How Many Square Feet Can A Space Heater Heat

The biting chill of winter often drives people indoors, seeking refuge from the cold. But for many, existing heating systems struggle to keep pace, leading to the consideration of supplemental heating options like space heaters. Understanding the heating capacity of these devices is critical for safety and effective use.
Determining how many square feet a space heater can adequately heat is not a straightforward calculation. It depends on a confluence of factors. These factors include the heater's wattage, the room's insulation, ceiling height, and the external climate.
Understanding Wattage and BTU
Space heater capacity is often expressed in watts. One watt equates to 3.412 British Thermal Units (BTUs), a common metric for measuring heat output. A general rule of thumb is that you need 10 watts of heating power for every square foot of space.
Therefore, a 1500-watt space heater, a common size, could theoretically heat up to 150 square feet, based on this estimate.
However, this calculation is a simplified baseline. Actual performance will vary based on real-world conditions.
The Impact of Insulation and Room Conditions
A poorly insulated room will bleed heat far more quickly than a well-insulated one. This forces the space heater to work harder and potentially struggle to maintain a comfortable temperature.
Old windows, drafty doors, and insufficient wall insulation significantly reduce a heater's effectiveness.
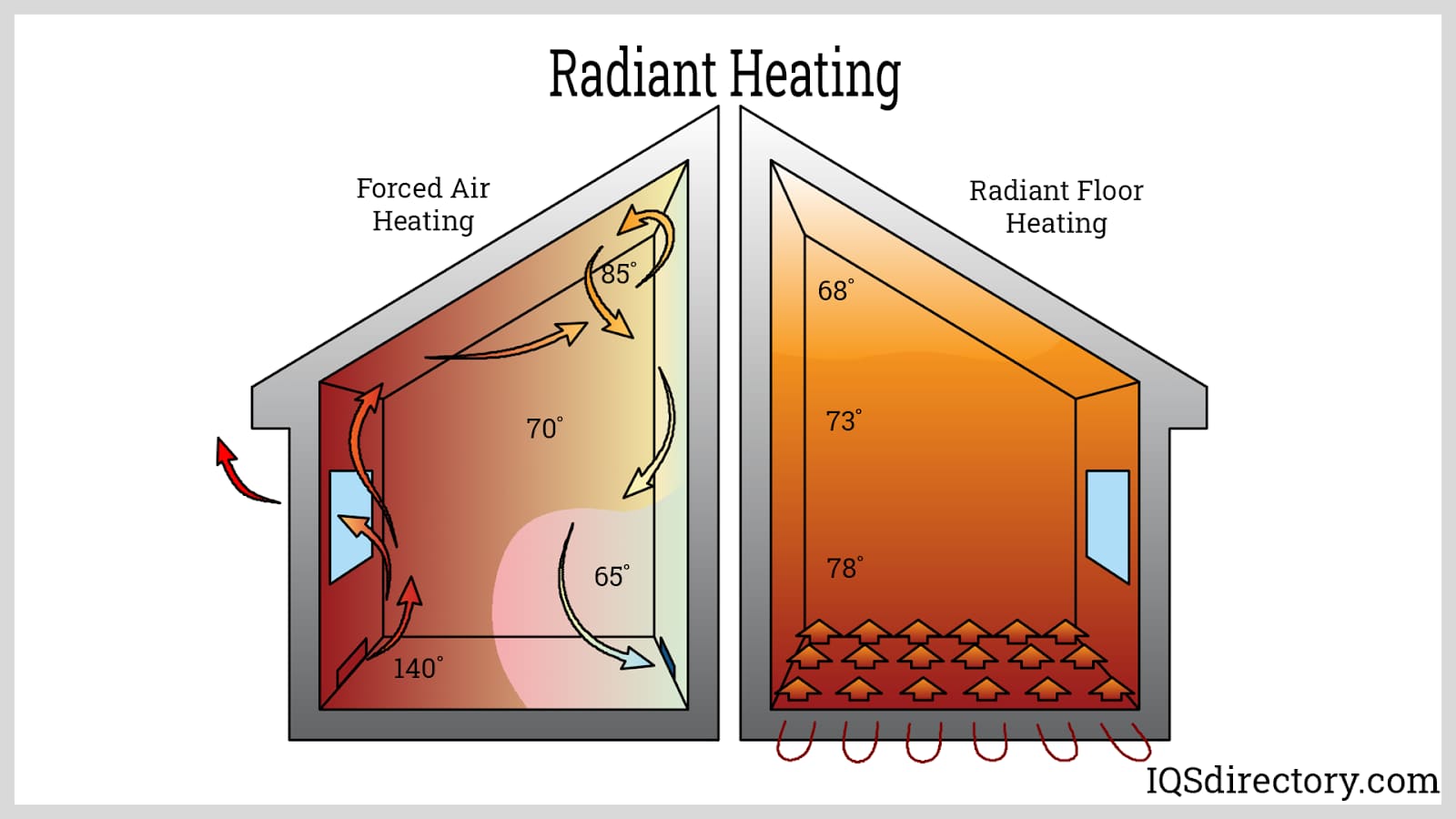
Rooms with high ceilings require more energy to heat. The warm air rises, leaving the lower portion of the room cooler.
External factors such as outdoor temperature and wind chill also play a significant role. A space heater might perform adequately on a moderately cold day but struggle during a deep freeze.
Types of Space Heaters and Their Efficiency
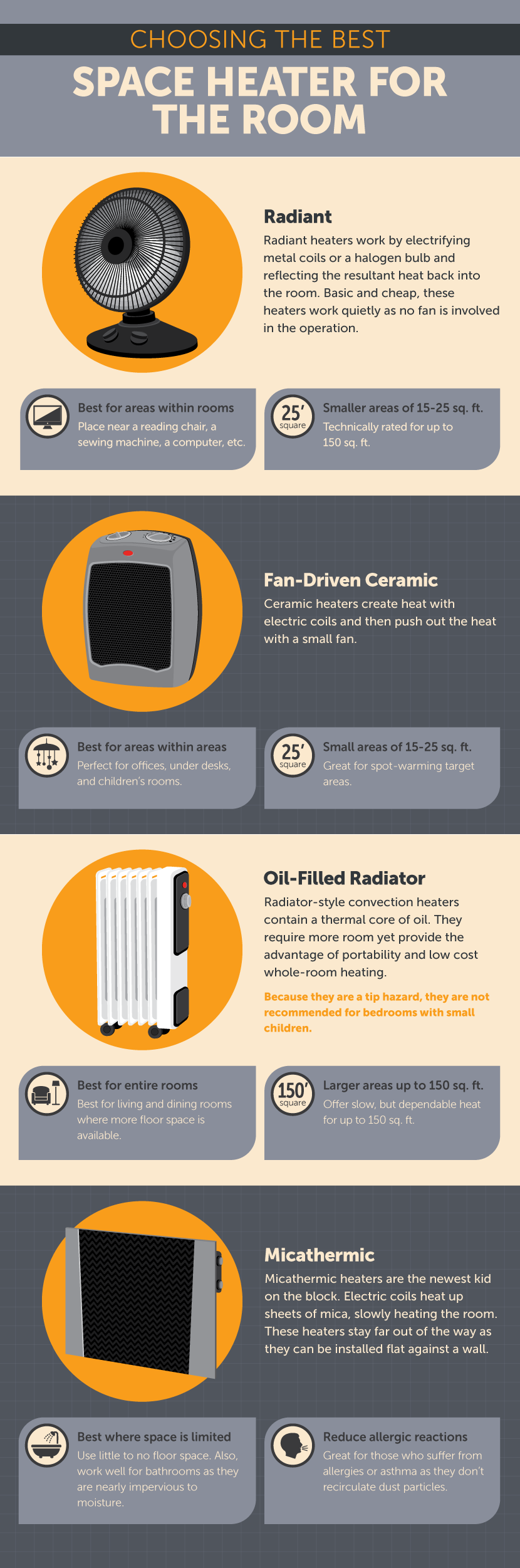
Space heaters come in various types, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Common types include ceramic, radiant, and oil-filled heaters.
Ceramic heaters are known for their rapid heating capabilities and are best suited for small spaces. Radiant heaters, on the other hand, provide direct heat to objects and people in their path.
Oil-filled heaters are known for maintaining a consistent temperature over a longer period. They are often considered better for larger rooms despite a slower initial heating time.
The efficiency of these heaters varies. Some models include features such as thermostats and programmable timers, which can help conserve energy and maintain a comfortable temperature more efficiently.
Safety Considerations
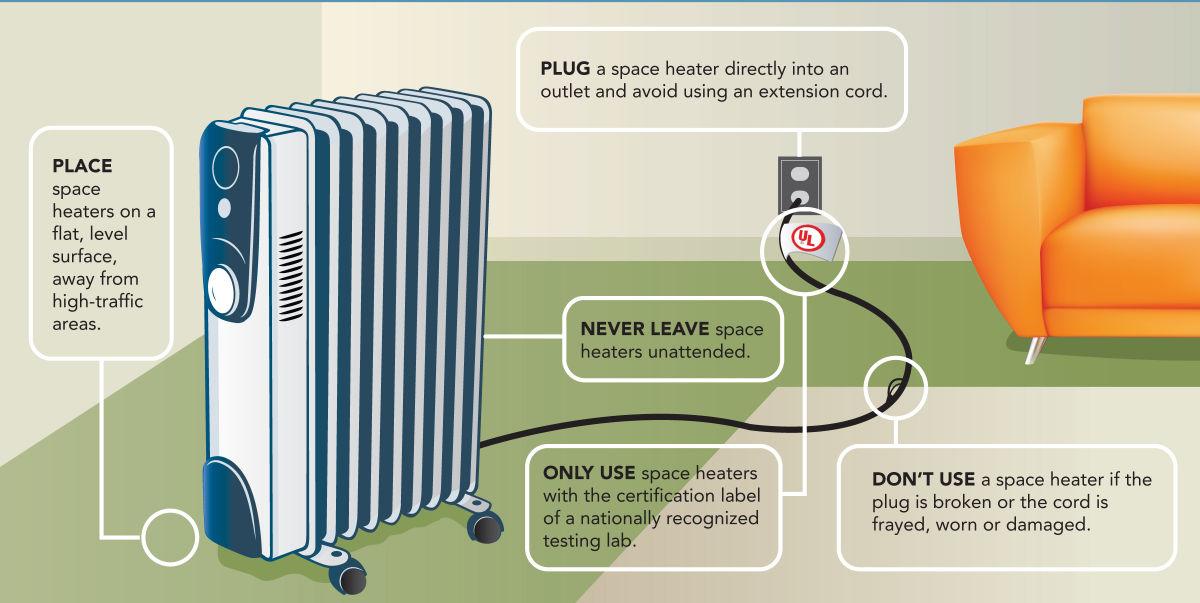
It's important to select a space heater with appropriate safety features, such as overheat protection and tip-over shut-off. These are critical in preventing fires and other accidents.
Always follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully and never leave a space heater unattended.
According to the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC), space heaters are a leading cause of residential fires, highlighting the importance of safe operation and maintenance.
Expert Perspectives
Heating and ventilation experts advise caution when relying solely on space heaters. They are intended as supplemental heating sources, not primary heating systems.
According to Energy.gov, a whole-house heating system is almost always more energy efficient. These systems provide consistent heat distribution throughout the entire home.
Experts also recommend having your home's insulation checked to improve overall energy efficiency and reduce the need for supplemental heating.
Future Trends in Heating Technology
Advancements in heating technology are continually emerging, with a focus on increased energy efficiency and improved safety features. Smart space heaters are becoming increasingly popular.
These smart space heaters can be controlled remotely via smartphone apps. They offer features like precise temperature control and energy usage monitoring.
These innovations aim to reduce energy consumption and provide users with greater control over their heating needs.
Conclusion
Determining the heating capacity of a space heater requires considering a multitude of variables. While the 10-watts-per-square-foot rule offers a starting point, factors such as insulation, ceiling height, and heater type profoundly affect performance.
Prioritizing safety features and using space heaters responsibly as supplemental heating sources is essential. Ongoing advancements in heating technology promise more efficient and safer solutions in the future.










:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/91BfDvRKGRL._AC_SL1500_-bbea8ef66bfb48678a874870d3de231e.jpg)