Nicotinamide Riboside Vs Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide

The pursuit of longevity and healthy aging has fueled a surge in interest surrounding cellular health, particularly concerning molecules vital for energy production and cellular repair. At the forefront of this research are two closely related compounds: Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) and Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+). While both play crucial roles in cellular function, understanding their distinct properties and potential benefits is critical for consumers and researchers alike.
This article delves into the science behind NR and NAD+, exploring their differences, how they function within the body, the evidence supporting their potential health benefits, and the ongoing research shaping our understanding of these vital molecules. Furthermore, the article seeks to provide a balanced overview of the current scientific understanding of both NR and NAD+, clarifying the nuances for a broad readership.
NAD+: The Cellular Powerhouse
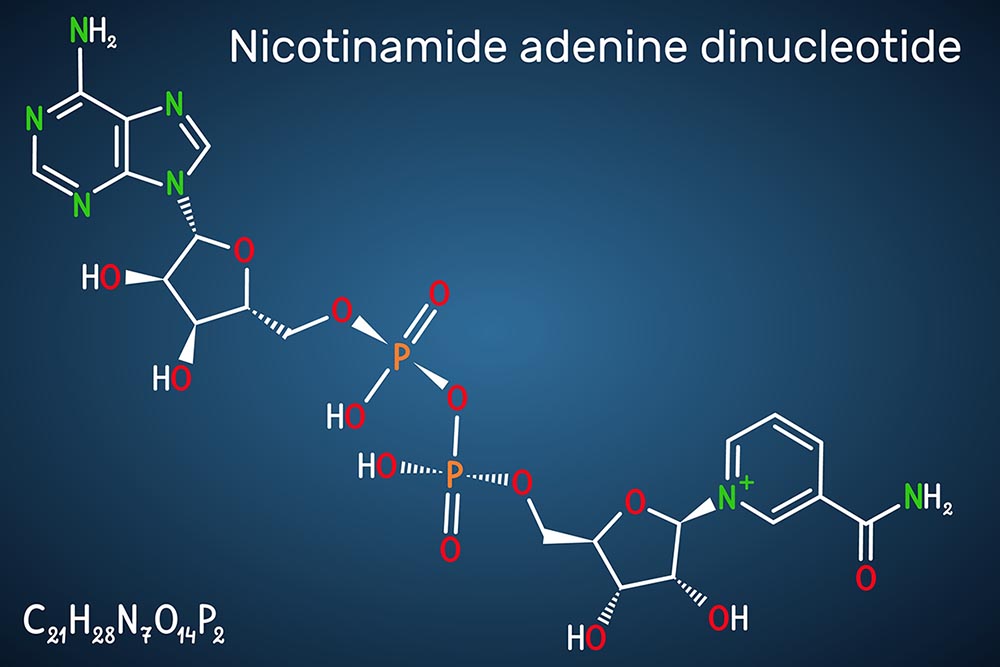
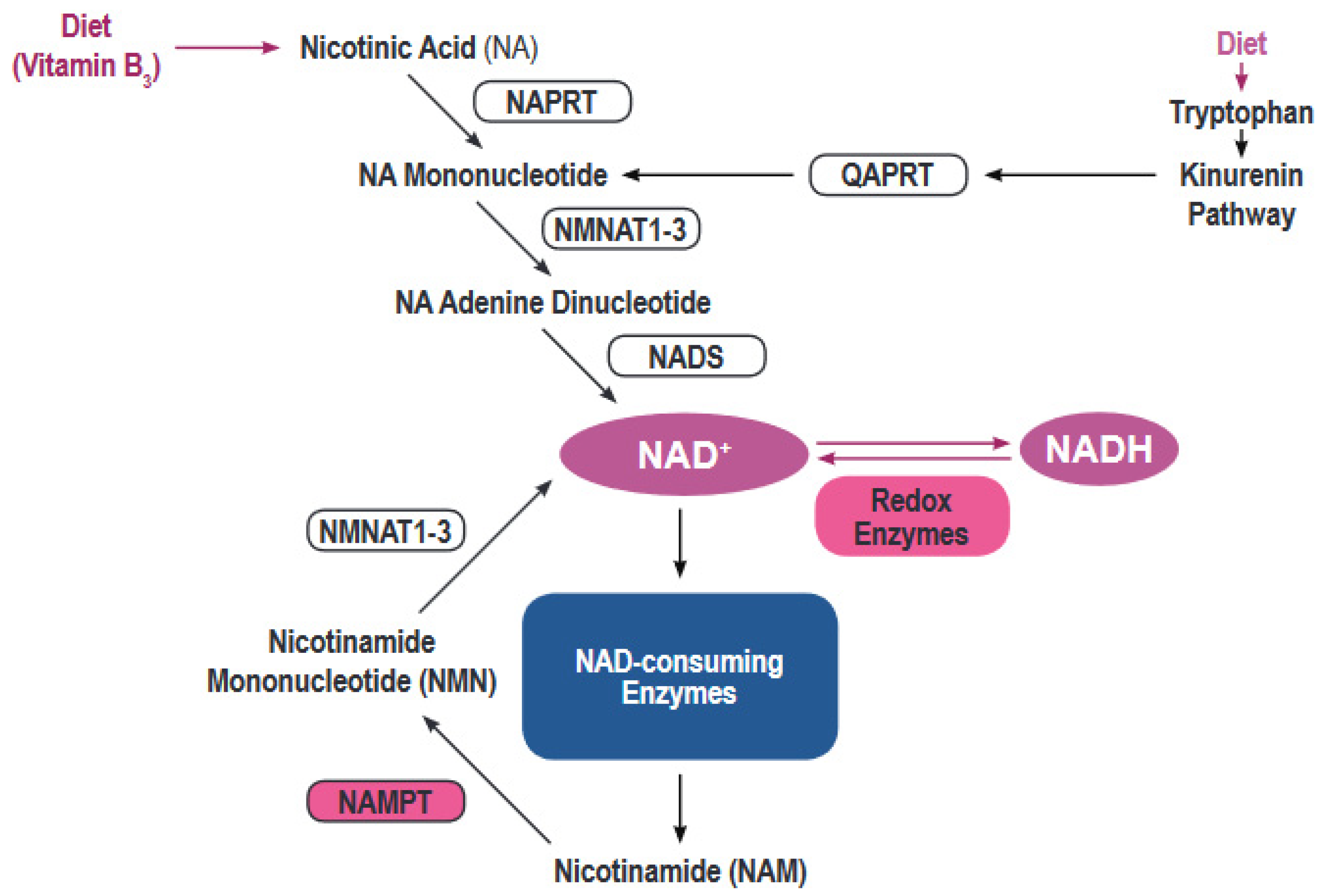
NAD+, a coenzyme found in every living cell, is essential for hundreds of metabolic processes. It acts as a crucial electron carrier in redox reactions, facilitating energy production within the mitochondria, the cell's power plant.
NAD+ is also a substrate for enzymes involved in DNA repair, gene expression, and cellular signaling. These processes are fundamental for maintaining cellular health and function over time. Declining NAD+ levels are associated with aging and age-related diseases, making it a key target in anti-aging research.
The Challenge of Direct NAD+ Supplementation
Directly supplementing with NAD+ faces significant challenges. The molecule's large size and charge make it difficult to cross cell membranes effectively, limiting its bioavailability.
Consequently, researchers have explored alternative strategies to boost NAD+ levels indirectly through precursors like NR.
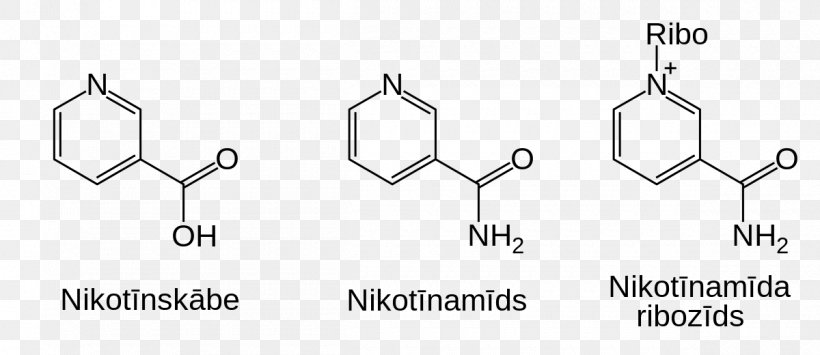
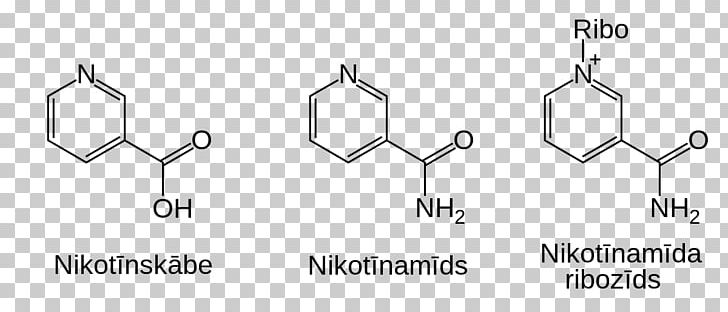
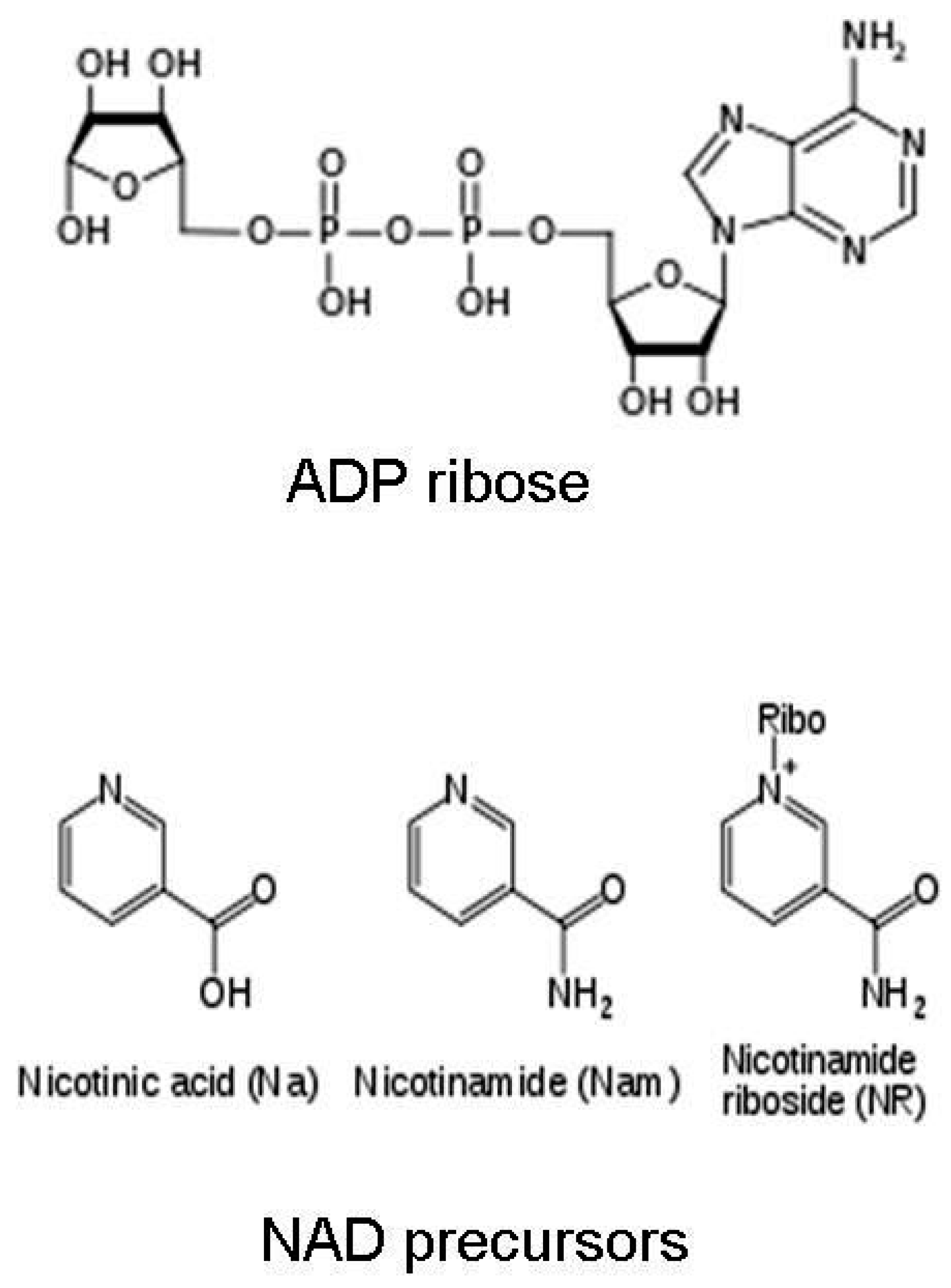
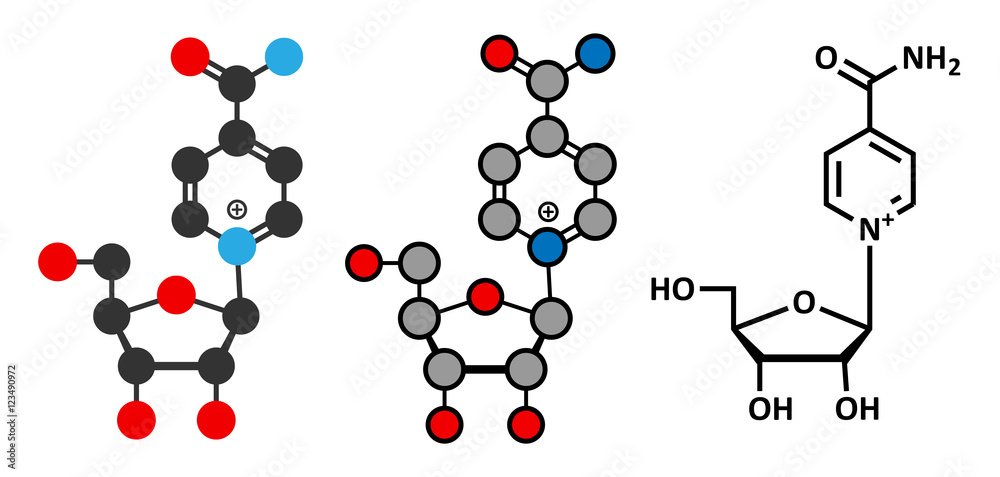
Nicotinamide Riboside (NR): A Potential NAD+ Booster
Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) is a form of vitamin B3 and a precursor to NAD+. It is considered a more efficient route to increasing NAD+ levels because it can enter cells more easily than NAD+ itself.
Once inside the cell, NR is converted into NAD+ through a series of enzymatic reactions. This pathway bypasses some of the limitations associated with direct NAD+ supplementation.
The Science Behind NR's Benefits
Studies suggest that NR supplementation can increase NAD+ levels in various tissues and organs. This increase in NAD+ has been linked to potential benefits, including improved mitochondrial function, enhanced DNA repair, and neuroprotection.
Animal studies have shown that NR can extend lifespan and improve healthspan in certain model organisms. However, it is crucial to note that these findings need to be replicated and confirmed in human clinical trials.
NR vs. NAD+: Key Differences and Considerations
The primary difference lies in their ability to enter cells and directly influence NAD+ levels. NR is a precursor, requiring cellular machinery to convert it into NAD+.
NAD+, while the desired endpoint, faces absorption challenges when taken directly. Therefore, NR is often preferred as a more bioavailable option for boosting NAD+.
Bioavailability and Cellular Uptake
NR has shown promising bioavailability in preclinical studies, making it an attractive option for supplementation. However, the efficiency of NR conversion to NAD+ can vary depending on individual factors and cellular conditions.
Factors like age, genetics, and overall health can influence the effectiveness of NR supplementation.
Current Research and Clinical Trials
Numerous clinical trials are underway to investigate the effects of NR supplementation in humans. These studies are exploring its potential benefits for various conditions, including aging, metabolic disorders, and neurological diseases.
Some studies are evaluating the impact of NR on markers of aging, such as inflammation, oxidative stress, and cellular senescence. Other trials are examining its effects on cognitive function, muscle strength, and cardiovascular health.
Promising Results and Future Directions
Preliminary findings from some clinical trials suggest that NR supplementation can be safe and well-tolerated, with some evidence of increased NAD+ levels and improved biomarkers. However, larger, well-controlled studies are needed to confirm these findings and determine the long-term effects of NR.
Future research should focus on optimizing NR dosage and delivery methods to maximize its efficacy. Additionally, studies are needed to identify specific populations that may benefit most from NR supplementation.
Safety and Potential Side Effects
NR is generally considered safe for most people when taken at recommended doses. However, some individuals may experience mild side effects such as flushing, nausea, or digestive discomfort.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking NR, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications. More studies are needed to understand the long-term effects and potential interactions of NR.
"While the scientific community is excited about the potential of NR to boost NAD+ levels and improve health, it's crucial to approach these supplements with informed caution and consult with a healthcare professional," states Dr. Emily Carter, a leading researcher in aging and metabolism.
The Future of NAD+ and Healthy Aging
The research surrounding NR and NAD+ is rapidly evolving. As our understanding of these molecules grows, we are gaining valuable insights into the mechanisms of aging and potential strategies for promoting healthy aging.
NR holds promise as a potential NAD+ booster, but more research is needed to fully understand its long-term effects and optimal use. The future may hold tailored interventions to optimize NAD+ levels for individuals based on their specific needs and genetic profiles.
The journey to unlock the secrets of cellular health and longevity is ongoing, and NR and NAD+ remain key players in this exciting field.