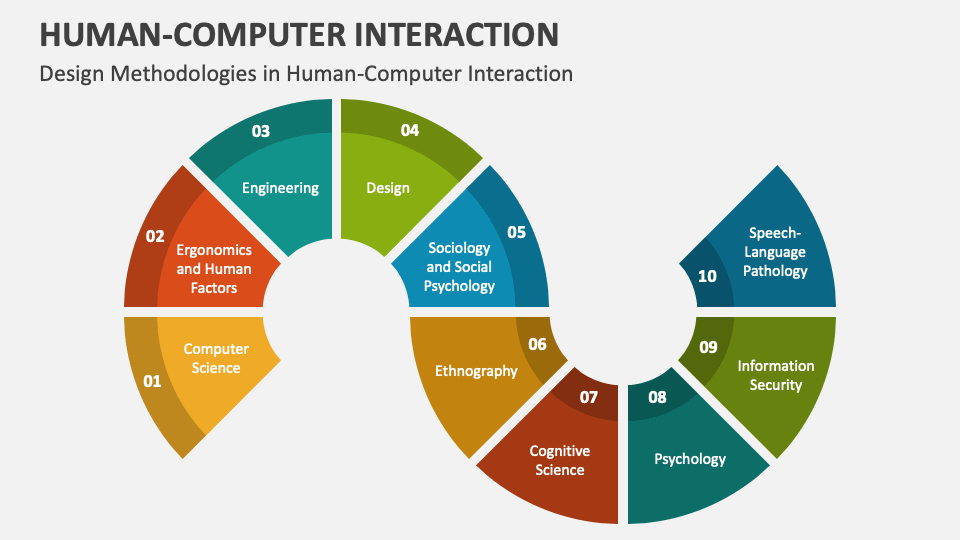
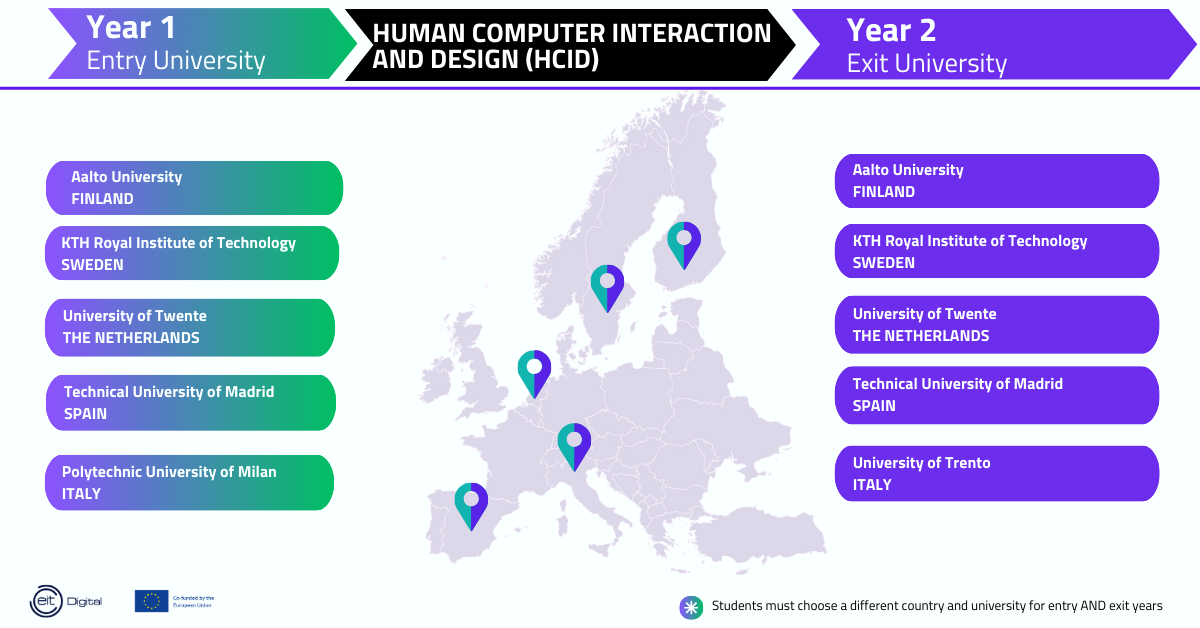
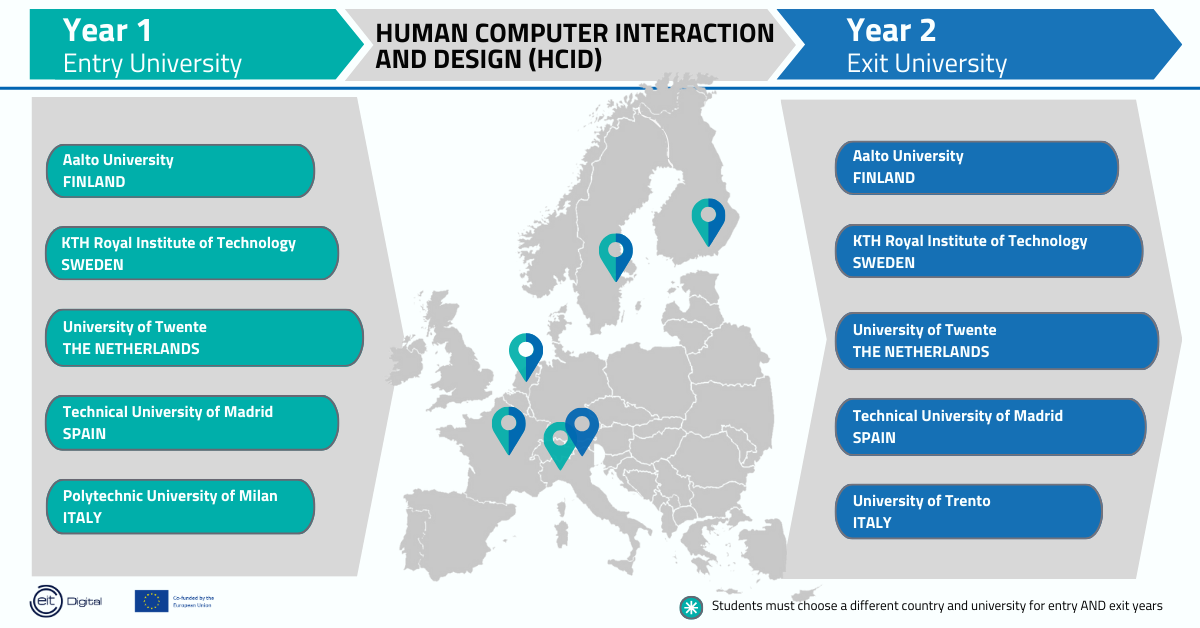
Master In Human Computer Interaction And Design Hcid

The digital landscape is rapidly evolving, demanding professionals who can bridge the gap between human needs and technological capabilities. As interfaces become increasingly complex and integral to daily life, the demand for skilled Human-Computer Interaction and Design (HCID) experts has surged, leading to a significant re-evaluation of the skill sets required in the modern workforce.
This article explores the burgeoning field of HCID, delving into the curricula of leading Master's programs, the industry demand for graduates, and the future trajectory of this vital discipline. It examines how these programs are equipping individuals with the skills to design intuitive, accessible, and user-centered technologies that shape the way we interact with the world.
The Rise of HCID Master's Programs
Universities worldwide are responding to the industry's call by expanding and refining their Master's in HCID programs. These programs typically offer a multidisciplinary approach, drawing from fields like computer science, psychology, design, and cognitive science.
The curriculum often includes courses in user research, interaction design, usability testing, information architecture, and visual design. Students learn to apply theoretical frameworks and practical skills to real-world problems.
Key Program Components
A core component of most HCID Master's programs is a strong emphasis on user-centered design principles. This means understanding the needs, behaviors, and motivations of users through rigorous research methods.
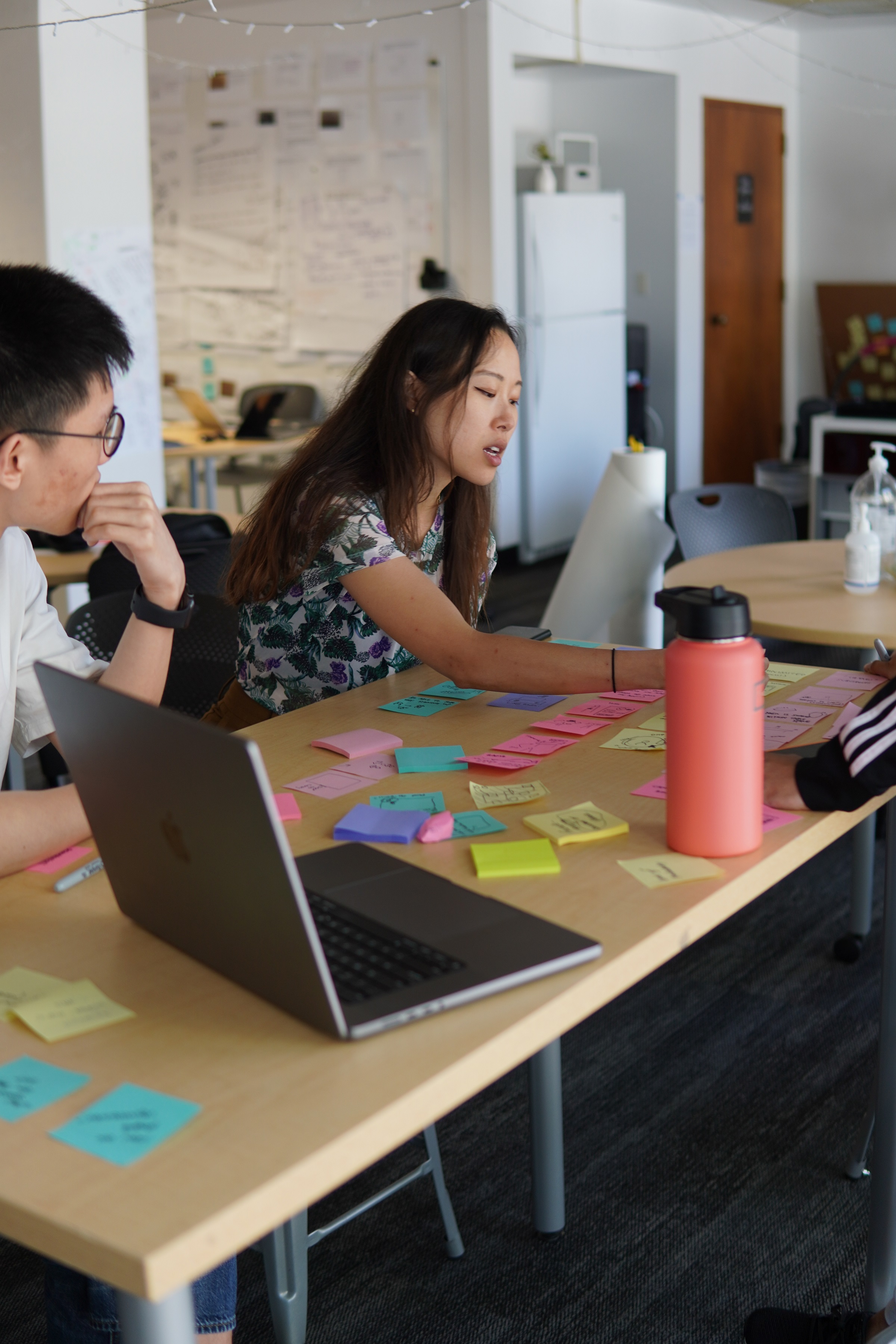
Students learn to conduct interviews, surveys, and ethnographic studies to gather insights that inform design decisions. They also learn to create personas and user journeys to visualize the user experience.
Another critical aspect is the development of prototyping skills. Students learn to create interactive prototypes using various tools and technologies, allowing them to test and refine their designs iteratively.
"Our HCID program focuses on equipping students with the ability to translate user needs into innovative and effective design solutions," says Dr. Anya Sharma, Director of the HCID program at the University of Technology.
Industry Demand and Career Opportunities
The demand for HCID professionals is consistently high across various industries. Companies are recognizing the value of user-centered design in creating products and services that are both usable and engaging.
Graduates of HCID programs find employment in a wide range of roles, including UX designers, UX researchers, interaction designers, information architects, and product managers. These professionals work in diverse sectors, such as technology, healthcare, finance, and education.
According to a recent report by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment in computer and information technology occupations is projected to grow significantly in the coming years, indicating a continued need for HCID specialists.
Specifically, the roles of User Experience (UX) designers and researchers are projected to grow at a faster rate than average. This growth is driven by the increasing importance of user-centered design in creating successful products and services.
Salaries and Compensation
The salaries for HCID professionals are competitive, reflecting the high demand for their skills. Entry-level positions typically offer salaries in the range of $70,000 to $90,000, while experienced professionals can earn upwards of $150,000 or more.
Factors such as experience, location, and company size can influence salary levels. However, the overall trend indicates a positive outlook for compensation in the field.
Challenges and Future Trends
Despite the growing demand and promising career prospects, the HCID field faces certain challenges. One challenge is keeping up with the rapid pace of technological change.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR) are creating new opportunities and challenges for HCID professionals. They need to adapt their skills and knowledge to design interfaces for these novel technologies.
Another challenge is ensuring that designs are inclusive and accessible to all users, regardless of their abilities or backgrounds. This requires a strong understanding of accessibility guidelines and inclusive design principles.
Looking ahead, the future of HCID is likely to be shaped by several key trends. One trend is the increasing focus on designing for mobile devices and wearable technologies.
Another trend is the growing importance of data-driven design. HCID professionals will need to leverage data analytics and user feedback to inform design decisions and optimize user experiences.
Furthermore, the ethical considerations of technology design are becoming increasingly important. HCID professionals will need to consider the ethical implications of their designs and strive to create technologies that are both beneficial and responsible.
The Master's in HCID is proving to be a critical pathway for individuals seeking to shape the future of technology. By equipping students with the skills and knowledge to design user-centered, accessible, and ethical technologies, these programs are contributing to a more human-centered digital world. As technology continues to evolve, the role of the HCID professional will only become more vital.











-Design.webp)