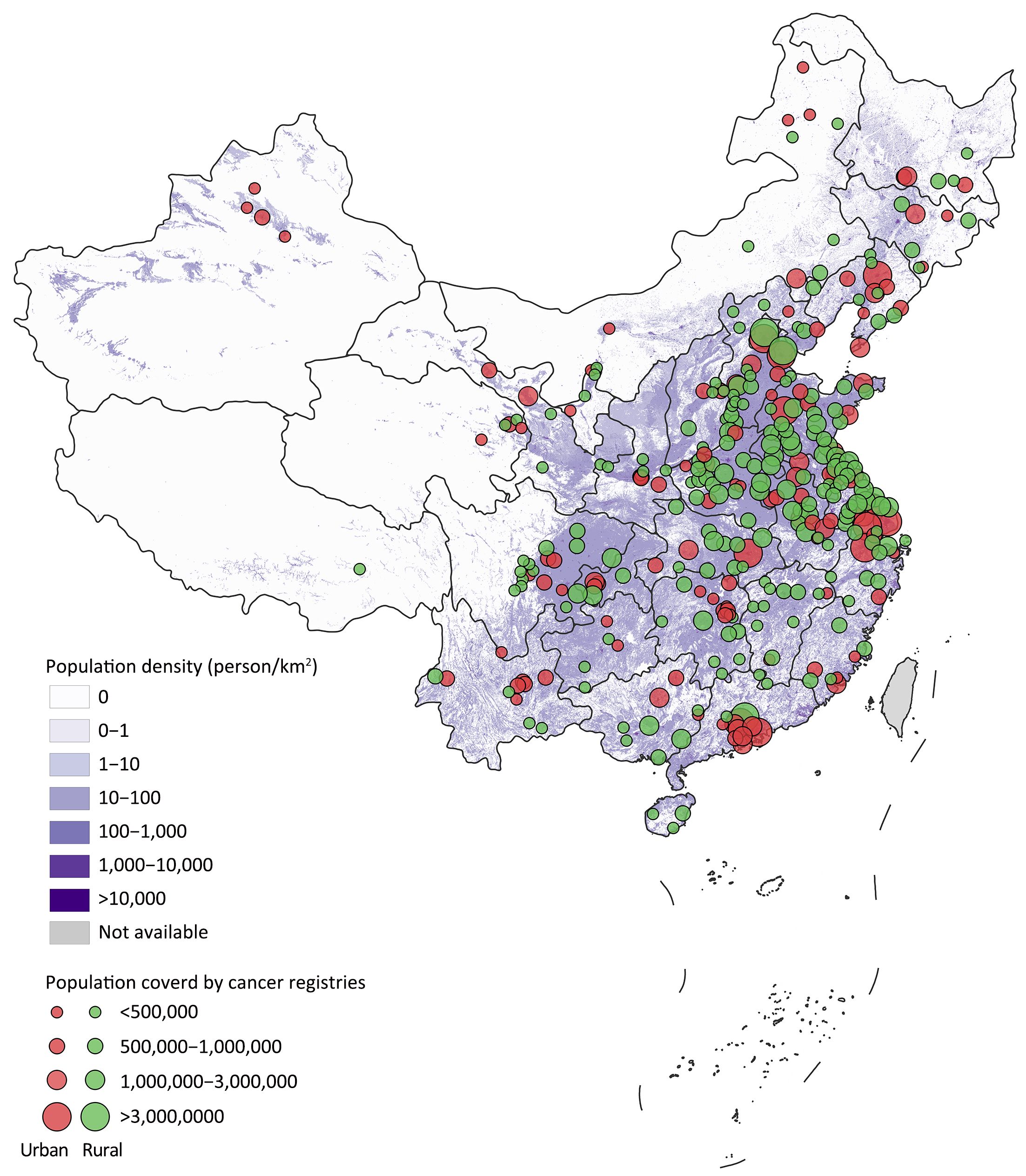
China's healthcare system has undergone significant reforms in recent years, expanding health insurance coverage and improving access to medical facilities.
However, challenges persist, particularly in rural areas, where access to specialized cancer care may be limited.
Early detection and screening programs are essential for improving cancer survival rates. The US has well-established screening programs for breast, cervical, and colorectal cancer.
China is expanding its screening programs, but coverage and participation rates still lag behind those of the US.
Research and Innovation: The Quest for a Cure
Both China and the US are investing heavily in cancer research. The US has long been a leader in cancer research, with numerous institutions and organizations dedicated to finding new treatments and prevention strategies.
The National Cancer Institute (NCI) plays a crucial role in funding and coordinating cancer research efforts across the country.
China's investment in cancer research has grown rapidly in recent years. Chinese scientists are making significant contributions to our understanding of cancer biology and developing novel therapies.
Collaboration between researchers in China and the US is becoming increasingly important for accelerating progress in the fight against cancer.
"The global cancer burden is a shared challenge that requires international collaboration and knowledge sharing." - Dr. [Hypothetical Name], Leading Oncologist.
Looking Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
Addressing the rising cancer burden requires a multifaceted approach. In the US, efforts are focused on improving access to affordable healthcare, promoting healthy lifestyles, and developing personalized cancer therapies.
In China, priorities include reducing environmental pollution, expanding cancer screening programs, and improving the quality of cancer care in rural areas.
Both countries have an opportunity to learn from each other's experiences and collaborate on research and prevention initiatives.
By working together, China and the US can make significant strides in reducing the global burden of cancer and improving the lives of millions of people.
Ultimately, the fight against cancer is a global battle that requires a concerted effort from researchers, healthcare providers, policymakers, and individuals around the world.