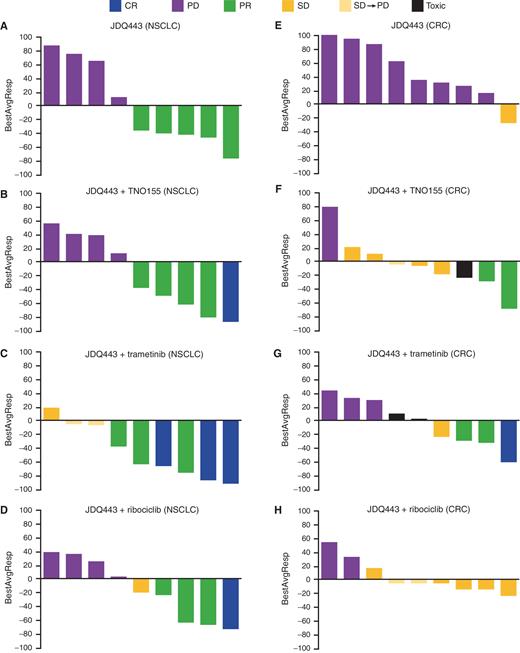
Jdq443 Kras G12c Inhibitor Clinical Trial

The pharmaceutical landscape is witnessing promising advancements in the fight against KRAS-mutated cancers, a notoriously challenging area of oncology. Early results from a clinical trial evaluating JDQ443, a novel KRAS G12C inhibitor, are generating cautious optimism among researchers and patient advocates alike. The drug is currently under development by Novartis.
This article delves into the emerging data surrounding JDQ443, exploring its mechanism of action, clinical trial design, preliminary findings, and potential implications for patients battling cancers driven by the KRAS G12C mutation. The focus remains on presenting factual information and expert perspectives, devoid of unsubstantiated claims or exaggerated expectations.
Understanding KRAS G12C and its Significance
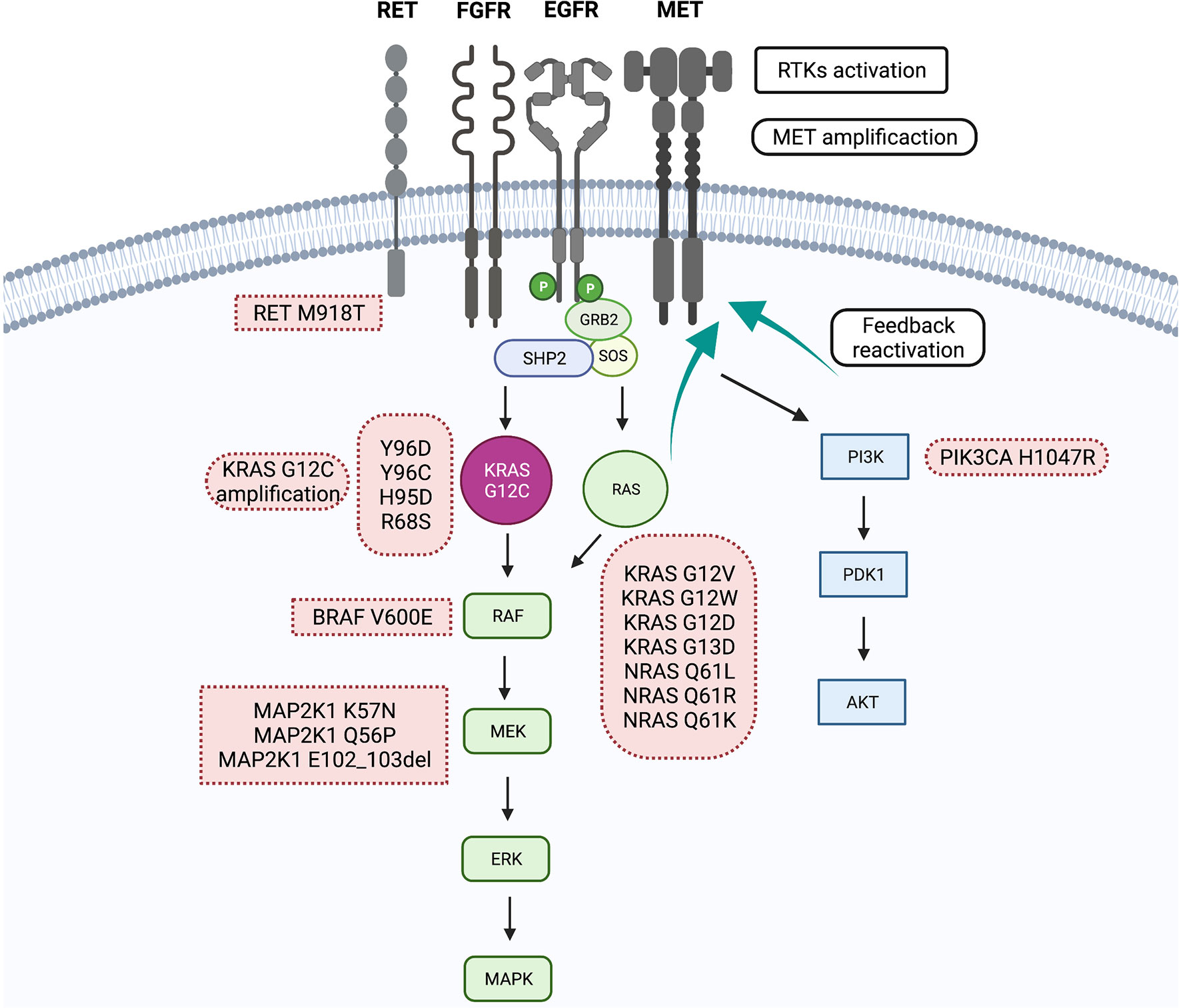
KRAS is a gene that plays a crucial role in cell growth and proliferation. When mutated, particularly the G12C variant, it can drive uncontrolled cell growth, leading to various cancers. These cancers are often aggressive and difficult to treat with conventional therapies.
The G12C mutation is present in a significant proportion of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cases, as well as in smaller percentages of colorectal cancer and other solid tumors. The development of inhibitors targeting this specific mutation represents a significant step forward in precision oncology.
JDQ443: A Novel KRAS G12C Inhibitor
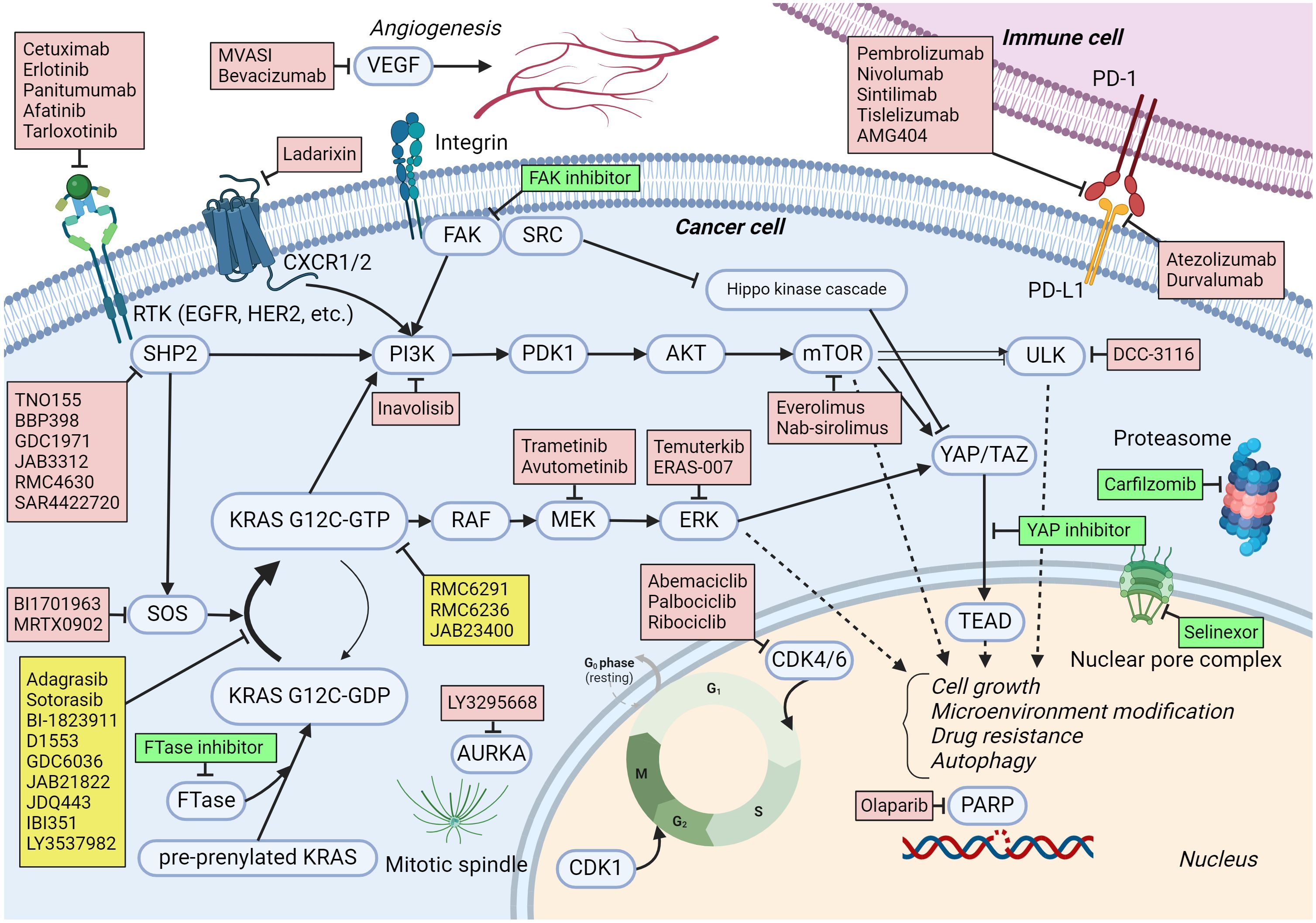
JDQ443 is an investigational, oral KRAS G12C inhibitor designed to specifically target and bind to the mutated KRAS G12C protein. By selectively inhibiting the activity of this protein, JDQ443 aims to disrupt the signaling pathways that fuel cancer cell growth and survival. This mechanism is distinct from traditional chemotherapy, offering a more targeted approach.
Unlike some earlier KRAS G12C inhibitors that require the KRAS protein to be in its inactive state, JDQ443 has been designed to bind to both the active and inactive forms. This broader binding profile potentially allows for a more complete and sustained inhibition of the mutated protein.
The Clinical Trial: Design and Early Findings
The ongoing clinical trial evaluating JDQ443 is a multi-center, open-label study enrolling patients with advanced solid tumors harboring the KRAS G12C mutation. The trial aims to assess the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of JDQ443 as a single agent and in combination with other therapies.
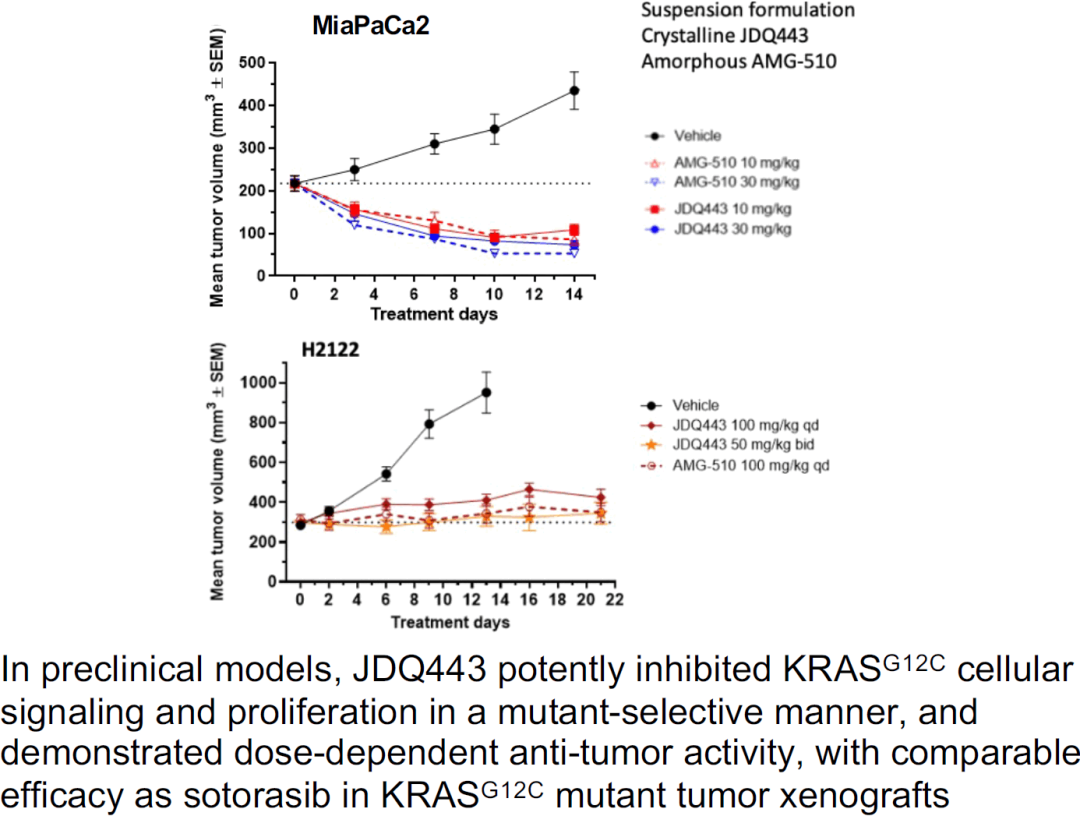
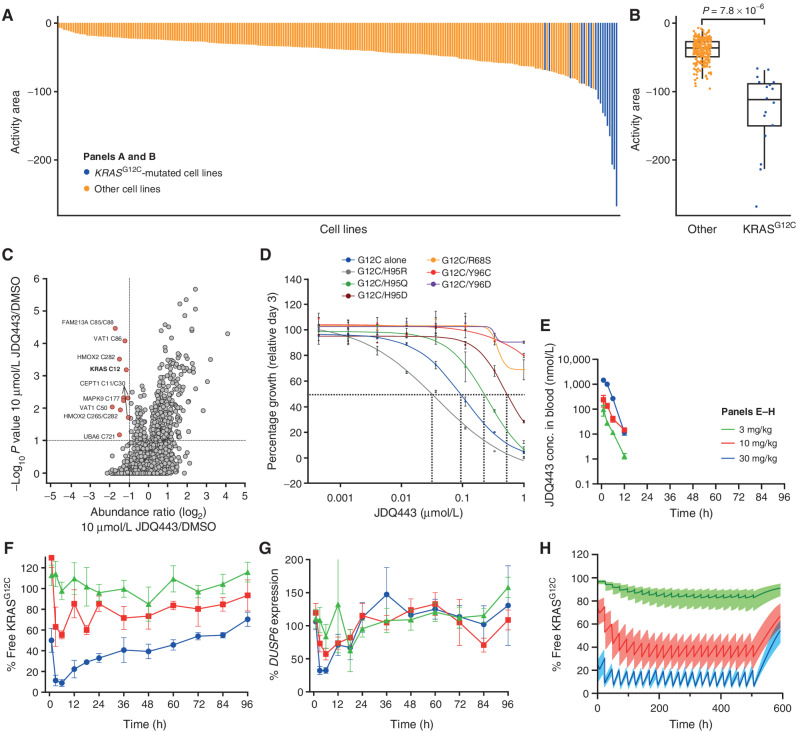
Preliminary data presented at recent medical conferences have shown promising signs of anti-tumor activity in some patients, including tumor shrinkage and disease stabilization. However, it is crucial to note that these are early results and further investigation is needed.
Specifically, the trial is evaluating different doses of JDQ443 to determine the optimal dose for efficacy and safety. Researchers are also analyzing biomarkers to identify which patients are most likely to respond to the treatment.
Safety and Tolerability
As with any investigational drug, safety and tolerability are paramount. Early data suggests that JDQ443 is generally well-tolerated, but some patients have experienced side effects, which are being carefully monitored and managed.
Common side effects reported in the trial include nausea, fatigue, and diarrhea. Researchers are working to understand the underlying mechanisms of these side effects and to develop strategies to mitigate them.
The Potential Impact and Future Directions
If JDQ443 proves to be safe and effective in larger clinical trials, it could represent a significant advance in the treatment of KRAS G12C-mutated cancers. It would provide another treatment option for patients who currently have limited options.
The development of JDQ443 also highlights the growing importance of precision medicine in oncology. By targeting specific genetic mutations, researchers are developing more effective and less toxic therapies.
Further studies are planned to evaluate JDQ443 in combination with other cancer therapies, such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy. These studies will help to determine the optimal way to use JDQ443 to improve patient outcomes.
A Note of Caution
It is important to emphasize that JDQ443 is still an investigational drug and is not yet approved for use by regulatory agencies. Patients should not seek access to JDQ443 outside of a clinical trial.
While the early data are encouraging, much more research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits and risks of JDQ443. The ongoing clinical trials will provide valuable information about the drug's efficacy and safety profile.
The information presented here is for informational purposes only and should not be interpreted as medical advice. Patients with cancer should consult with their healthcare providers to discuss the most appropriate treatment options for their individual circumstances.