How To Know If Business Is Profitable

For entrepreneurs and business owners, the question of profitability isn't just academic; it's the lifeblood of their venture. But understanding if a business is truly making money can be more complex than simply looking at the bank balance. Several key metrics and analytical tools offer a clearer picture of a company's financial health.
Understanding profitability involves digging deeper than revenue. Business owners need to analyze key financial statements, track relevant ratios, and consider various factors influencing their bottom line.
Understanding Key Financial Statements
The cornerstone of profitability assessment lies in three primary financial statements: the income statement, the balance sheet, and the cash flow statement.
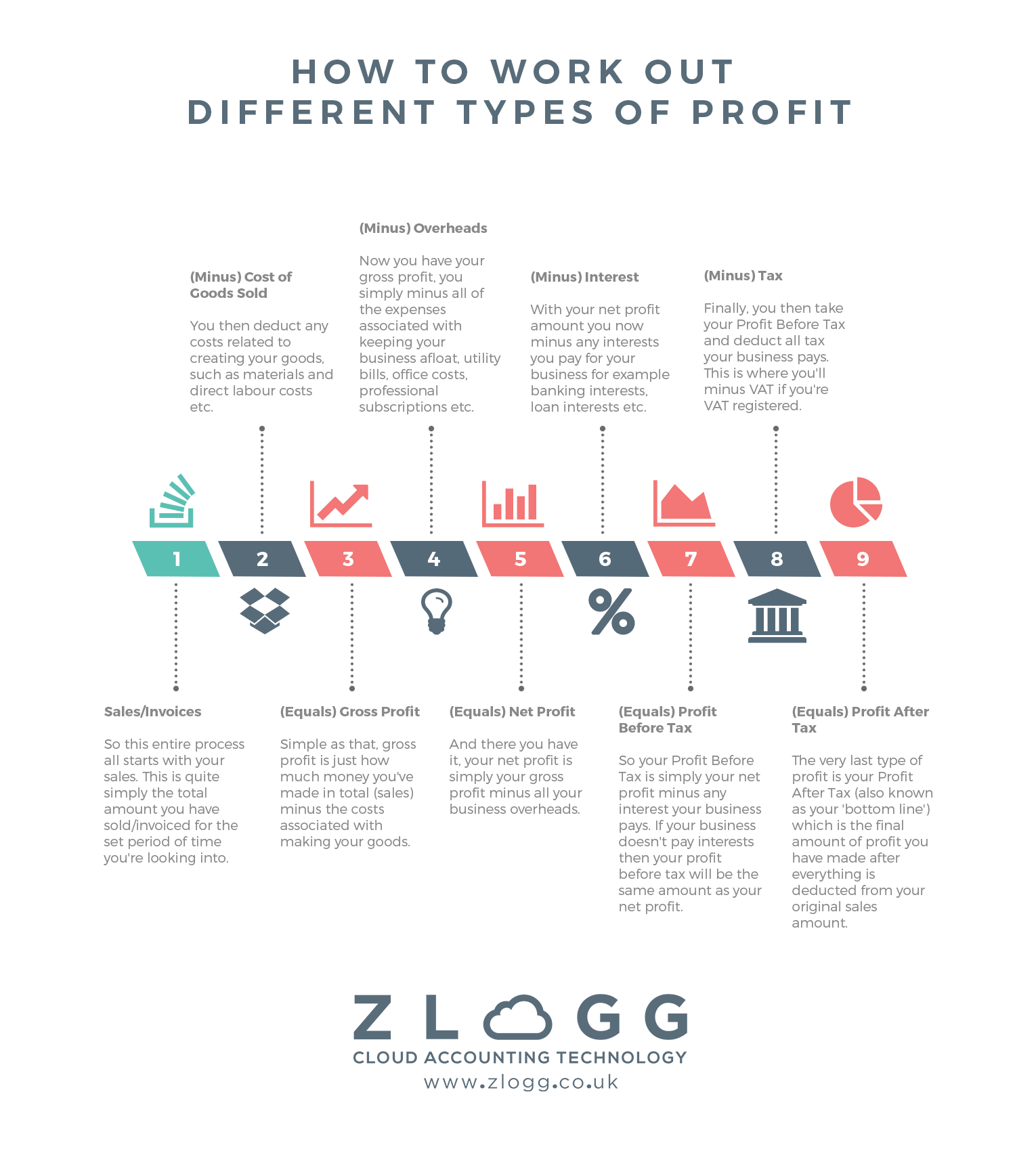
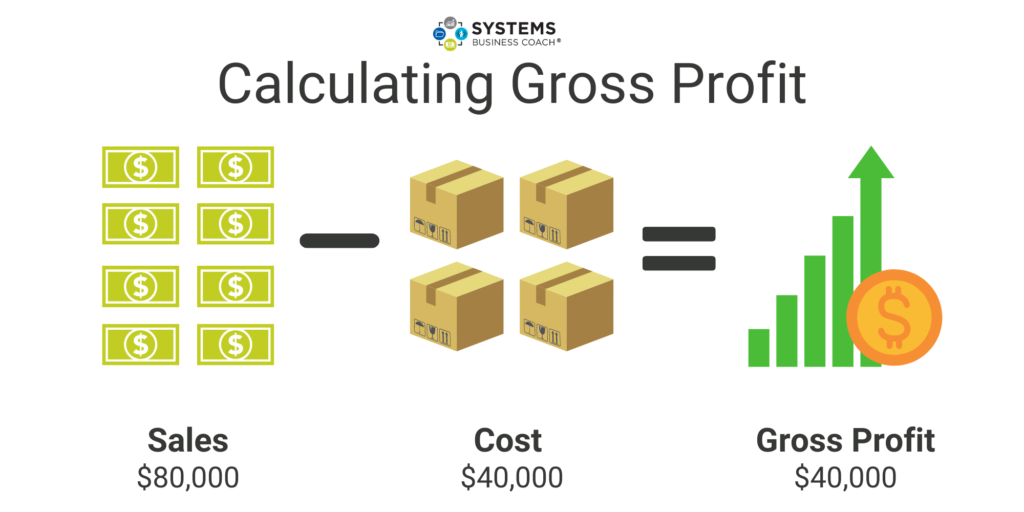
The income statement, also known as the profit and loss (P&L) statement, reveals revenues, expenses, and profits over a specific period, typically a month, quarter, or year. Gross profit, calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from revenue, indicates the profitability of core business activities.
Operating profit then factors in operating expenses such as salaries, rent, and marketing. Finally, net profit, or the bottom line, reflects the profitability after all expenses, including taxes and interest, are deducted.
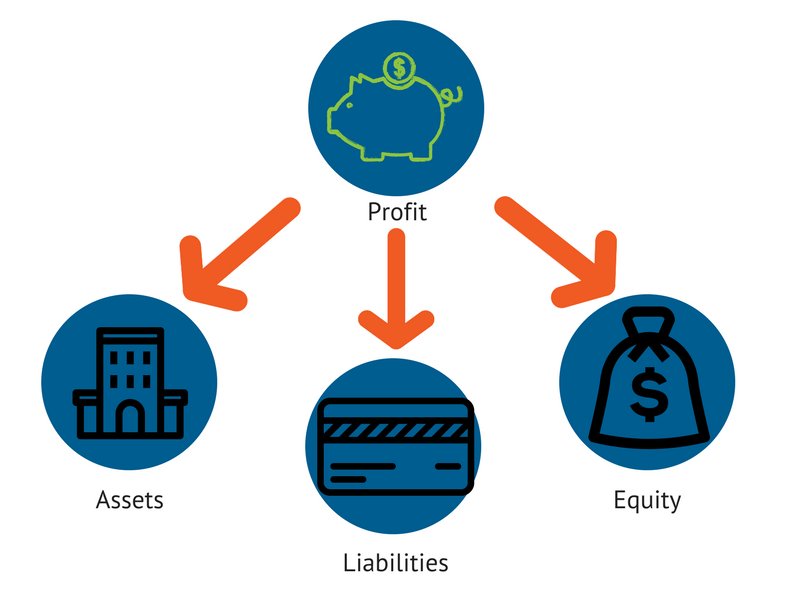
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. Analyzing trends in assets and liabilities can reveal important insights into financial stability and efficiency.
The cash flow statement tracks the movement of cash both into and out of a business. It categorizes these cash flows into operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities, providing a comprehensive view of how a company generates and uses cash.
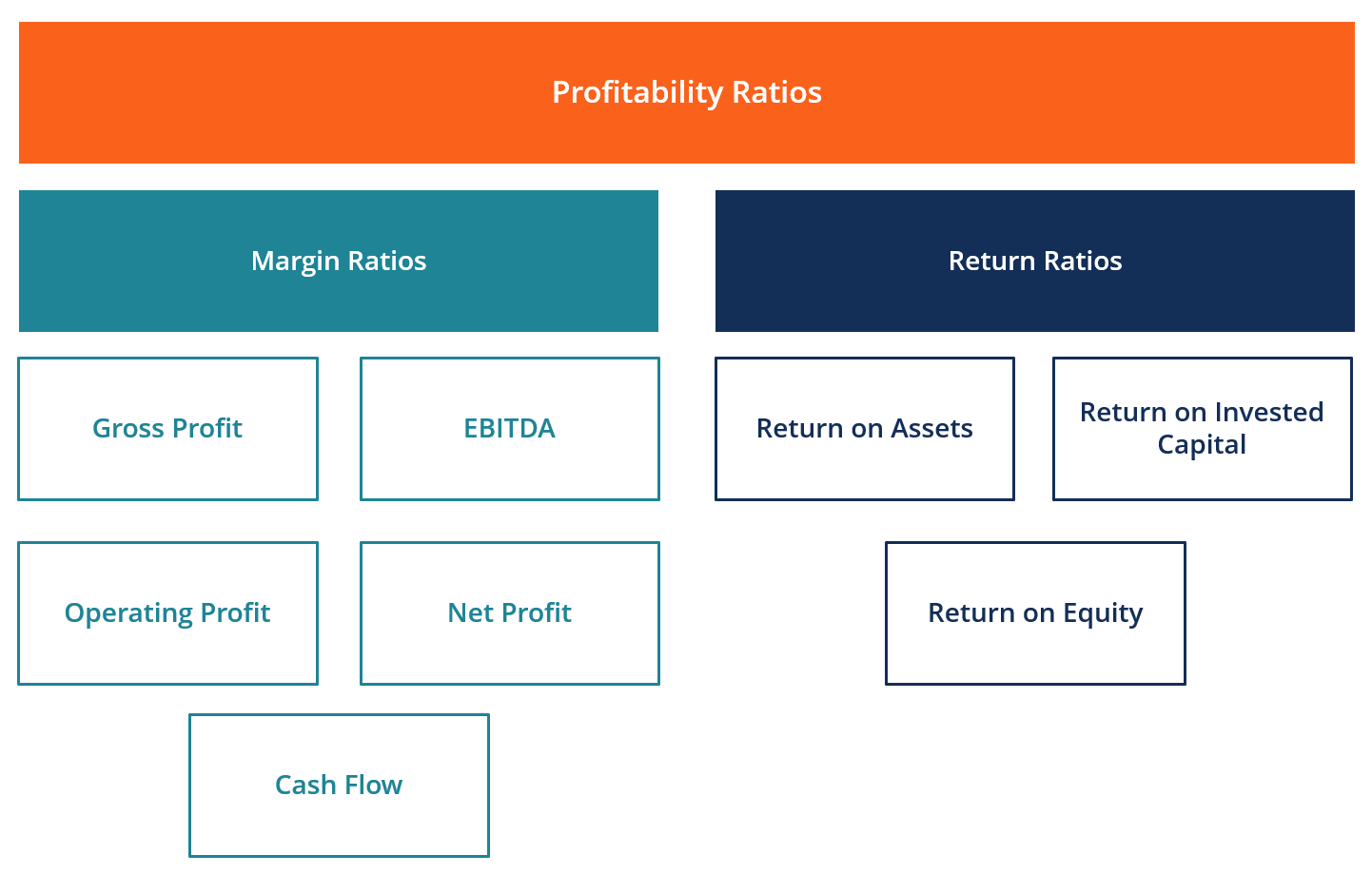
Key Profitability Ratios
Financial ratios provide valuable insights into a company’s performance by comparing different line items on financial statements.
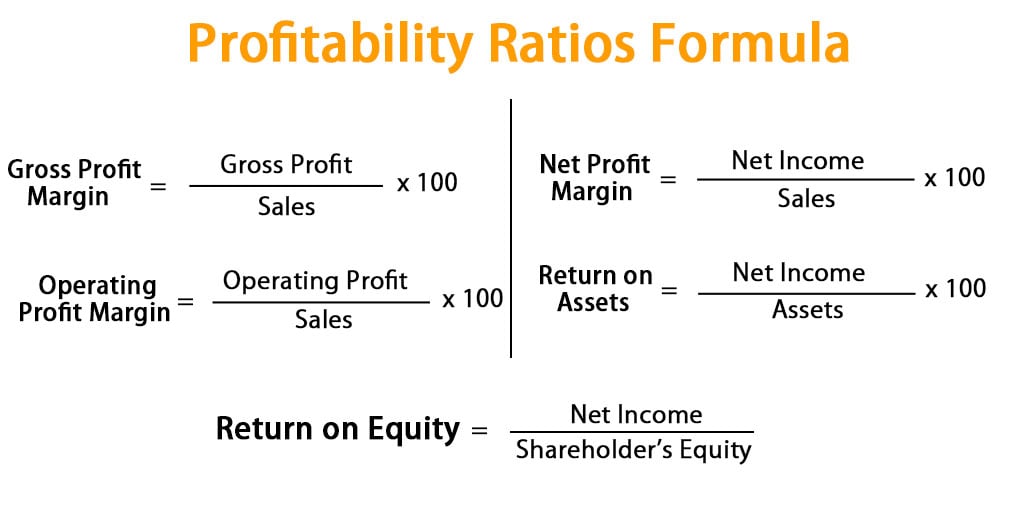
The gross profit margin, calculated by dividing gross profit by revenue, indicates the percentage of revenue remaining after covering the cost of goods sold. A higher gross profit margin suggests greater efficiency in production and pricing strategies.
The net profit margin, calculated by dividing net profit by revenue, measures the percentage of revenue that translates into profit after all expenses are considered. This ratio offers a comprehensive view of overall profitability.
The return on equity (ROE), calculated by dividing net income by shareholder equity, measures how effectively a company is using investments to generate profits. A higher ROE indicates better efficiency in generating returns for investors.
Beyond the Numbers: Qualitative Factors
While financial statements and ratios provide quantitative insights, qualitative factors also significantly influence profitability.
Market conditions, competitive landscape, and regulatory changes can all impact a business's ability to generate profits. Internal factors such as management effectiveness, employee morale, and operational efficiency also play a critical role.
The Human Element
Sarah Chen, owner of a small bakery in Chicago, emphasizes the importance of combining financial analysis with a deep understanding of her business operations. "I track my margins closely, but I also talk to my employees, listen to customer feedback, and adapt to changing trends," she says. "Profitability isn't just about numbers; it's about building a thriving ecosystem."
Technology plays an increasingly vital role in profitability analysis. Accounting software, data analytics tools, and cloud-based platforms enable businesses to automate data collection, generate insightful reports, and make informed decisions in real-time.
The Significance of Profitability
Profitability is a critical indicator of a business's financial health and sustainability. It demonstrates the business's ability to generate revenues that exceed expenses.
A profitable business can attract investors, secure loans, and reinvest in growth opportunities. Conversely, a business consistently struggling with profitability may face challenges in securing funding, retaining employees, and remaining competitive in the long run.
Ultimately, knowing if your business is profitable requires a holistic approach. Analyzing financial statements, tracking key ratios, and considering qualitative factors enables business owners to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and drive long-term success.