Is Thca Stronger Than Delta 9

Imagine strolling through a sun-drenched cannabis farm, the air thick with the earthy aroma of terpenes, the leaves shimmering with crystalline trichomes. Farmers carefully inspect each bud, assessing its potential, not just for its immediate psychoactive punch, but for the chemical dance that occurs when heat is applied. The question on everyone's mind, whispered among cultivators and consumers alike: is THCA, the raw, unheated form of THC, somehow secretly more potent than its famous counterpart, Delta 9 THC?
The debate surrounding THCA and Delta 9 THC centers on a key chemical process called decarboxylation. Essentially, THCA, in its natural state, is non-psychoactive. It only transforms into the intoxicating Delta 9 THC when exposed to heat, like when smoking, vaping, or baking cannabis. But recent anecdotal evidence and evolving research suggest the story might be more complex than previously understood, raising questions about THCA's potential effects and its legal implications.
Understanding the Chemistry
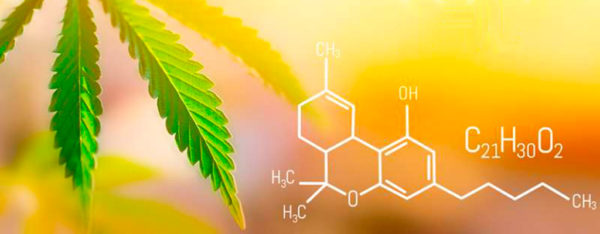
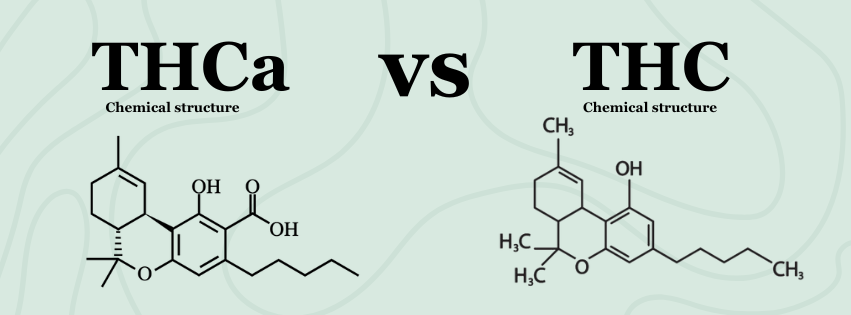
To understand the buzz, let's delve into the basics. Cannabis plants produce a range of cannabinoids, including both THCA and Delta 9 THC. THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is the precursor to Delta 9 THC.
Think of it as the "before" picture. Delta 9 THC, on the other hand, is the "after" picture – the cannabinoid primarily responsible for the euphoric and psychoactive effects associated with cannabis.
The magic happens with decarboxylation, a process that involves removing a carboxyl group (COOH) from the THCA molecule. This is most commonly achieved through heat.
When you light a joint, vape cannabis oil, or bake edibles, you're essentially forcing THCA to convert into Delta 9 THC. Without that heat, THCA remains largely inactive in terms of psychoactive effects.
The Conventional Wisdom vs. Emerging Theories
For years, the understanding has been straightforward: THCA is not psychoactive until it's converted to Delta 9 THC. This is because THCA doesn't bind efficiently to the CB1 receptors in the brain, the primary receptors responsible for THC's intoxicating effects.
Delta 9 THC, with its altered molecular structure, fits perfectly into these receptors, triggering the release of neurotransmitters and creating the familiar high.
However, some consumers are reporting experiencing effects from consuming raw cannabis or THCA isolates, even without significant heating. This has led to several emerging theories and lines of inquiry.
Some researchers propose that while THCA may not directly bind to CB1 receptors in the same way as Delta 9 THC, it might interact with other receptors in the endocannabinoid system (ECS), or influence other biological pathways.
The ECS is a complex network of receptors, enzymes, and neurotransmitters that plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including mood, pain, appetite, and sleep.
It's possible that THCA's interaction with these other components of the ECS contributes to subtle, but noticeable, effects, even without a traditional "high."
Another theory suggests that even in the absence of intentional heating, some small amount of decarboxylation may occur naturally over time, converting a tiny percentage of THCA into Delta 9 THC. This minute amount of Delta 9 THC, combined with THCA's potential interaction with other receptors, could be responsible for the observed effects.
Anecdotal Evidence and Consumer Experiences
Beyond the scientific theories, a growing body of anecdotal evidence from cannabis consumers suggests that THCA may have effects of its own. Some individuals report experiencing anti-inflammatory benefits, pain relief, and neuroprotective effects after consuming raw cannabis juice or THCA isolates.
Many users specifically seek out raw cannabis for its potential health benefits, believing that THCA, in its unheated form, offers a unique therapeutic profile distinct from Delta 9 THC.
However, it's important to acknowledge the limitations of anecdotal evidence. Personal experiences can be subjective and influenced by factors such as the placebo effect, individual sensitivities, and the specific strain of cannabis consumed.
Furthermore, the concentration of THCA and other cannabinoids can vary significantly between different cannabis products, making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions based solely on individual reports.
The Legal Landscape
The legal status of THCA is somewhat ambiguous and varies depending on jurisdiction. In many areas, cannabis laws focus primarily on the Delta 9 THC content of cannabis products.
Because THCA itself is not considered psychoactive under traditional definitions, it may fall into a legal gray area in some regions. However, it's crucial to remember that laws are constantly evolving, and the legal status of THCA could change rapidly.
The 2018 Farm Bill, for example, legalized hemp (cannabis with less than 0.3% Delta 9 THC) at the federal level in the United States. This has led to the proliferation of THCA products derived from hemp, as these products technically comply with the legal limit for Delta 9 THC until heated.
However, some states have begun to crack down on THCA products, arguing that they are essentially a loophole that allows for the sale of psychoactive cannabis under the guise of hemp.
Consumers should always be aware of the local laws and regulations regarding cannabis and cannabinoids before purchasing or using any THCA products.
The Importance of Further Research
The debate surrounding THCA's effects and potency highlights the need for more rigorous scientific research. While anecdotal evidence and emerging theories are intriguing, they must be substantiated by controlled clinical trials.
Studies are needed to investigate THCA's interaction with the endocannabinoid system, its potential therapeutic benefits, and its safety profile. Researchers also need to develop more accurate and reliable methods for testing and quantifying THCA content in cannabis products.
Ultimately, a deeper understanding of THCA will benefit both consumers and the cannabis industry as a whole. It will allow consumers to make informed decisions about the products they use and empower cultivators and manufacturers to develop more targeted and effective cannabis-based therapies.
Conclusion: A Budding Field of Discovery
The question of whether THCA is "stronger" than Delta 9 THC is not a simple yes or no answer. It depends on how you define "stronger." In terms of immediate psychoactive intensity, Delta 9 THC clearly takes the lead. However, THCA may possess unique properties and potential benefits that are only beginning to be understood.
The cannabis plant continues to surprise us with its complexity and its potential to offer novel therapeutic solutions. As research progresses, we can expect to learn even more about the fascinating world of cannabinoids and their impact on human health and well-being.
For now, the conversation around THCA serves as a reminder that the world of cannabis is not just about getting high; it's about exploring the diverse potential of this remarkable plant and harnessing its power to improve lives.