Do Stop Losses Work After Hours

The closing bell echoes through the trading floor, a metallic punctuation mark on a day of frenzied activity. Screens flicker, displaying the final prices, a snapshot frozen in time. But for many investors, the market doesn't truly sleep. News breaks, earnings are announced, and global events unfold, all while the official exchanges are closed. This begs a critical question: what happens to your carefully placed stop-loss orders when the lights go down?
The question of whether stop-loss orders function during after-hours trading is crucial for investors aiming to manage risk and protect their investments. The effectiveness of these orders hinges on the brokerage's policies and the specific market in which the security is traded. Understanding the nuances of after-hours trading and the limitations of stop-loss orders is essential for informed decision-making and effective risk management.
Understanding After-Hours Trading
After-hours trading, also known as extended-hours trading, occurs outside the regular trading hours of a stock exchange. Typically, this includes pre-market trading (before the official opening bell) and post-market trading (after the official closing bell).
These extended sessions allow investors to react to news and events that occur outside of standard market hours, providing an opportunity to adjust positions before the next day's open. However, after-hours trading differs significantly from regular trading in several key aspects.
Liquidity and Volatility
One of the most significant differences is liquidity. During regular trading hours, the sheer volume of participants ensures a relatively smooth flow of buy and sell orders, keeping price fluctuations in check.
After-hours trading, however, sees a substantial drop in participation. This reduced liquidity can lead to increased volatility, meaning prices can fluctuate more dramatically and unpredictably.
Wider bid-ask spreads are also common, making it more difficult to execute trades at desirable prices. This increased volatility and reduced liquidity can significantly impact the behavior of stop-loss orders.
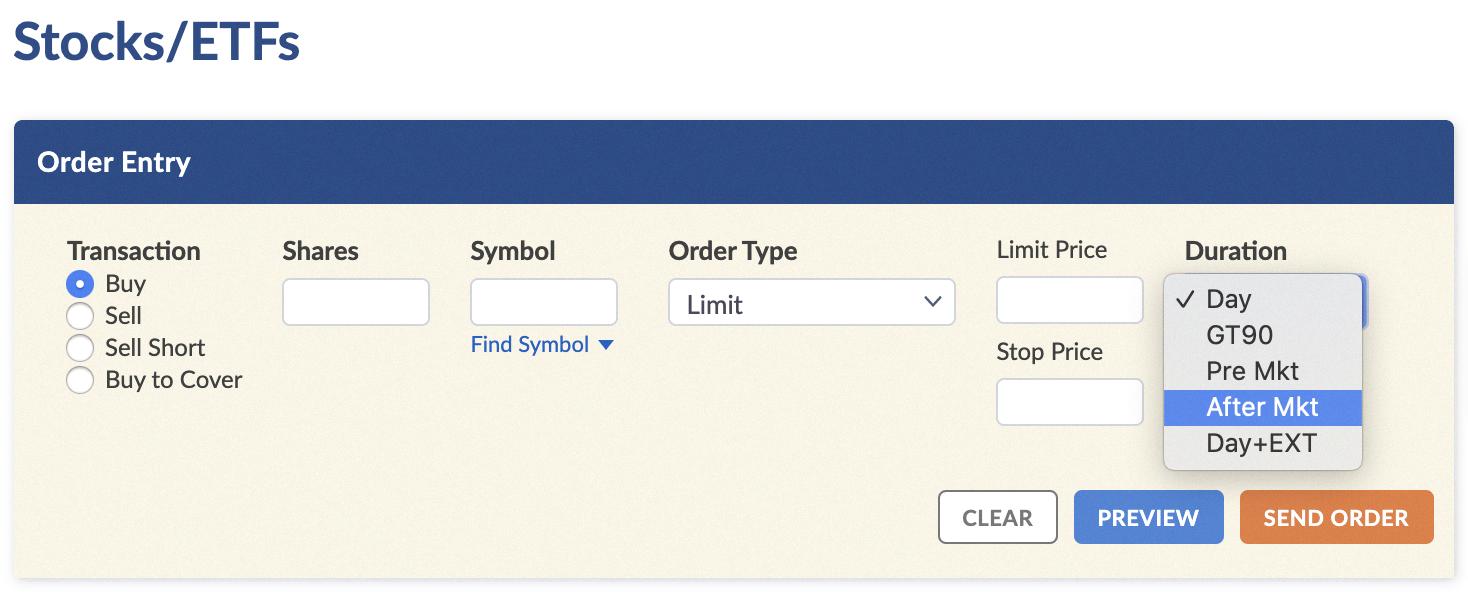
Order Types and Brokerage Policies
Another crucial factor is the type of orders accepted during after-hours trading. Not all brokerages offer the same range of order types during these extended sessions.
While some brokers allow limit orders and market orders, others may restrict the types of orders that can be placed or executed outside of regular trading hours. It is imperative to check with your brokerage firm to understand their specific policies regarding after-hours trading and order types.
Furthermore, even if a brokerage accepts stop-loss orders during after-hours trading, their execution is not guaranteed. The order will only be triggered if the stock price reaches the stop-loss level during the extended session.
The Reality of Stop-Loss Orders After Hours
The core purpose of a stop-loss order is to limit potential losses on an investment. It instructs a broker to sell a security when it reaches a specific price, the "stop price."
Ideally, this mechanism should automatically protect investors from significant price declines. However, the reality of after-hours trading introduces complexities that can render stop-loss orders ineffective or even counterproductive.
Execution Challenges
The biggest challenge lies in the execution of the order. Even if your broker accepts stop-loss orders during after-hours trading, the order will only be triggered if a matching buy order exists at or above your stop price.
Due to the reduced liquidity, this may not always be the case. If the price plunges through your stop price with no buyers present, your order may not be executed until the next trading day's open, potentially at a much lower price.
This situation can be particularly problematic for stocks that experience significant after-hours price swings due to news events or earnings announcements. The lack of liquidity can result in a "gap down," where the stock opens significantly lower than your stop price, rendering your order useless.
Brokerage Specifics
It's essential to understand that brokerage policies vary significantly. Some brokers do not execute stop-loss orders during after-hours trading at all.
Their systems are simply not set up to monitor and execute orders outside of regular market hours. Other brokers might allow after-hours stop-loss orders but only execute them as limit orders.
This means that the order will only be filled at the stop price or better, further reducing the likelihood of execution in a volatile after-hours environment. Consult your brokerage's policies meticulously to understand how your stop-loss orders will be handled during extended trading sessions.
Alternatives and Strategies
Given the limitations of stop-loss orders after hours, investors should consider alternative strategies for managing risk during these extended sessions.
One approach is to simply avoid holding positions overnight, especially if you anticipate significant news events that could impact the stock's price. This eliminates the risk of after-hours volatility altogether.
However, if holding positions is necessary, consider these strategies:
Using Guaranteed Stop-Loss Orders
Some brokers offer guaranteed stop-loss orders. These orders guarantee that your position will be sold at the stop price, regardless of price gaps or liquidity issues. However, guaranteed stop-loss orders usually come with a higher premium and may not be available for all stocks.
Careful Position Sizing
Another risk management technique is careful position sizing. By limiting the amount of capital allocated to any single trade, you reduce the potential impact of adverse price movements, both during regular and after-hours trading.
Monitoring News and Earnings
Staying informed about upcoming news events and earnings announcements is crucial. If you anticipate significant news that could impact a stock you hold, consider reducing your position or closing it out entirely before the news is released.
Using Options
Options strategies can provide a more sophisticated way to manage risk. For example, buying protective put options can limit your downside risk in case of a significant price decline. However, options trading requires a thorough understanding of the underlying instruments and their associated risks.
Conclusion
While stop-loss orders are a valuable tool for managing risk in regular trading hours, their effectiveness during after-hours trading is limited and subject to numerous caveats. Reduced liquidity, brokerage policies, and the potential for price gaps can all hinder the execution of these orders.
Investors must understand these limitations and consider alternative strategies for protecting their investments during extended trading sessions. Staying informed, carefully managing position sizes, and exploring options strategies are all effective ways to mitigate risk when the market doesn't sleep. Ultimately, proactive risk management and a thorough understanding of your brokerage's policies are the best defense against the uncertainties of after-hours trading.
The closing bell may signal the end of the official trading day, but for savvy investors, the learning and adaptation never stop. Understanding the nuances of market mechanics, even in the quiet hours, is key to navigating the complex world of finance and protecting your hard-earned capital.