In A Service Type Business Revenue Is Recognized

The seemingly simple question of when to recognize revenue in a service-based business can be a surprisingly complex issue, impacting everything from financial reporting to investor confidence. Misunderstanding or misapplying revenue recognition principles can lead to inaccurate financial statements, potentially misleading stakeholders and even inviting regulatory scrutiny. The stakes are high, demanding careful attention to detail and a thorough understanding of accounting standards.
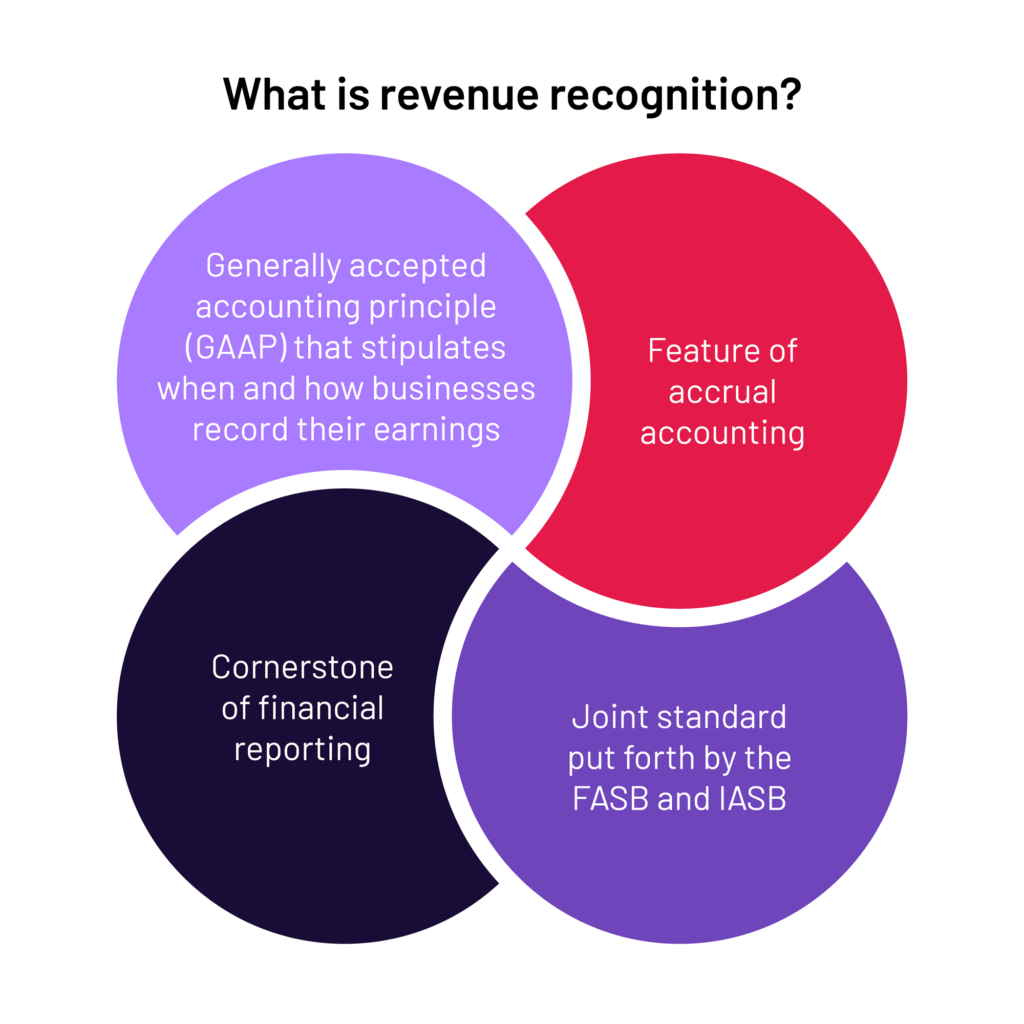
At its core, revenue recognition in a service business hinges on the principle of recognizing revenue when it is earned, not necessarily when cash is received. This "earned" concept means that revenue should be recognized when the service has been substantially performed or completed. This article delves into the intricacies of revenue recognition for service-based businesses, exploring the relevant accounting standards, common challenges, and strategies for ensuring accurate and compliant financial reporting.
Understanding the Core Principles
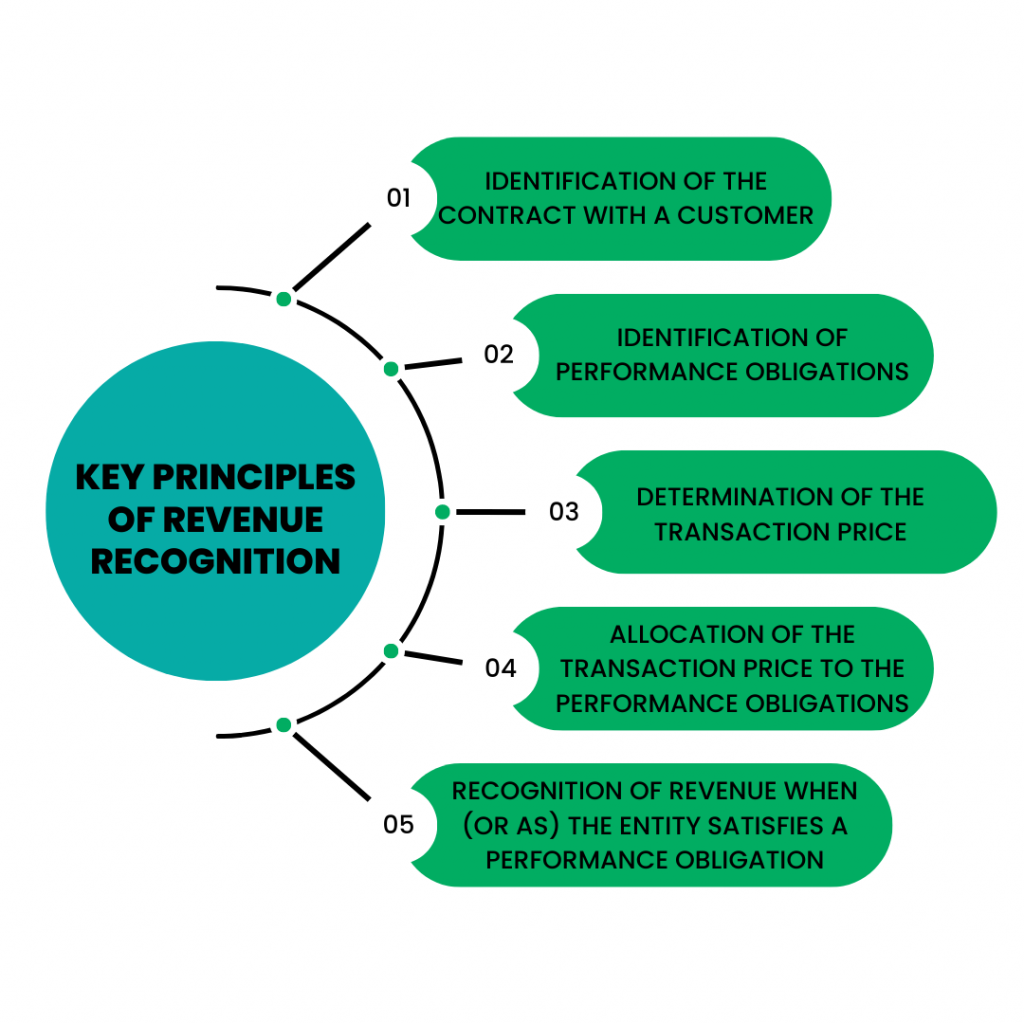
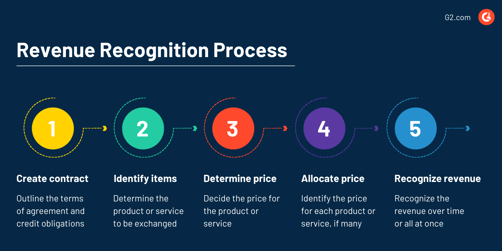
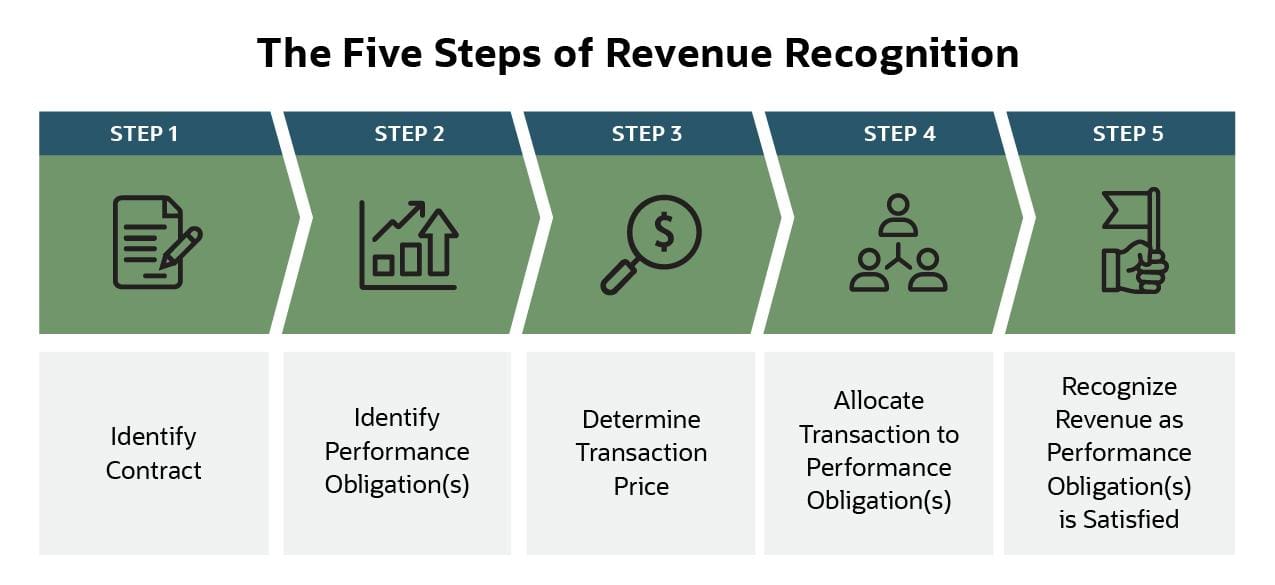
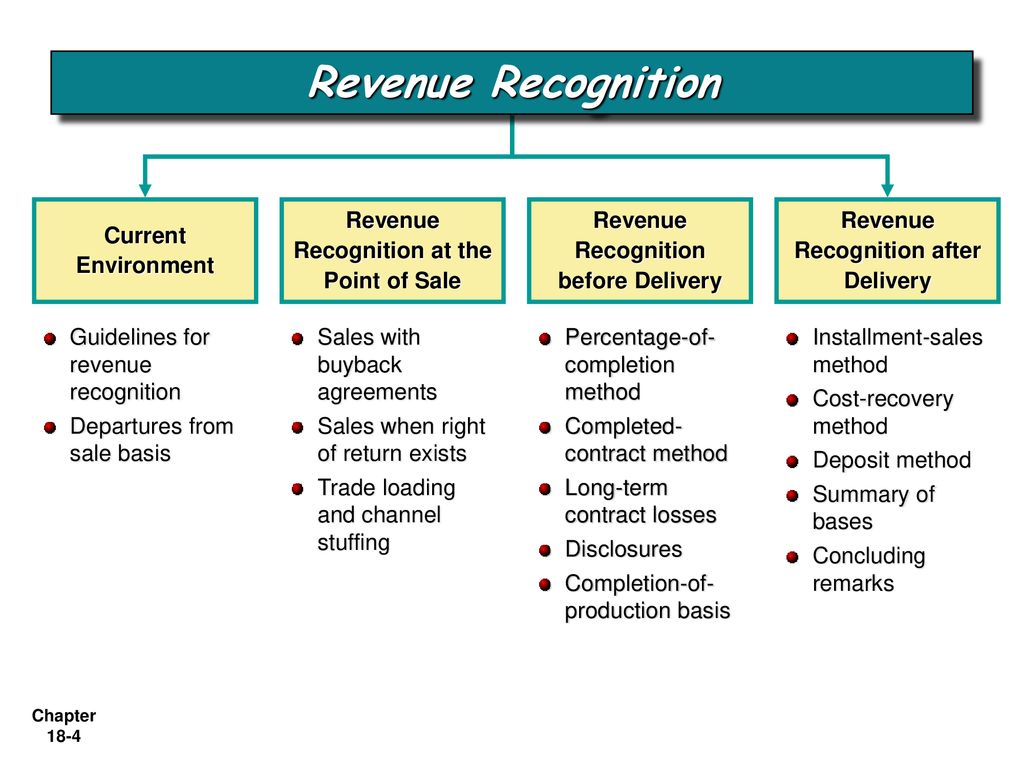
The foundational accounting standard guiding revenue recognition is ASC 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. This standard provides a five-step framework for recognizing revenue: Identify the contract with a customer; Identify the performance obligations in the contract; Determine the transaction price; Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations; Recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation.
For service businesses, the key challenge lies in determining when a performance obligation is satisfied. Unlike selling a tangible product where transfer of ownership is a clear trigger, services are often delivered over time or in stages. Therefore, careful consideration must be given to the nature of the service and the terms of the contract.
Performance obligations are promises to transfer goods or services to a customer. Identifying these obligations within a contract is crucial for proper revenue allocation and recognition. For instance, a consulting firm might have separate performance obligations for initial assessment, strategy development, and implementation support.
Common Scenarios and Their Revenue Recognition Implications
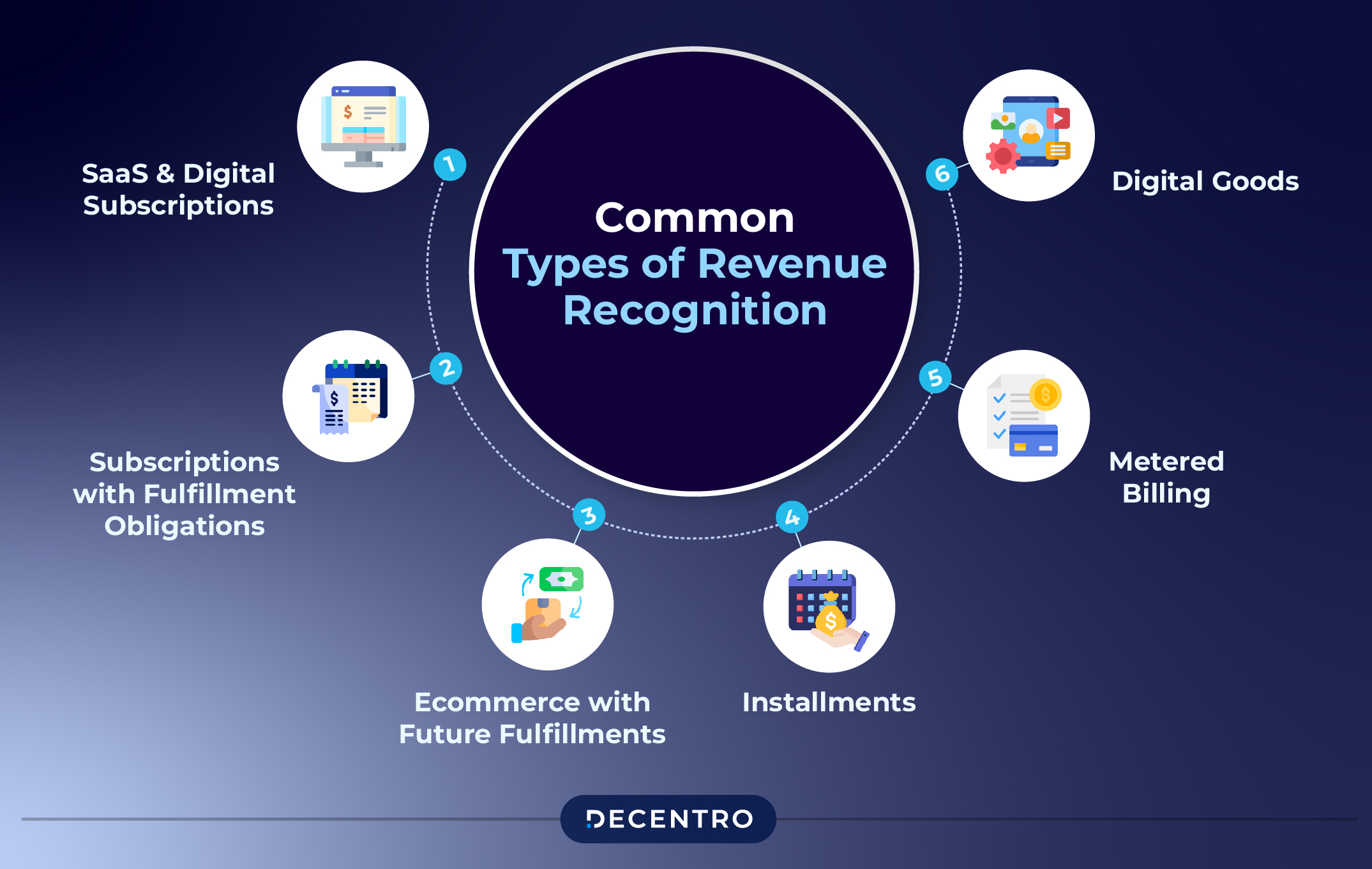
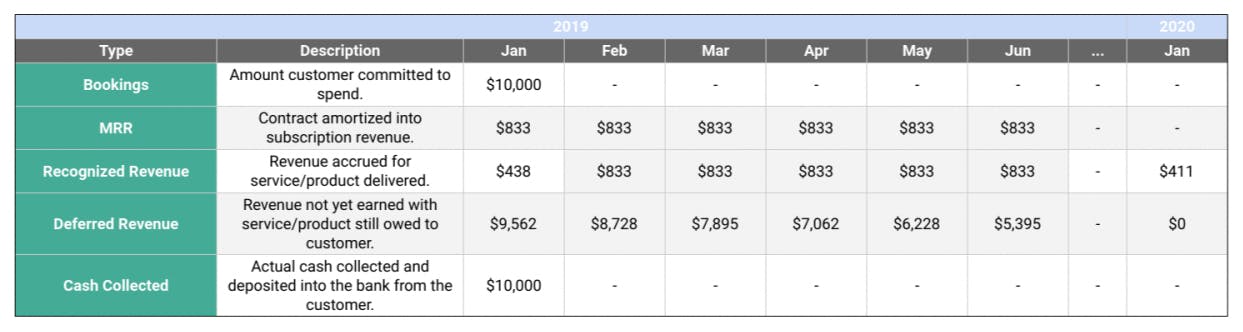
Consider a subscription-based software as a service (SaaS) company. They provide access to their software for a monthly fee. Revenue is typically recognized ratably over the subscription period, as the service is delivered continuously throughout the month.
Contrast this with a one-time service like a home repair. Revenue is recognized when the repair is completed and the customer accepts the work. Progress billing may be involved, but revenue is not recognized until the service is substantially performed.
Professional services, such as legal or accounting services, often operate on an hourly or project basis. Revenue is generally recognized as the services are performed, often tracked through billable hours or milestones achieved.
Challenges in Applying ASC 606
Despite the framework provided by ASC 606, several challenges can arise in its application. One common issue is determining the appropriate allocation of the transaction price when multiple performance obligations exist. This requires careful judgment and may involve estimating the standalone selling price of each performance obligation.
Another challenge is accounting for contract modifications. Changes to the scope of work or the price require reassessment of the performance obligations and the transaction price. This can be particularly complex in long-term service contracts.
Estimating the collectibility of revenue is also important. If there is significant uncertainty about whether a customer will pay, revenue recognition may be deferred until collectibility is reasonably assured.
Best Practices for Accurate Revenue Recognition
To ensure accurate revenue recognition, service businesses should implement robust accounting policies and procedures. These policies should be clearly documented and consistently applied.
Accurate time tracking is essential for services billed on an hourly basis. This provides support for the amount of work performed and the corresponding revenue recognized. Software solutions are available to help with time tracking and project management.
Regular reviews of contracts and billing practices are important for identifying potential issues and ensuring compliance with ASC 606. This review should include assessing the completeness of performance and the collectibility of revenue.
It is important to consult with qualified accounting professionals to navigate the complexities of ASC 606 and ensure compliance. They can provide guidance on specific industry practices and help develop appropriate accounting policies.
The Impact of Technology
Technology plays a significant role in streamlining revenue recognition processes. Accounting software with built-in revenue recognition capabilities can automate many tasks, such as allocating transaction prices and tracking performance obligations. These systems can also generate reports that provide insights into revenue trends and performance.
Furthermore, cloud-based solutions offer enhanced accessibility and collaboration, allowing for real-time visibility into revenue data. This can improve decision-making and enable more proactive management of revenue streams.
Looking Ahead: Future Trends in Revenue Recognition
The landscape of revenue recognition is constantly evolving. As business models become more complex and technology advances, new challenges and opportunities will emerge. Keeping abreast of these developments is crucial for maintaining accurate financial reporting.
One trend to watch is the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in revenue recognition. These technologies can automate complex tasks, such as identifying patterns in revenue data and predicting future revenue streams.
Ultimately, successful revenue recognition in service businesses requires a combination of technical expertise, sound judgment, and a commitment to accuracy. By understanding the core principles of ASC 606, implementing best practices, and leveraging technology, service businesses can ensure reliable and transparent financial reporting, building trust with stakeholders and driving sustainable growth. Accurate revenue recognition is not just a compliance requirement; it's a strategic imperative.