Is L Carnitine And Acetyl L Carnitine The Same

Confusion reigns supreme in the supplement world as consumers grapple with the nuances of L-Carnitine and Acetyl L-Carnitine (ALCAR). Are they the same? The answer is a resounding no, and understanding their differences is crucial for making informed health decisions.
This article breaks down the core distinctions between these two popular compounds, revealing why choosing the right one can significantly impact your health goals. We'll dissect their unique benefits, bioavailability, and specific applications, cutting through the marketing hype to deliver clear, actionable information.
Decoding Carnitine: The Basics
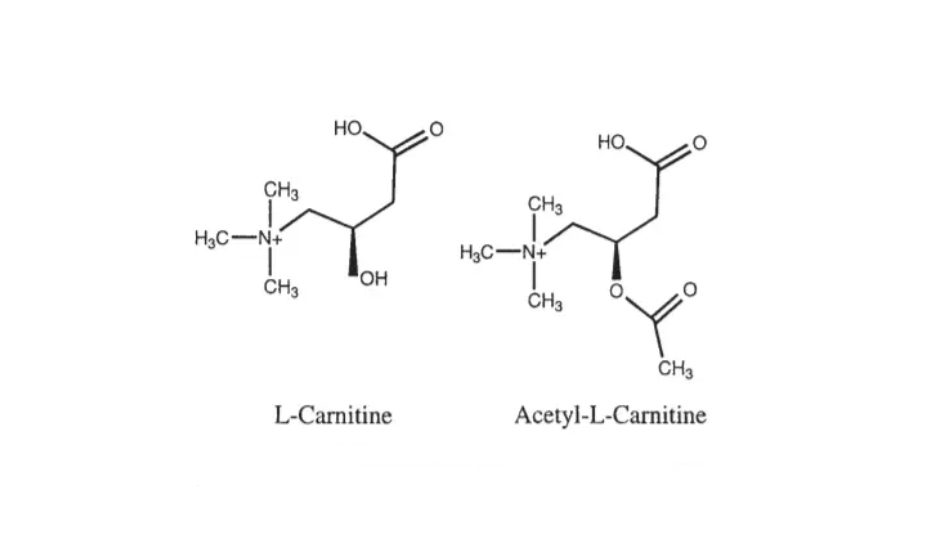
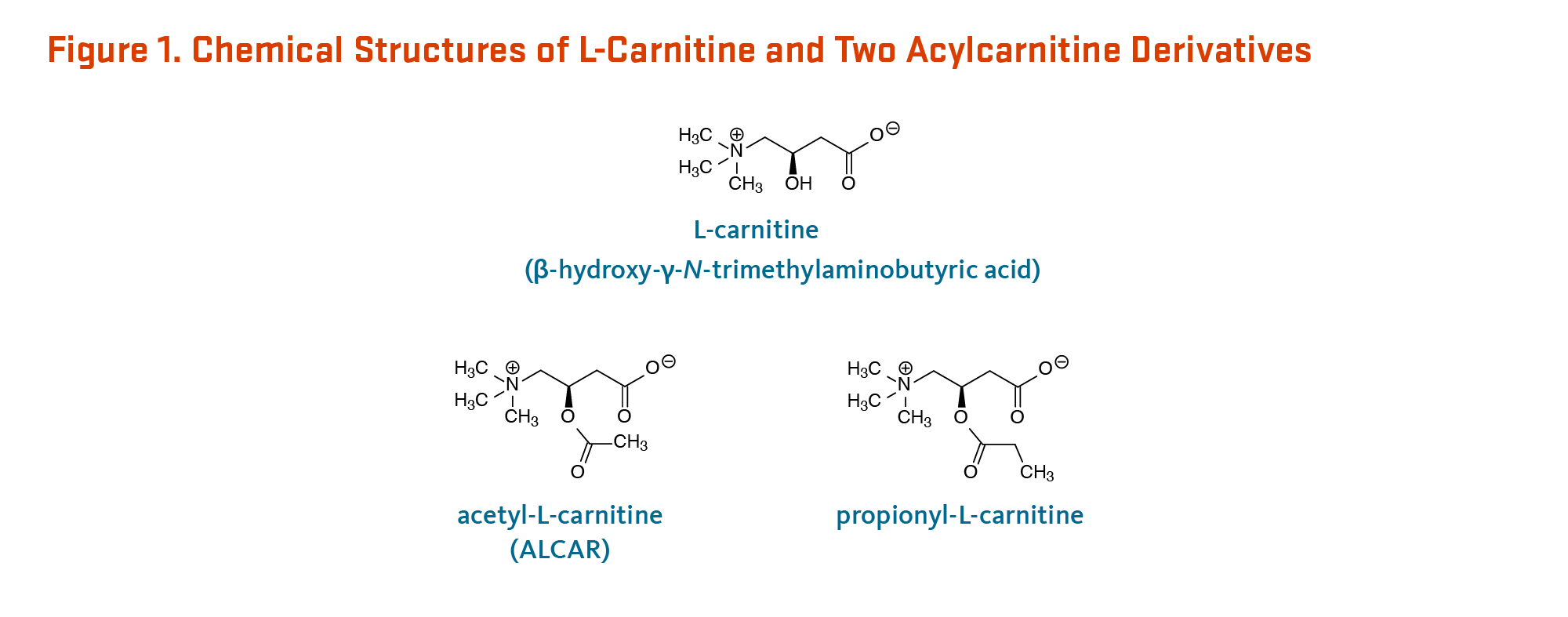
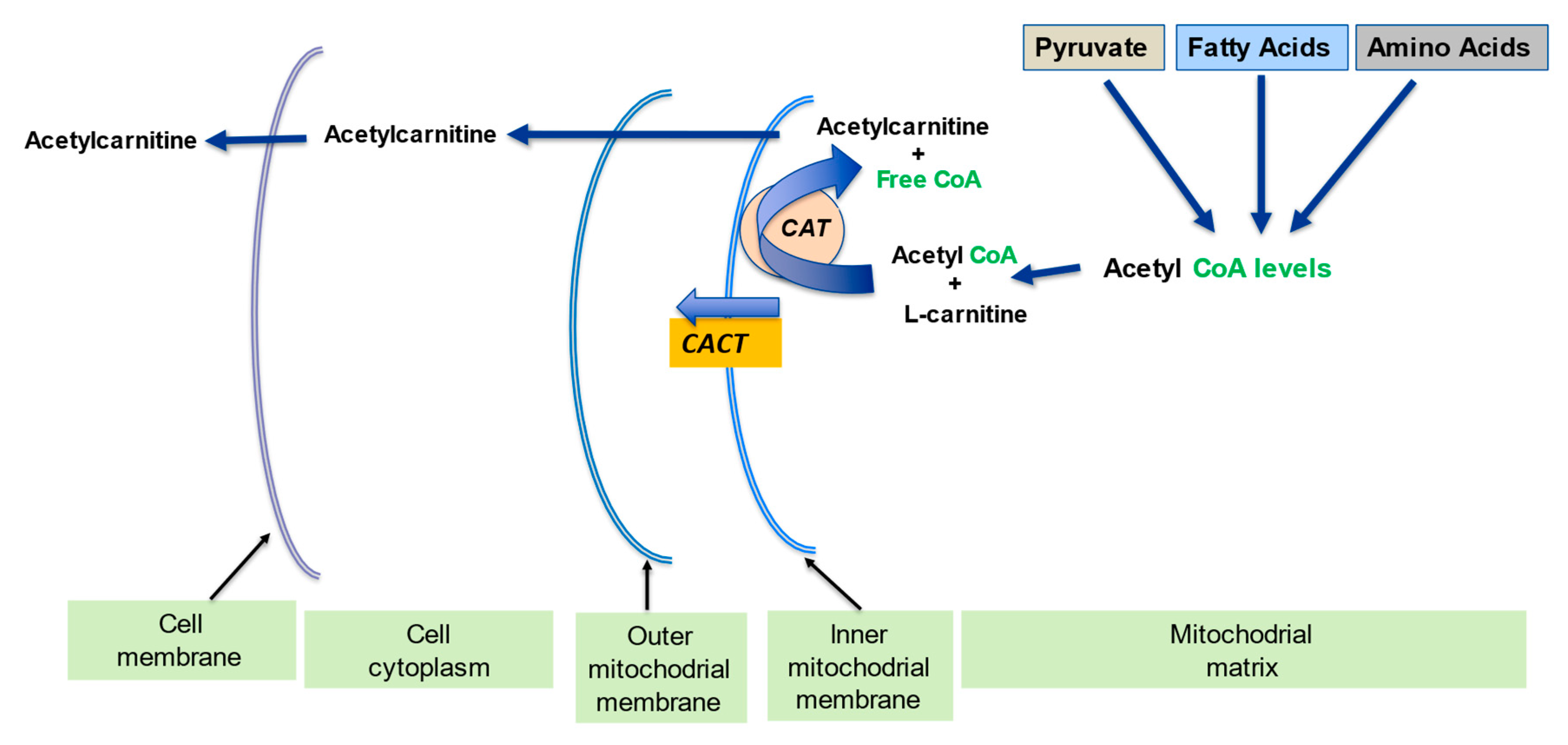
L-Carnitine is a naturally occurring amino acid derivative that plays a vital role in energy production. It's synthesized in the body from lysine and methionine, and is primarily found in muscle tissue. Its main function is to transport fatty acids into the mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell, where they can be burned for energy.
Think of L-Carnitine as a shuttle service, ferrying fuel to the engine. Without it, fat metabolism grinds to a halt. This is why it's often touted for its potential to aid in weight management and improve athletic performance.
Acetyl L-Carnitine (ALCAR): A Brain Booster?
Acetyl L-Carnitine (ALCAR) is a modified form of L-Carnitine. The key difference lies in the acetyl group attached to the molecule. This seemingly small addition dramatically alters its properties, allowing it to cross the blood-brain barrier more effectively.
This enhanced permeability unlocks a range of cognitive benefits. Studies suggest that ALCAR may improve memory, focus, and overall brain function. It’s this targeted delivery to the brain that sets it apart.
Key Differences: A Side-by-Side Comparison
The core difference between L-Carnitine and ALCAR lies in their bioavailability and target areas. L-Carnitine primarily impacts the body's energy metabolism. ALCAR, on the other hand, is much more effective at reaching the brain and influencing cognitive function.
Here's a breakdown:
L-Carnitine:
- Primary Function: Facilitates fat transport into mitochondria for energy production.
- Bioavailability: Limited, particularly in crossing the blood-brain barrier.
- Benefits: May improve athletic performance, support weight management, and reduce muscle fatigue.
- Best For: Individuals seeking to enhance physical performance or support fat loss.
Acetyl L-Carnitine (ALCAR):
- Primary Function: Enhances cognitive function by increasing acetylcholine production and protecting neurons.
- Bioavailability: Higher bioavailability, especially in the brain.
- Benefits: May improve memory, focus, cognitive function, and protect against age-related cognitive decline.
- Best For: Individuals seeking to improve cognitive function, enhance memory, or support brain health.
Scientific Evidence: What Does the Research Say?
Research supports the distinct benefits of both L-Carnitine and ALCAR. A 2016 meta-analysis published in the journal "Obesity Reviews" found that L-Carnitine supplementation was associated with a modest but significant reduction in body weight, BMI, and fat mass.
Numerous studies have explored ALCAR's effects on cognitive function. One study published in the journal "Neurology" demonstrated that ALCAR supplementation improved cognitive performance in patients with mild cognitive impairment.
It's crucial to note that dosages vary depending on the specific application. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for your individual needs.
Who Should Use Which?
Choosing between L-Carnitine and ALCAR depends entirely on your goals. Athletes or individuals seeking to improve their physical performance might benefit more from L-Carnitine.
Those looking to enhance their cognitive function, improve memory, or protect against age-related cognitive decline should consider ALCAR. For example, someone experiencing brain fog might find ALCAR more helpful.
Dosage and Safety Considerations
While generally considered safe, both L-Carnitine and ALCAR can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects may include nausea, vomiting, stomach upset, and diarrhea.
It is important to adhere to recommended dosages and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen. Individuals with kidney disease, liver disease, or seizure disorders should exercise particular caution. For L-Carnitine, typical dosages range from 500mg to 2000mg per day, while for ALCAR, dosages range from 500mg to 1500mg per day.
The Bottom Line: Not Interchangeable
L-Carnitine and Acetyl L-Carnitine are not the same. While both are related and share a common ancestor, their distinct structures give them unique properties and benefits. L-Carnitine shines as a metabolic enhancer, while ALCAR excels in cognitive support.
Understanding these differences is vital for making informed choices about your health and well-being. Don't fall for misleading marketing—knowledge is power when it comes to supplementation.
Next Steps and Ongoing Research
Ongoing research continues to explore the full potential of both L-Carnitine and ALCAR. Future studies will likely delve deeper into their roles in specific conditions and populations.
Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine which form, if any, is right for you. Stay informed and prioritize evidence-based information to optimize your health outcomes. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) also provides useful information on dietary supplements.