How Long Can You Live With Afib And Kidney Failure

The gentle rhythm of a heartbeat, a steady drumbeat of life, can sometimes falter. Imagine a quiet morning disrupted by a frantic, irregular pulse. Then, consider the tireless kidneys, silently filtering and cleansing, gradually losing their ability to do so. When these two vital systems – the heart and the kidneys – begin to struggle simultaneously, the question that often arises is both weighty and deeply personal: How long can one live?
This article explores the complexities of living with both atrial fibrillation (Afib) and kidney failure, shedding light on the factors influencing prognosis and the potential for managing these conditions to live a fulfilling life. It is important to remember that every individual's experience is unique, and the information provided here is not a substitute for personalized medical advice.
Understanding the Intersection
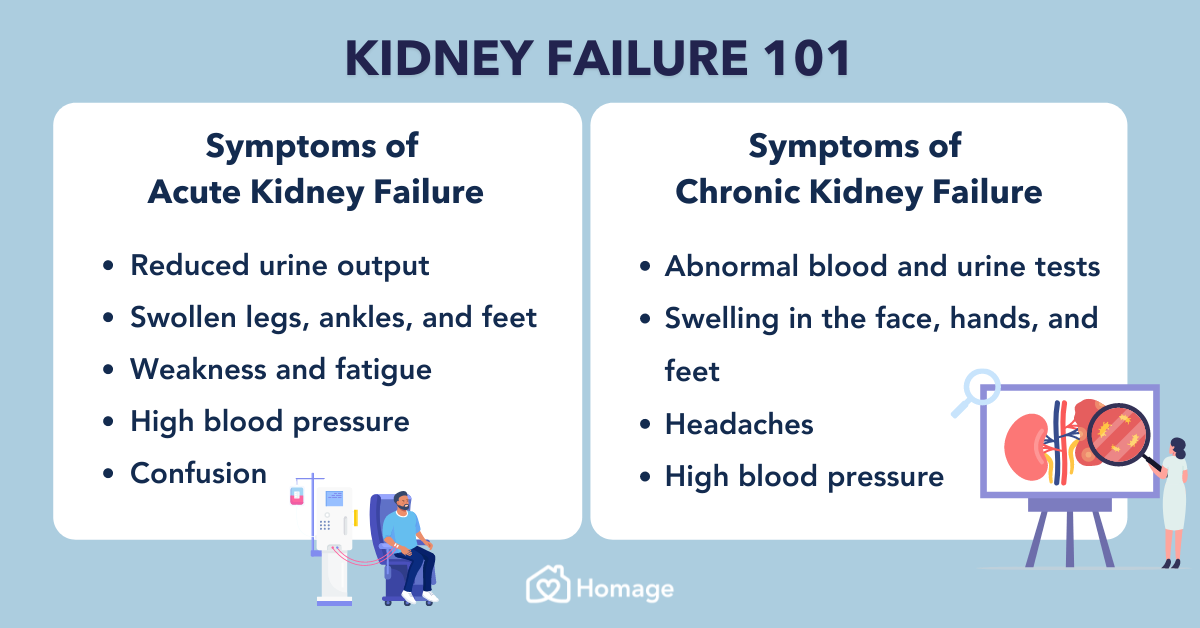
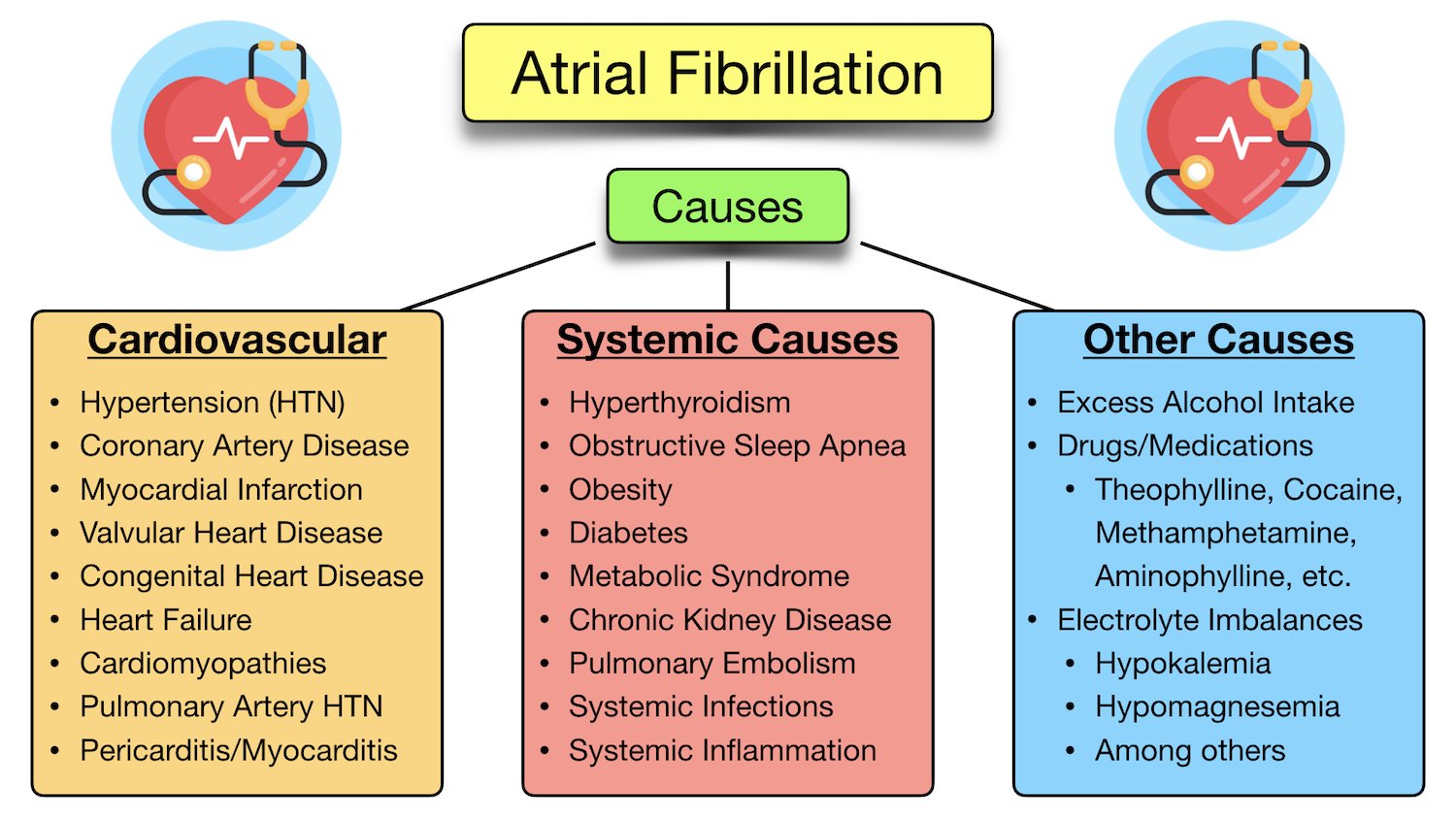
Afib, characterized by a rapid and irregular heartbeat, affects millions worldwide. Kidney failure, also known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD), signifies the kidneys' inability to effectively filter waste and excess fluid from the blood.
The coexistence of these conditions presents a significant challenge, as they can exacerbate each other. Afib can increase the risk of stroke and heart failure, while kidney failure often leads to fluid overload, electrolyte imbalances, and increased cardiovascular risk. This intricate interplay necessitates a comprehensive approach to management.
The Grim Reality of Co-occurrence
The statistics surrounding individuals living with both Afib and kidney failure can be sobering. Studies consistently show a reduced life expectancy compared to individuals with either condition alone. The severity of each condition, along with other comorbidities like diabetes and hypertension, greatly influences the overall prognosis.
One study published in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology indicated a significantly lower survival rate for patients with ESRD who also had Afib. It is important to note that these are population-level trends and do not predict an individual's outcome.
Factors Influencing Life Expectancy
Several factors play a critical role in determining how long someone can live with Afib and kidney failure. These factors can be broadly categorized into disease-specific factors and patient-specific factors.
Disease-Specific Considerations
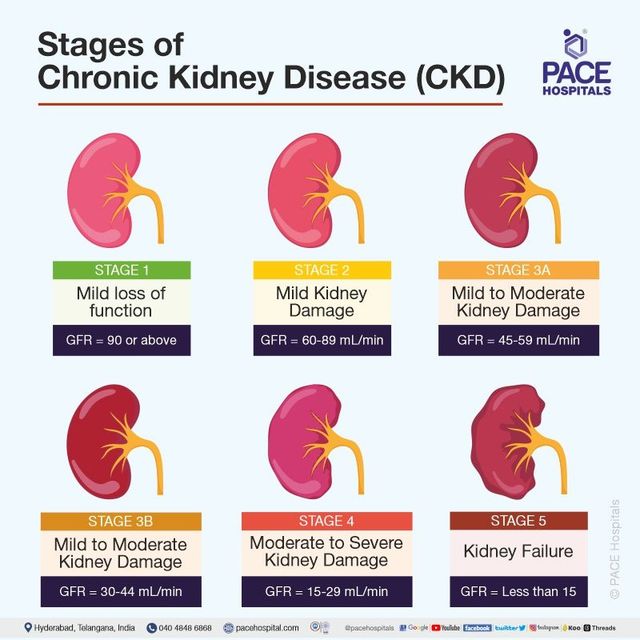
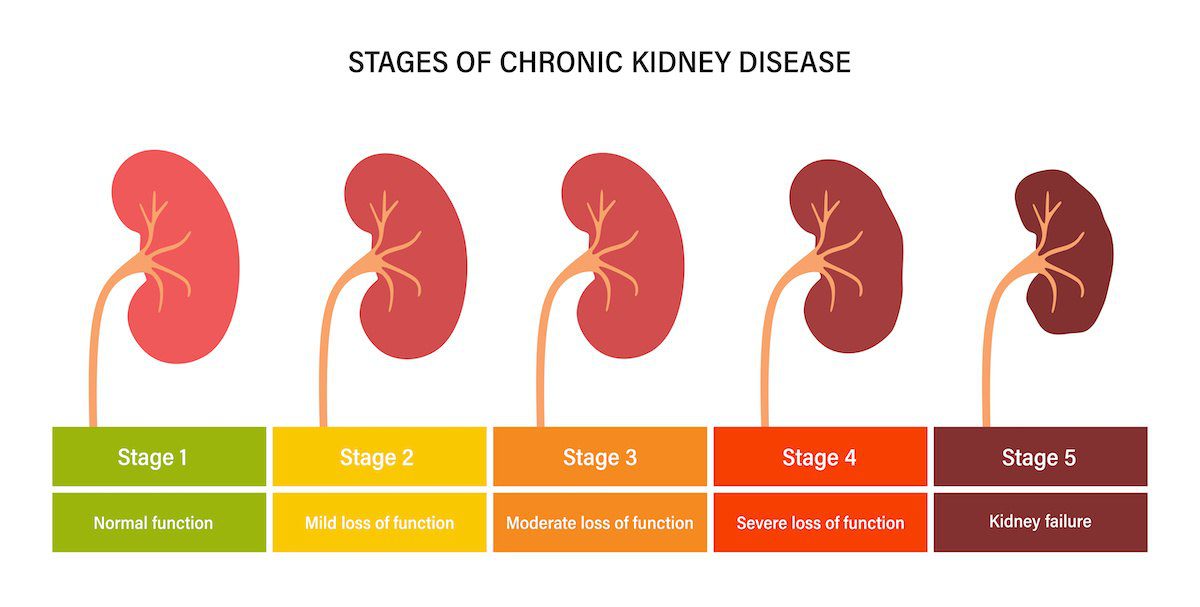
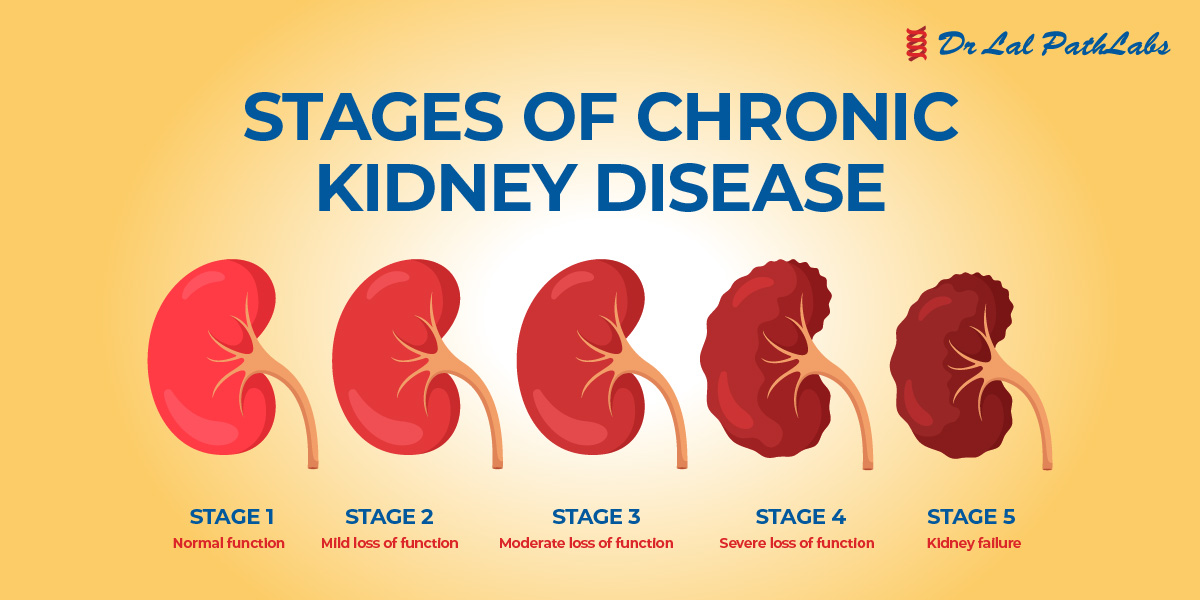
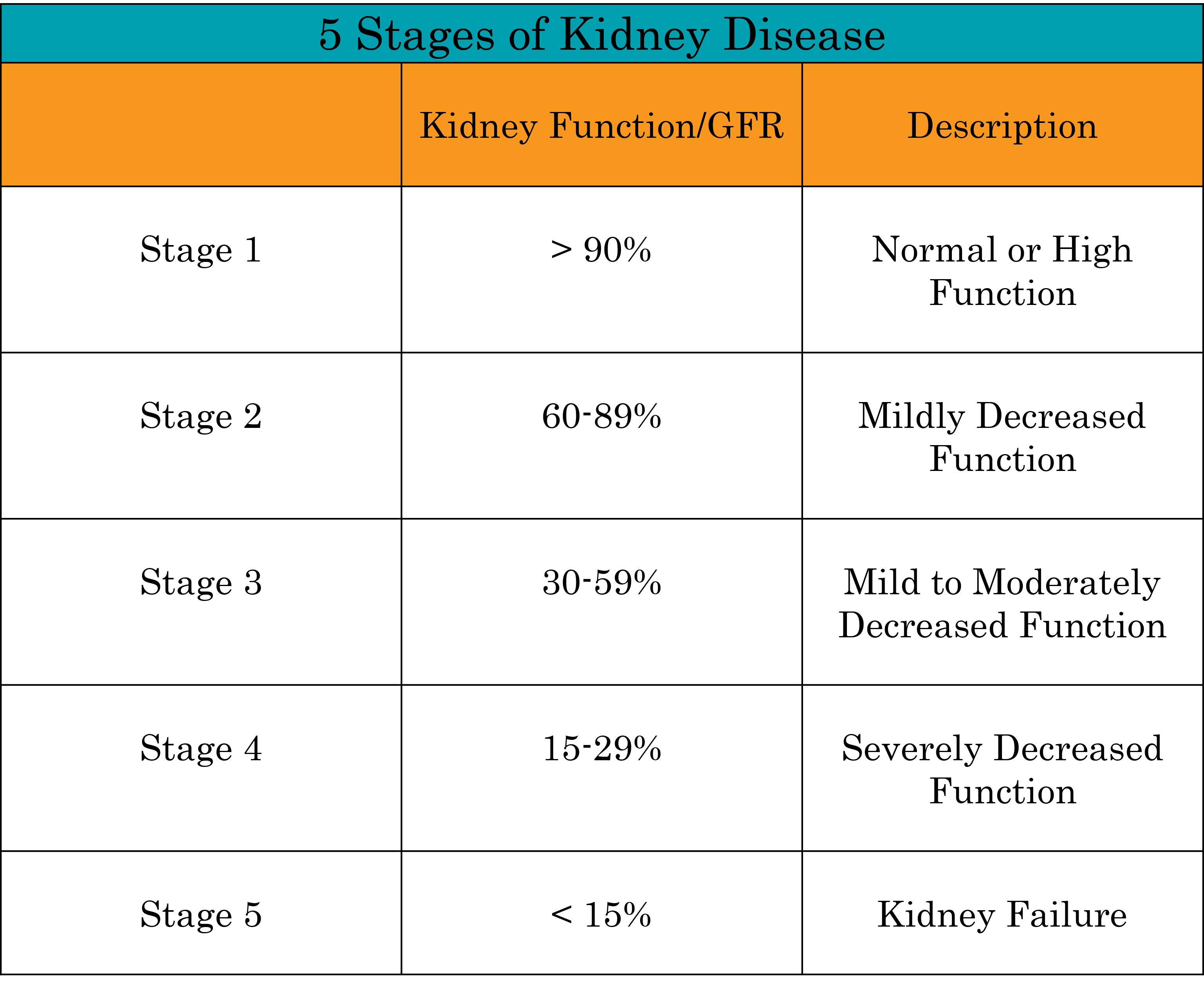
The severity and type of Afib, ranging from paroxysmal (intermittent) to persistent or permanent, significantly impacts prognosis. The stage of kidney failure, measured by glomerular filtration rate (GFR), dictates the extent of kidney function loss and influences treatment options.
Effective management of both conditions is crucial. This involves controlling heart rate and rhythm in Afib and managing fluid balance, blood pressure, and anemia in kidney failure.
Patient-Specific Aspects
Age, overall health, and the presence of other medical conditions are all vital factors. Younger, healthier individuals generally tolerate the combined burden of Afib and kidney failure better.
Lifestyle choices, such as diet, exercise, and adherence to medical advice, also play a significant role. Social support and access to quality healthcare are also crucial determinants of long-term outcomes.
Navigating Treatment Options
Managing Afib and kidney failure requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving cardiologists, nephrologists, and other specialists. The treatment plan is tailored to the individual's specific needs and circumstances.
Addressing Afib
Treatment strategies for Afib often involve medications to control heart rate (e.g., beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers) or rhythm (e.g., antiarrhythmics). Anticoagulants, such as warfarin or direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), are often prescribed to reduce the risk of stroke.
However, kidney function significantly impacts the choice and dosage of these medications. Some medications are contraindicated or require careful monitoring in patients with kidney failure.
Managing Kidney Failure
The primary treatment options for kidney failure include dialysis and kidney transplantation. Dialysis, either hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis, replaces the function of the kidneys by filtering the blood.
Kidney transplantation offers the best chance for long-term survival and improved quality of life. However, access to transplantation is limited, and recipients require lifelong immunosuppression, which carries its own risks.
The Importance of a Holistic Approach
Beyond medical interventions, a holistic approach is essential for managing Afib and kidney failure. This includes dietary modifications, such as limiting sodium, potassium, and phosphorus intake.
Regular exercise, within the limits of physical capacity, can improve cardiovascular health and overall well-being. Stress management techniques, such as meditation and yoga, can help reduce the burden of chronic illness.
Living Well with the Challenges
While the diagnosis of Afib and kidney failure can be daunting, it is important to focus on what can be controlled. Adherence to medical advice, a healthy lifestyle, and a positive attitude can significantly impact quality of life and potentially extend lifespan.
Building a strong support system is crucial. Connecting with family, friends, or support groups can provide emotional support and practical assistance. Engaging in activities that bring joy and purpose can help maintain a sense of normalcy and fulfillment.
Remember, every day is a gift. Focusing on the present moment and appreciating the simple pleasures of life can help navigate the challenges of living with chronic illness.
Looking Ahead
Research continues to advance our understanding of Afib and kidney failure, leading to new and improved treatment options. Ongoing studies are exploring novel therapies for Afib, including catheter ablation and left atrial appendage closure.
Advances in dialysis technology and transplantation techniques are also improving outcomes for patients with kidney failure. Personalized medicine, tailoring treatment to an individual's unique genetic and clinical profile, holds great promise for the future.
Hope lies in continued innovation and a commitment to providing compassionate and comprehensive care. Increased awareness, early detection, and effective management of risk factors can help prevent or delay the progression of both Afib and kidney failure.
A Note of Hope and Resilience
Living with both Afib and kidney failure is undoubtedly a significant challenge. The road ahead may be filled with uncertainties, but it is also paved with opportunities for resilience, adaptation, and finding joy in the face of adversity.
By working closely with their healthcare team, embracing a healthy lifestyle, and nurturing their emotional well-being, individuals can navigate these conditions and live meaningful, fulfilling lives. The human spirit is remarkably strong, and even in the face of serious illness, hope can endure.
The key takeaway is that while statistics provide a general overview, they do not define an individual's journey. With proactive management, unwavering determination, and a supportive community, it's possible to extend both lifespan and, more importantly, enhance the quality of life. Never underestimate the power of the human spirit to adapt and thrive, even when faced with significant health challenges. This is not just about adding years to life, but adding life to years.





+Symptoms-+Causes-+Risk+factors-+Complications-+Prevention+-+Treatment.jpg)