Goleman Components Of Emotional Intelligence

In an increasingly interconnected and complex world, the spotlight on emotional intelligence (EI) continues to intensify. Businesses, educational institutions, and individuals alike are recognizing its pivotal role in fostering success, building strong relationships, and navigating the challenges of modern life.
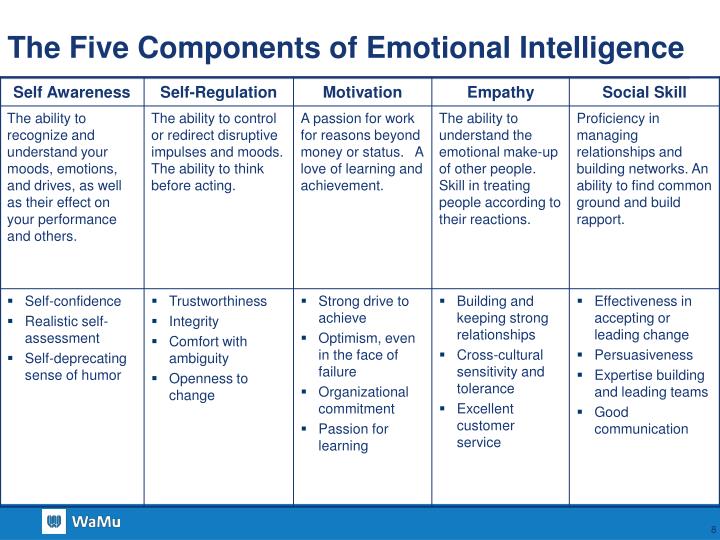
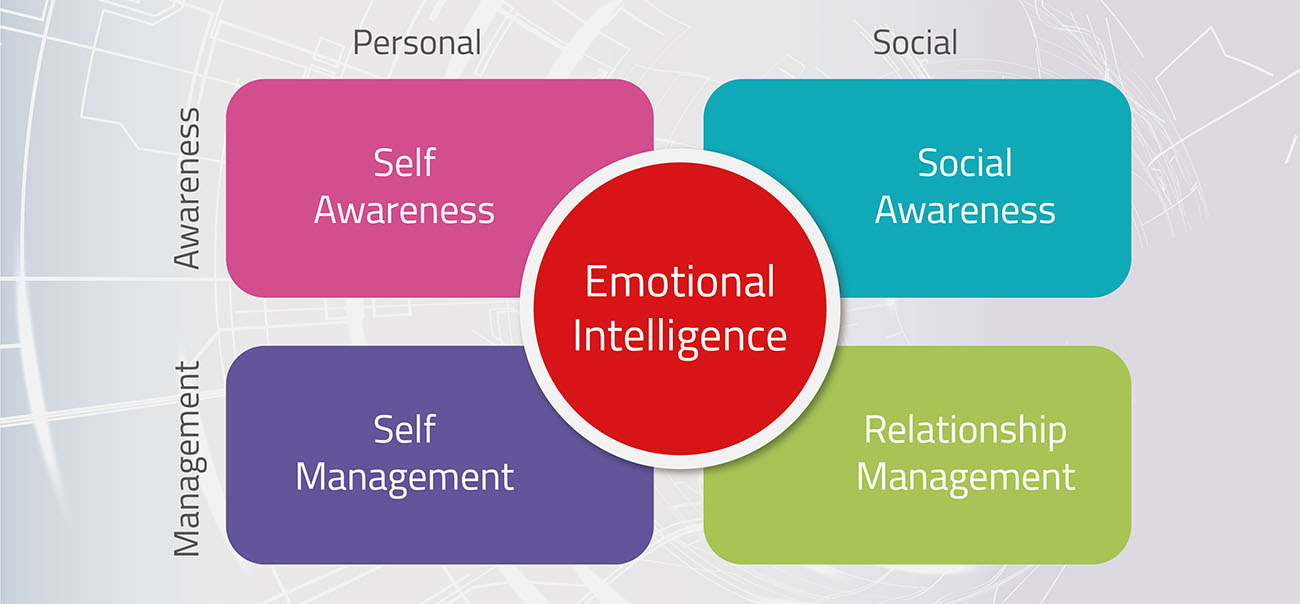
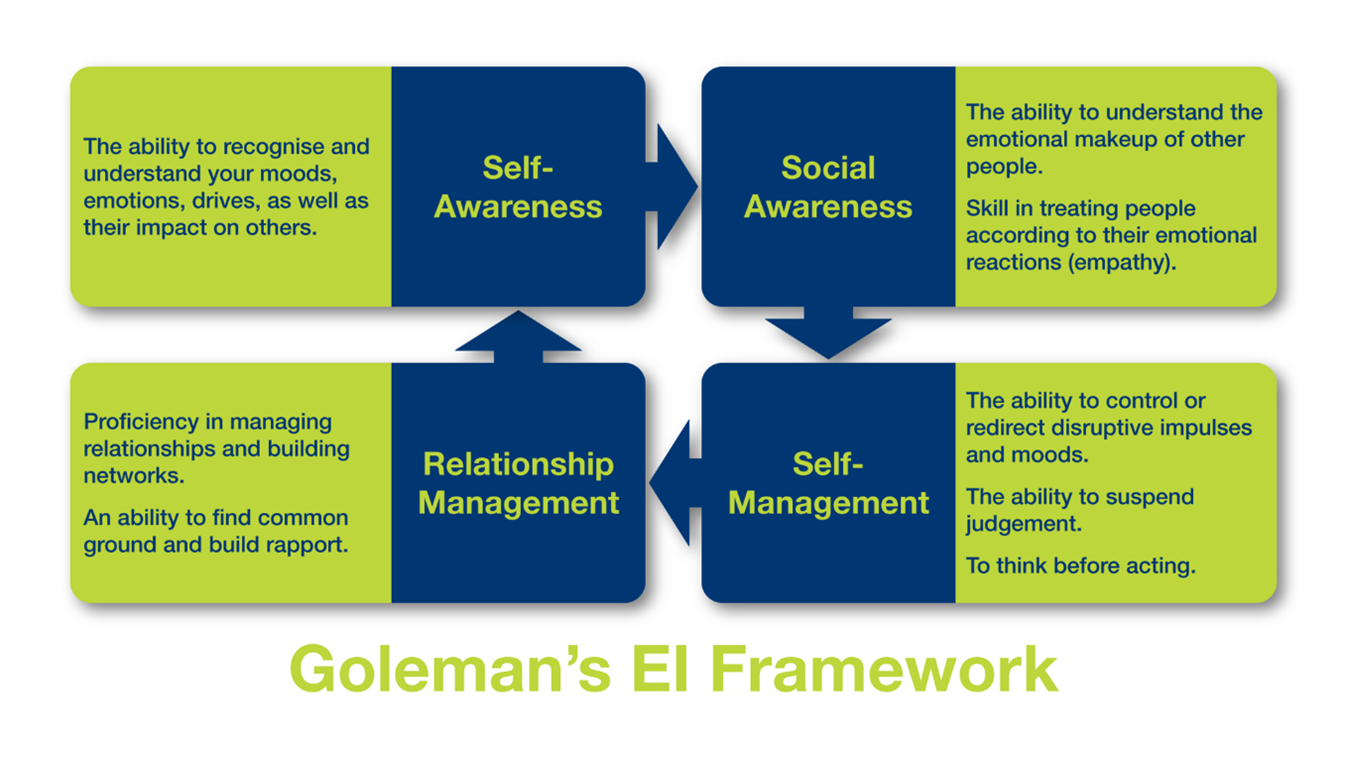
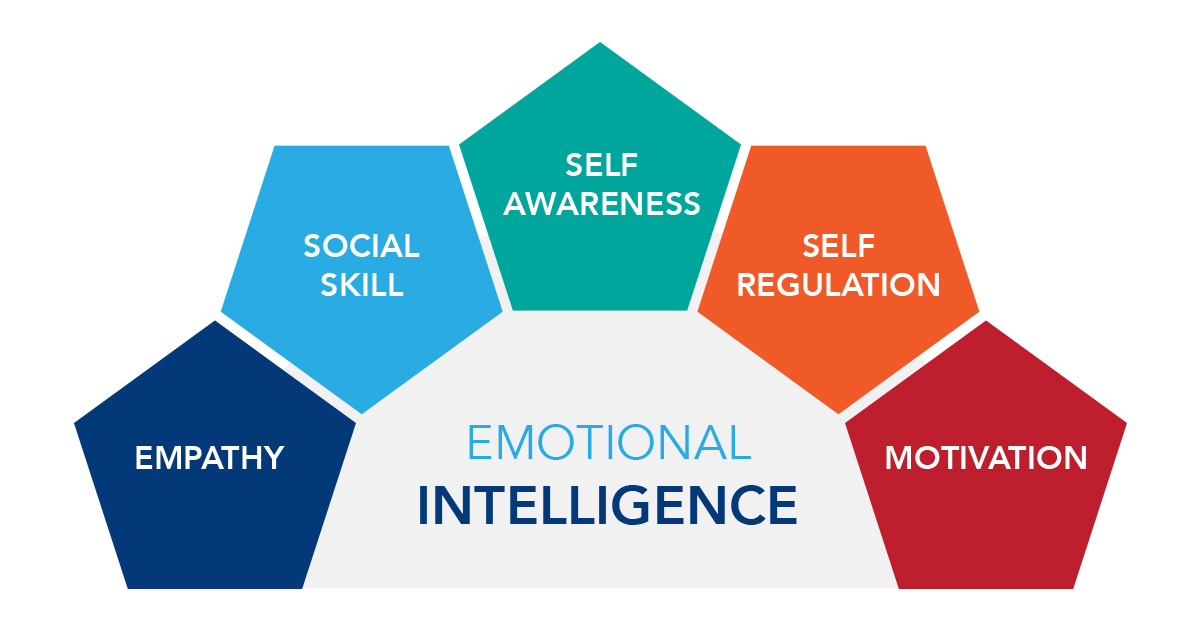
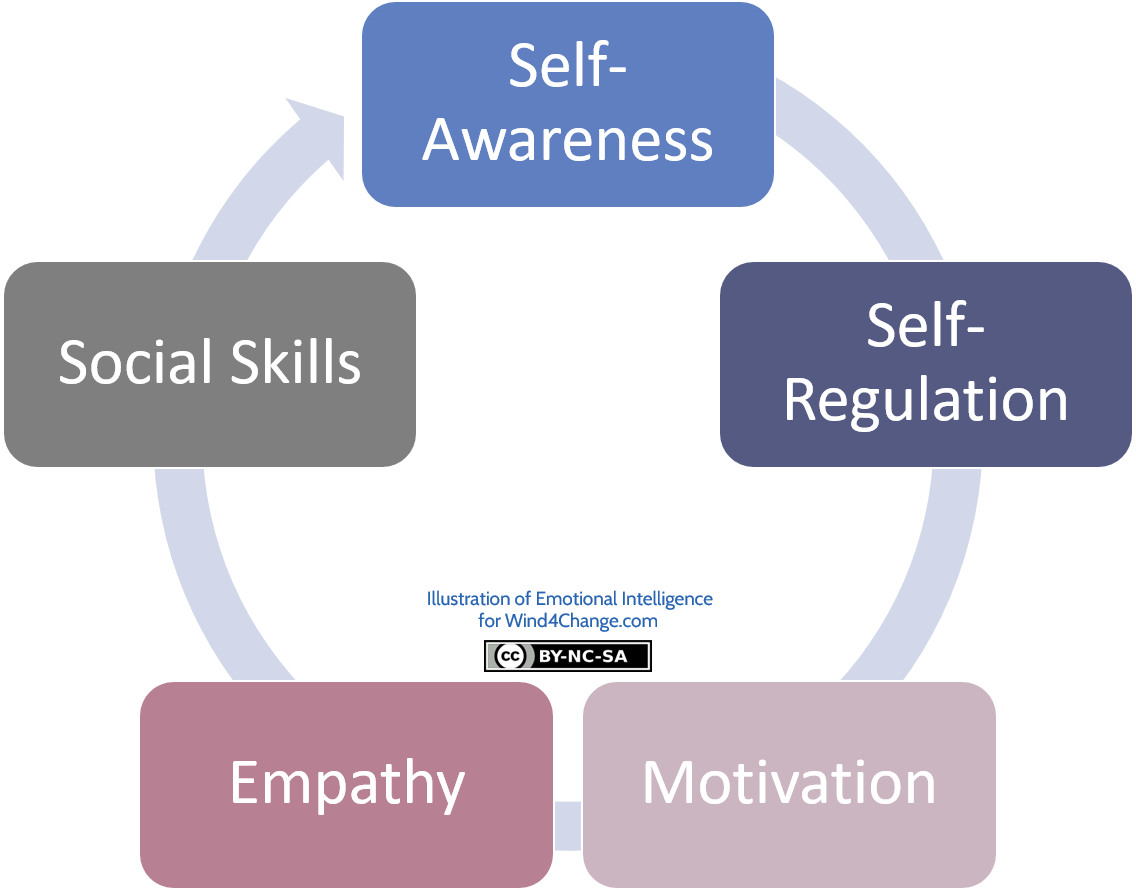
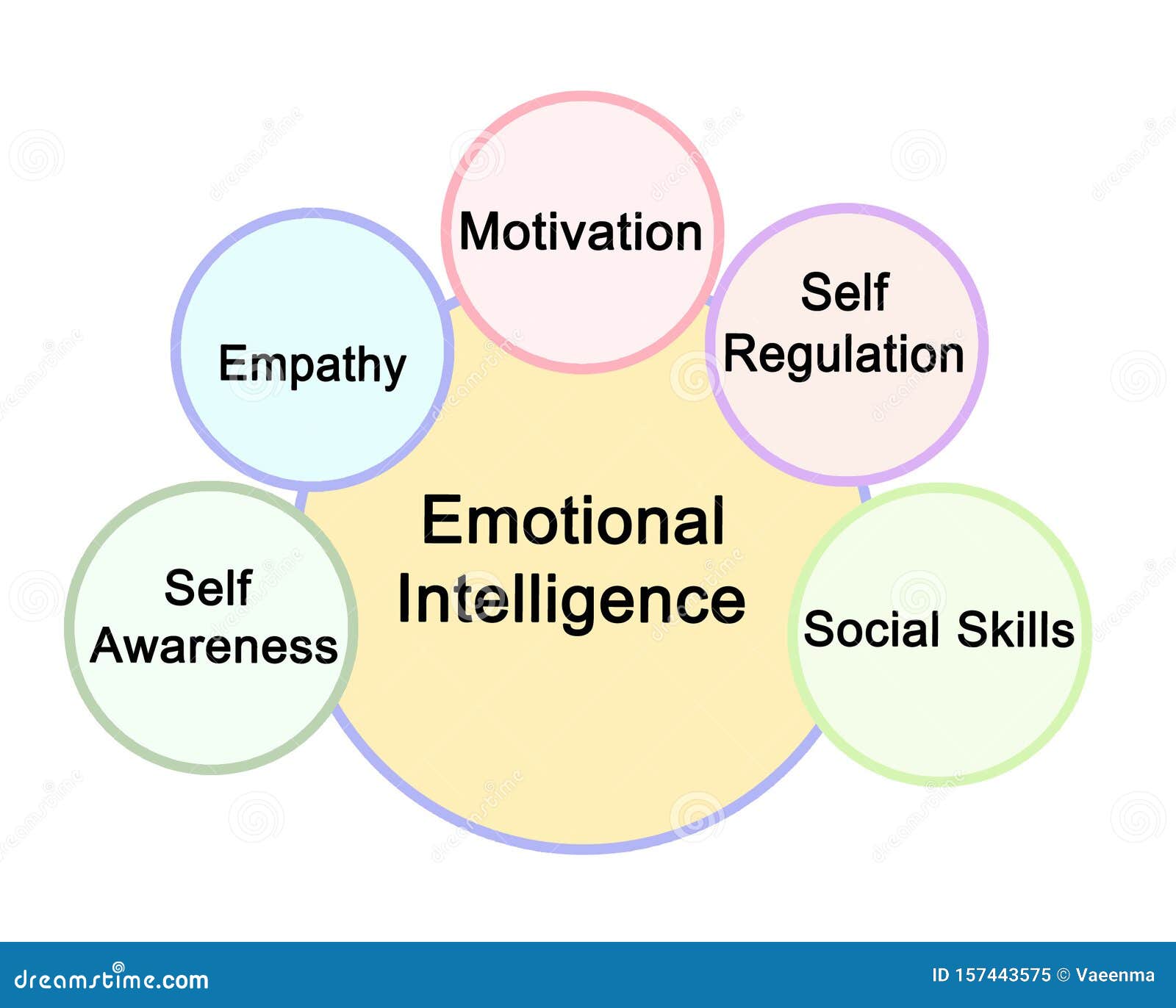
This growing awareness stems largely from the groundbreaking work of Daniel Goleman, whose research and writings have popularized the concept and provided a framework for understanding its core components. His model of EI, often cited and implemented across various sectors, emphasizes five key areas: self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills.
The Five Pillars of Emotional Intelligence
Goleman's framework provides a practical roadmap for developing and enhancing EI. Understanding these components is the first step towards leveraging their power in both personal and professional contexts.
Self-Awareness: Knowing Your Emotions
Self-awareness is the cornerstone of EI. It involves recognizing and understanding one's own emotions, strengths, weaknesses, values, and motivations.
Individuals with high self-awareness are attuned to their feelings and how they impact others. This understanding enables them to make more informed decisions and respond appropriately in various situations.
Self-Regulation: Managing Your Emotions
Self-regulation refers to the ability to control and manage one's emotions and impulses. It's about staying calm under pressure, adapting to changing circumstances, and thinking before reacting.
Those proficient in self-regulation exhibit traits like trustworthiness, integrity, and comfort with ambiguity. They can handle stressful situations without becoming overwhelmed.
Motivation: Driving Yourself Forward
Motivation, in the context of EI, is about being driven to achieve goals for reasons beyond money or status. It involves a passion for the work itself, a desire to learn, and a commitment to excellence.
Goleman highlights that self-motivated individuals are optimistic even in the face of failure, resilient, and committed to pursuing their objectives with energy and persistence.
Empathy: Understanding Others' Emotions
Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. It involves being able to put oneself in another person's shoes and see the world from their perspective.
Empathy is crucial for building strong relationships, fostering collaboration, and providing effective leadership. Empathetic individuals are good listeners and are sensitive to the needs of others.
Social Skills: Building Relationships
Social skills encompass the ability to manage relationships effectively, build rapport, and communicate clearly. It involves being skilled at persuasion, conflict resolution, and teamwork.
Individuals with strong social skills are adept at building networks, finding common ground, and fostering positive interactions with others. These skills are essential for success in collaborative environments.
Impact and Application
The Goleman model has had a profound impact on various fields. Businesses are increasingly using EI assessments and training programs to improve leadership, teamwork, and customer service.
Educational institutions are integrating EI into curricula to help students develop social and emotional skills that contribute to academic success and well-being. Furthermore, EI principles are being applied in healthcare, social work, and other areas where strong interpersonal skills are essential.
"Emotional intelligence is not the opposite of intelligence, it is not the triumph of heart over head – it is the unique intersection of both." - Daniel Goleman
Criticisms and Considerations
While widely embraced, Goleman's model has also faced some criticisms. Some researchers argue that EI is difficult to measure objectively and that it overlaps with personality traits.
Others question the validity of using EI as a predictor of job performance. Despite these concerns, the concept of EI continues to be a valuable framework for understanding the importance of emotions in human behavior and relationships.
Moving Forward
The Goleman components of emotional intelligence provide a valuable framework for personal and professional development. By understanding and developing these key areas, individuals can enhance their relationships, improve their performance, and navigate the complexities of modern life with greater success.
As awareness of EI continues to grow, its importance in shaping a more empathetic, collaborative, and effective society will only become more pronounced.








![Goleman Components Of Emotional Intelligence Daniel Goleman's Emotional Intelligence framework [4]. | Download](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Mushtak-Al-Atabi/publication/311950762/figure/fig1/AS:444453933588480@1482977483044/Daniel-Golemans-Emotional-Intelligence-framework-4.png)