Problem Solving Strategies At Work
In today's dynamic business landscape, organizations face a relentless barrage of challenges, from supply chain disruptions and shifting market trends to internal conflicts and technological disruptions. The ability to effectively navigate these complexities hinges on a company's capacity for robust problem-solving, a skill that increasingly distinguishes successful entities from those that struggle to adapt and thrive. The stakes are high: poor problem-solving can lead to financial losses, damaged reputations, and a demoralized workforce, while innovative solutions can unlock new opportunities and drive sustainable growth.
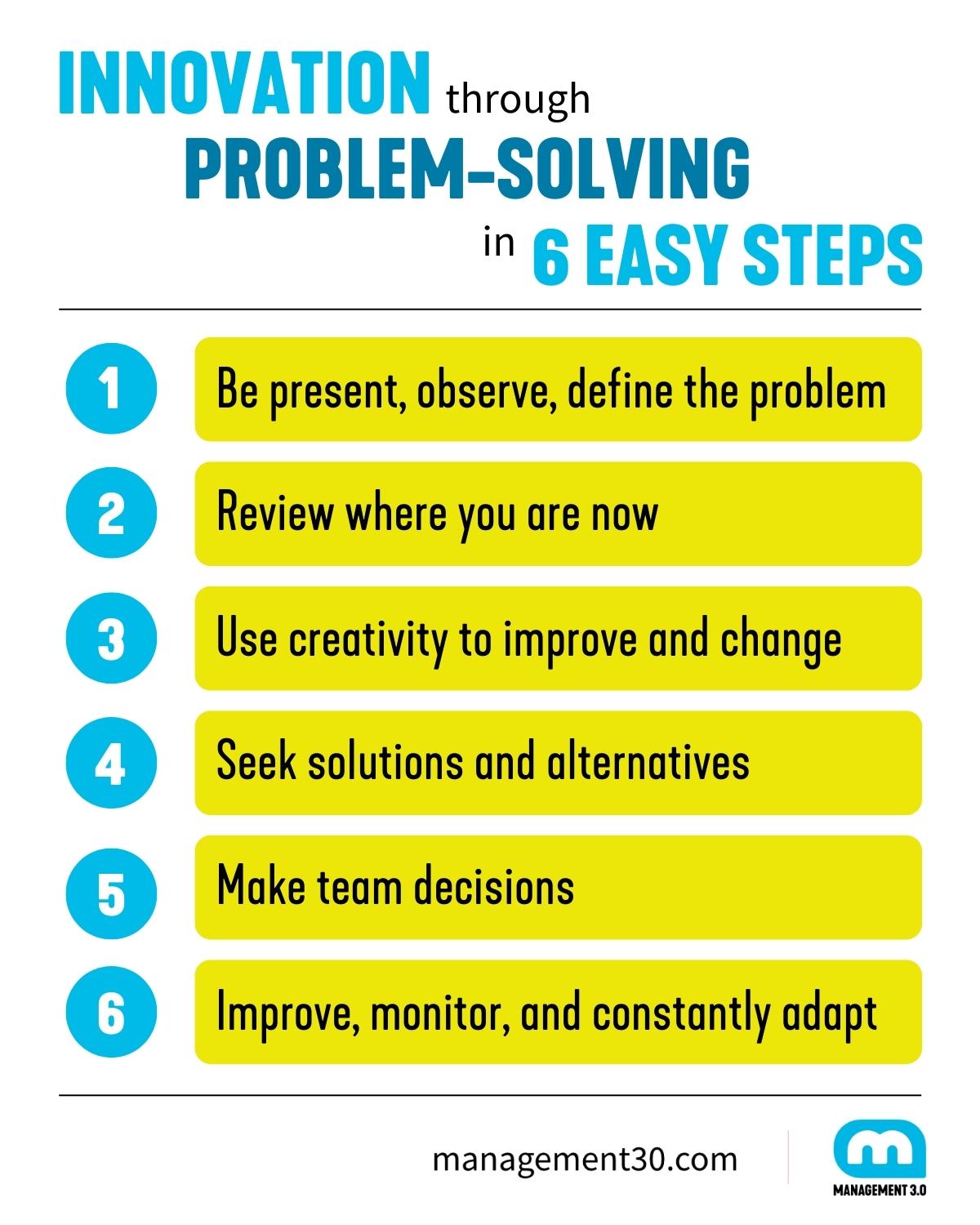
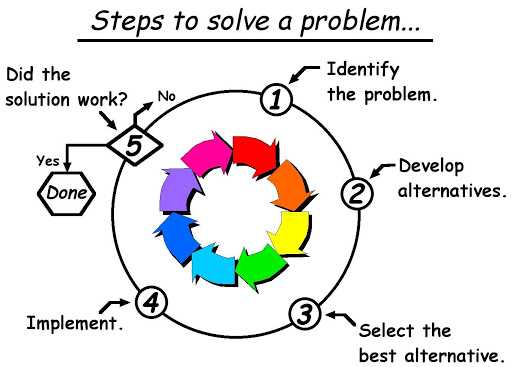
At its core, effective problem-solving in the workplace is a systematic process that involves identifying a problem, analyzing its root causes, generating potential solutions, evaluating those solutions, implementing the best option, and then monitoring its effectiveness. This process isn't a linear one; it often requires iteration and adaptation as new information emerges or the situation evolves. Crucially, fostering a culture that encourages diverse perspectives and open communication is paramount to successful problem-solving, as this allows for a wider range of ideas and a more comprehensive understanding of the issue at hand.
Understanding the Problem-Solving Toolkit
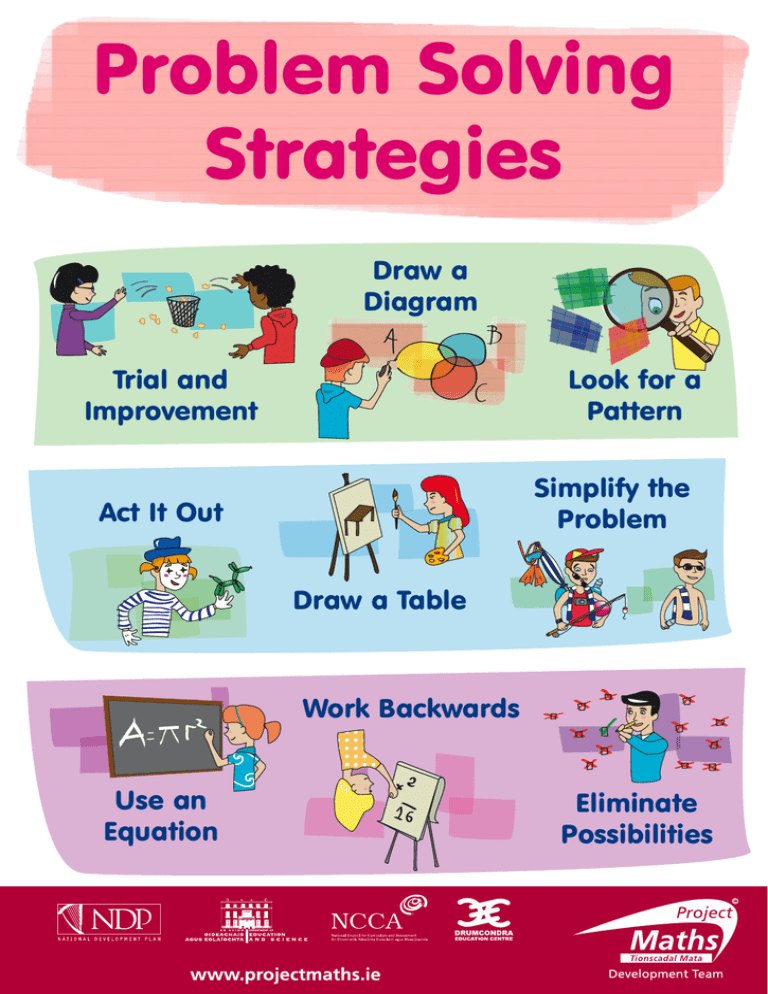
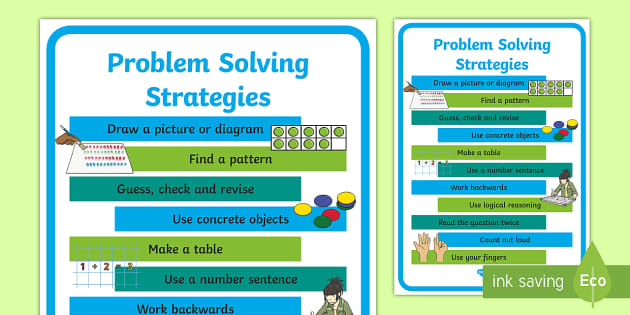
A multitude of strategies and frameworks can be employed to tackle workplace challenges. One popular approach is the "5 Whys" technique, a simple yet powerful method of repeatedly asking "why" to drill down to the fundamental cause of a problem. This iterative questioning helps uncover the layers of complexity that often obscure the true source of the issue, enabling more targeted and effective solutions.
Another valuable tool is the SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats), which provides a structured framework for evaluating both internal and external factors that influence a problem. By identifying these key elements, organizations can develop strategies that leverage their strengths, mitigate weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and defend against threats.
Design Thinking, a human-centered approach, emphasizes empathy and experimentation in the problem-solving process. It encourages teams to deeply understand the needs and perspectives of those affected by the problem, and to iteratively prototype and test solutions until they arrive at an optimal outcome.
Cultivating a Problem-Solving Culture
The most effective problem-solving strategies are only as good as the environment in which they are implemented. Companies must actively cultivate a culture that encourages employees to identify and address problems without fear of reprisal. This requires fostering open communication channels, empowering employees to take ownership, and providing them with the necessary training and resources.
According to a 2023 report by Deloitte, organizations with a strong problem-solving culture are significantly more likely to innovate and adapt to change. "Creating a safe space for employees to experiment, learn from failures, and collaborate on solutions is crucial for building a resilient and adaptable workforce," the report stated.
Google, renowned for its innovative culture, actively promotes a problem-solving mindset through its "20% time" program, which allows employees to dedicate a portion of their work hours to projects of their own choosing. This encourages exploration, experimentation, and the development of novel solutions to real-world problems.
The Role of Technology in Problem-Solving
Technology plays an increasingly important role in augmenting human problem-solving capabilities. Data analytics tools can help organizations identify patterns and trends that might otherwise go unnoticed, providing valuable insights into the root causes of problems.
Collaboration platforms facilitate seamless communication and knowledge sharing among team members, enabling them to brainstorm ideas, share information, and coordinate their efforts more effectively. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are also being leveraged to automate certain aspects of the problem-solving process, such as identifying potential risks and generating preliminary solutions.
However, it's crucial to remember that technology is merely a tool, and its effectiveness depends on how it is used. Organizations must ensure that their employees have the skills and training necessary to effectively utilize these technologies and to critically evaluate the results they produce.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Problem-Solving
As the world becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, the ability to solve problems effectively will become even more critical for organizational success. Organizations must invest in developing their employees' problem-solving skills, fostering a culture of innovation, and leveraging technology to augment human capabilities.
The future of problem-solving will likely involve a greater emphasis on collaboration, both within and between organizations. As problems become more multifaceted, it will be increasingly important to bring together diverse perspectives and expertise to develop comprehensive solutions.
By embracing a proactive and strategic approach to problem-solving, organizations can not only navigate challenges more effectively but also unlock new opportunities for growth and innovation, ensuring their long-term success in an ever-changing world.