How Long Does Methylene Blue Last
Urgent reports indicate concerns regarding the longevity of methylene blue, a compound gaining traction for various applications. Understanding its stability and shelf life is crucial for efficacy and safety.
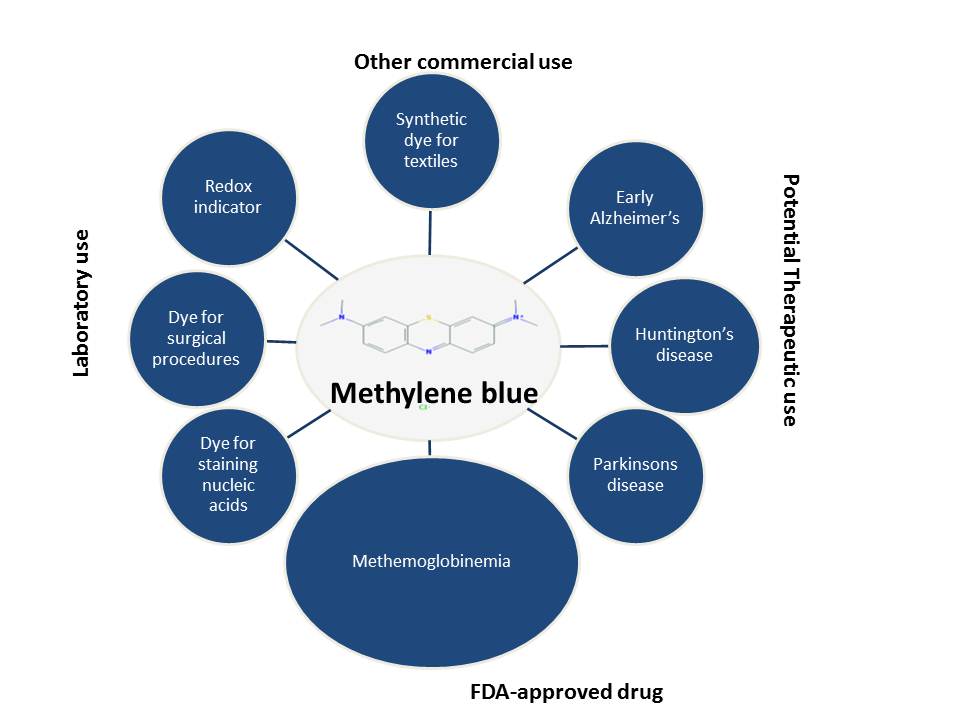
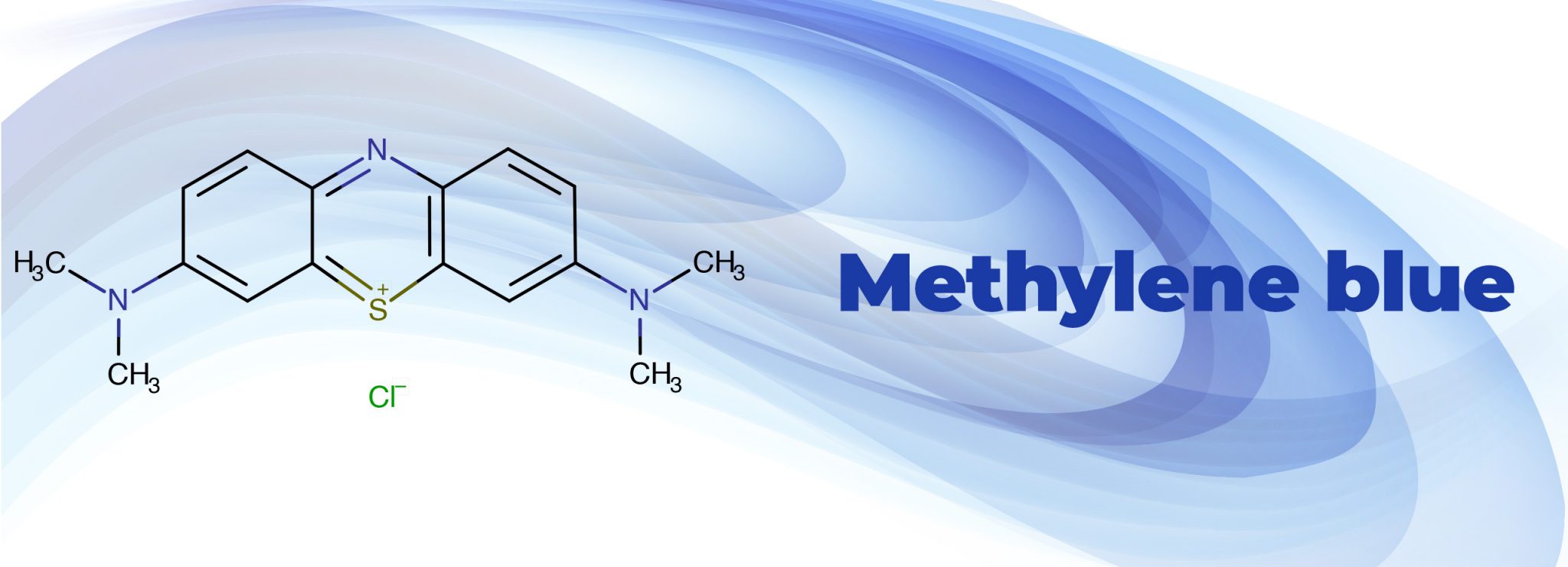
Methylene blue, a heterocyclic aromatic chemical compound with the molecular formula C₁₆H₁₈ClN₃S, is used for everything from treating methemoglobinemia to potential cognitive enhancement. Its degradation over time impacts its intended effects, necessitating a clear understanding of its duration of effectiveness.
Understanding Methylene Blue's Stability
The stability of methylene blue is influenced by several factors, primarily light, temperature, and pH. Exposure to light, especially ultraviolet (UV) light, accelerates its degradation process.
Higher temperatures also expedite the decomposition of the compound. The pH of the solution plays a significant role as well; alkaline conditions tend to degrade it faster than acidic conditions.
Factors Affecting Longevity
The purity of the methylene blue product directly impacts its shelf life. Impurities can catalyze degradation reactions, shortening its effective period.
The type of storage container is equally critical. Amber-colored glass bottles are recommended to minimize light exposure, unlike clear plastic containers.
Dilution also matters. Concentrated solutions of methylene blue generally maintain stability for longer compared to dilute solutions due to reduced surface area for degradation.
Shelf Life and Storage Recommendations
When stored properly, methylene blue in powder form can remain stable for several years, potentially up to 5 years or more. This assumes storage in a cool, dark, and dry environment in a tightly sealed container.
However, once dissolved in solution, its shelf life drastically reduces. A solution prepared for intravenous use, for example, should be used immediately or within a few hours if refrigerated, according to some pharmaceutical guidelines.
A solution intended for lab use may last longer, possibly a few weeks to a few months, if stored in a dark, refrigerated environment in an amber bottle. Visual cues like color change indicate degradation.
Practical Considerations for Users
Individuals using methylene blue for personal or clinical purposes should pay close attention to the product's expiration date and storage instructions provided by the manufacturer. Always check the solution for any signs of discoloration or precipitation before use.
For compounded preparations, it is imperative to adhere to the expiration date assigned by the compounding pharmacy. Due to the variability in preparation methods, relying solely on the general shelf life is unsafe.
It's also crucial to understand the concentration of the solution. Lower concentrations, frequently used in aquaculture, may degrade more rapidly compared to higher concentrations stored in pharmaceutical settings.
Scientific Studies and Data
Research on the degradation kinetics of methylene blue reveals that its breakdown often follows first-order kinetics. This means the rate of degradation is proportional to the concentration of the compound.
Studies have demonstrated that exposure to direct sunlight can reduce the concentration of methylene blue solutions by as much as 50% within a few days. This highlights the critical importance of light protection.
Furthermore, research published in the Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences details how pH levels above 7 significantly accelerate degradation, especially when combined with exposure to light and air.
Visual Signs of Degradation
The most noticeable sign of degradation is a change in color. Methylene blue solutions, which are originally a deep blue, may fade to a lighter blue, green, or even become colorless as the compound breaks down.
Precipitation, where solid particles form in the solution, is another indicator of degradation. This suggests that the compound is no longer in its original, stable form.
Any unexpected odors can also signal that the methylene blue has degraded and should not be used. These changes indicate compromised purity and potential ineffectiveness or even harmful byproducts.
Regulatory Oversight and Safety
Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA, provide guidelines for the storage and handling of methylene blue, particularly for pharmaceutical applications. These guidelines emphasize proper labeling and adherence to storage recommendations.
The FDA requires pharmaceutical products containing methylene blue to have an expiration date based on stability testing. This ensures that the product maintains its potency and safety throughout its shelf life.
For non-pharmaceutical uses, such as in aquariums, the regulations are often less stringent, placing a greater emphasis on user awareness and responsible practices.
Moving Forward
Ongoing research continues to explore methods for enhancing the stability of methylene blue. This includes encapsulation techniques and the development of more stable formulations.
Users must stay informed about best practices for storage and handling, prioritizing safety and efficacy. Consultation with healthcare professionals or qualified experts is advised for any medical applications.
Further updates will be provided as new data and research emerge, focusing on prolonging the compound's effective lifespan and minimizing degradation risks.