Iris Xe Graphics For Video Editing

For years, integrated graphics were relegated to basic display duties, a far cry from the power needed for serious video editing. Now, Intel's Iris Xe graphics are challenging that perception, promising a viable option for creators on the go or those on a budget.
But can an integrated GPU truly handle the demands of video editing? This article dives deep into the capabilities of Iris Xe graphics, exploring its strengths, limitations, and how it stacks up against dedicated graphics cards in the realm of video production. We’ll examine real-world performance, software compatibility, and the future implications for aspiring video editors.
The Rise of Integrated Graphics
Integrated graphics processors (GPUs) have historically been the underdogs of the computing world. They share system memory with the CPU, limiting their performance compared to dedicated GPUs with their own dedicated memory. However, recent advancements, particularly with Intel's Iris Xe, are changing the game.
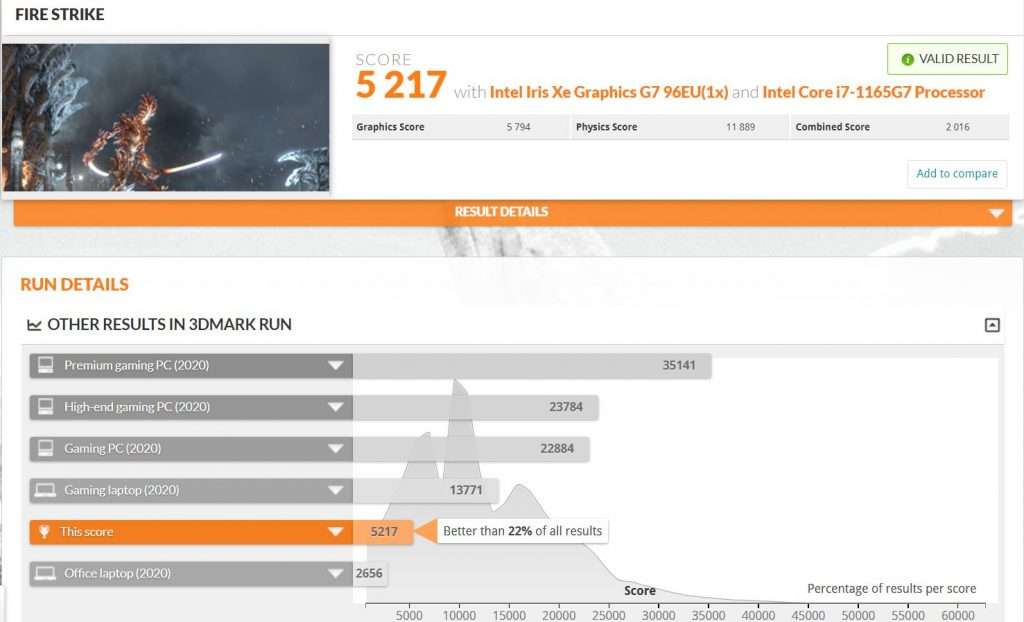
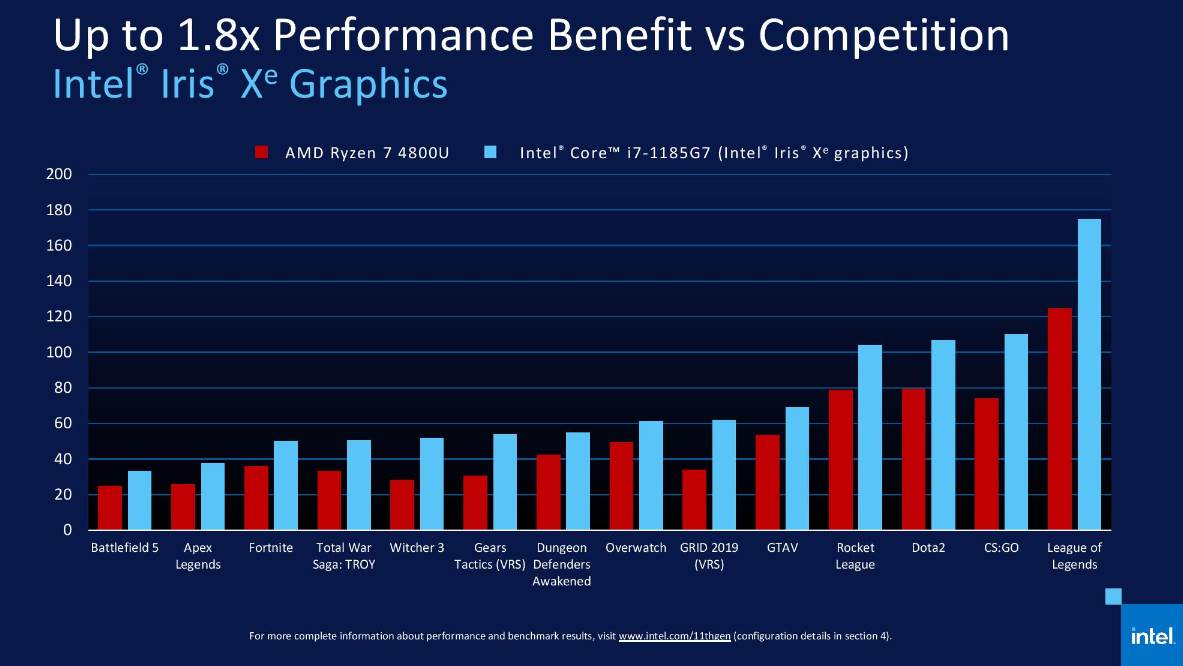
Iris Xe boasts a significant leap in performance compared to previous Intel integrated graphics. This progress is primarily driven by architectural improvements and increased execution units.
Iris Xe: A Video Editing Contender?
The key question is whether Iris Xe can handle video editing tasks effectively. The answer, as with most things, is nuanced.
For basic editing tasks, such as cutting clips, adding transitions, and simple color correction, Iris Xe performs admirably. Many users report smooth playback of 1080p footage and even some 4K projects.
However, when it comes to more demanding tasks like heavy color grading, complex effects, or editing multiple streams of 4K footage, Iris Xe starts to show its limitations. Rendering times can be significantly longer compared to a dedicated GPU.
According to Intel, Iris Xe is designed to provide a balanced experience for both everyday computing and light content creation. This positions it as a suitable option for amateur editors or those who work on smaller projects.
Real-World Performance and Software Compatibility
Numerous benchmarks and user reviews provide insights into Iris Xe's real-world performance. These tests often involve popular video editing software like Adobe Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve, and Final Cut Pro (on compatible systems).
Reports indicate that Iris Xe can handle 1080p editing in Premiere Pro without major issues, especially with optimized settings and proxy workflows. However, rendering 4K footage or applying complex effects can result in noticeable slowdowns.
DaVinci Resolve, known for its resource-intensive color grading capabilities, generally requires a more powerful GPU for optimal performance. While Iris Xe can run Resolve, users may need to lower the resolution or use optimized media to avoid lag.
Software compatibility is generally good, as Iris Xe supports modern APIs like DirectX 12 and OpenGL. This ensures that most video editing software will run without major compatibility issues.
Iris Xe vs. Dedicated GPUs
While Iris Xe has made significant strides, it's crucial to understand its limitations compared to dedicated GPUs. Dedicated graphics cards offer significantly more processing power and dedicated video memory (VRAM), allowing them to handle complex tasks with ease.
A dedicated GPU, even an entry-level one, will generally outperform Iris Xe in demanding video editing scenarios. This is especially true for 4K editing, motion graphics, and 3D rendering.
However, laptops with Iris Xe graphics are often more affordable and energy-efficient than those with dedicated GPUs. This makes them a compelling option for users who prioritize portability and battery life.
The Future of Integrated Graphics in Video Editing
The advancements in integrated graphics signal a promising future for video editors. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further improvements in performance and efficiency.
Intel's ongoing development of its Xe architecture suggests that future generations of integrated graphics will offer even more capabilities. This could potentially bridge the gap between integrated and dedicated GPUs, making video editing more accessible to a wider range of users.
The rise of cloud-based video editing platforms also plays a role. By offloading some processing tasks to the cloud, even less powerful devices can handle complex editing projects.
In conclusion, while Iris Xe may not replace dedicated GPUs for professional-grade video editing, it presents a viable and increasingly capable option for hobbyists, students, and those who need a portable and affordable editing solution. The future of integrated graphics in video editing looks bright, with continued advancements promising to democratize content creation for everyone.






![Iris Xe Graphics For Video Editing Intel UHD vs Iris Xe Graphics — Which is Better? [2024 Update]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2023/09/Intel-UHD-vs-Iris-Xe-Graphics-—-Which-is-Better-Twitter.jpg)