Profit Is Determined By Subtracting The Costs Of

The fundamental principle of profit calculation – deducting costs from revenue – remains a cornerstone of business, influencing everything from individual investment decisions to global economic trends. Understanding this basic equation is crucial for businesses of all sizes, investors, and even consumers aiming to make informed financial choices.
This article delves into the significance of this calculation, exploring its components, implications, and impact on various sectors. It will also highlight the nuances of cost accounting and revenue generation that can dramatically affect the bottom line.
The Basic Equation: Revenue Minus Costs
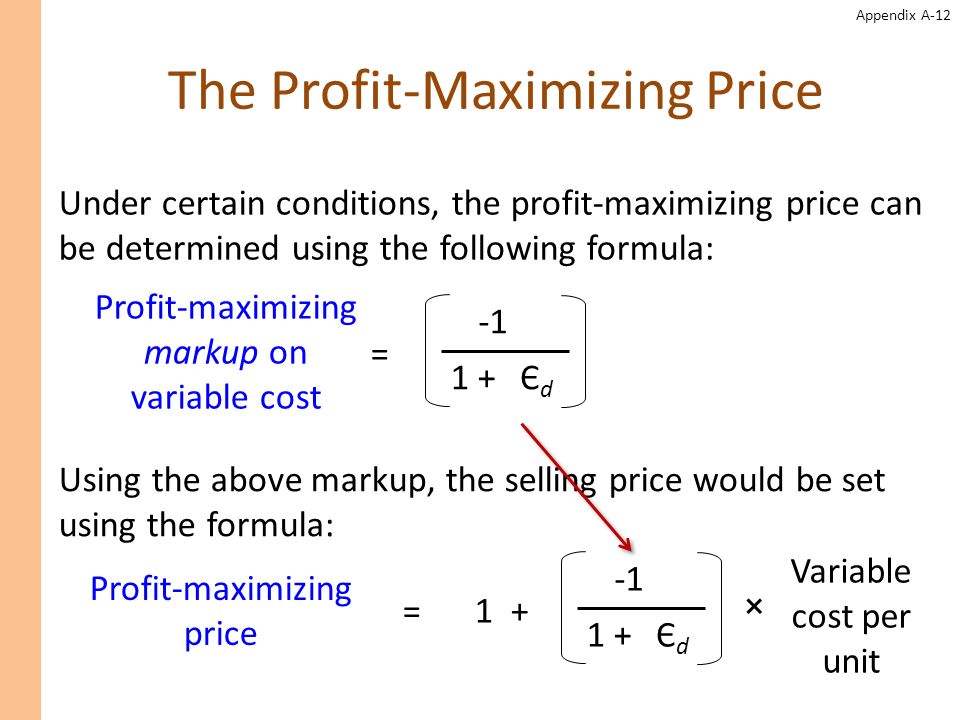
At its core, profit calculation is a straightforward subtraction: Revenue - Costs = Profit. Revenue represents the total income generated from sales of goods or services. Costs encompass all expenses incurred in producing and delivering those goods or services.
These costs can be categorized as fixed (rent, salaries) or variable (raw materials, direct labor). A clear understanding of both revenue streams and cost structures is essential for accurately determining profitability.
Significance Across Industries
The 'revenue minus costs' equation applies universally, regardless of industry. A tech startup needs to calculate the cost of development, marketing, and cloud services against revenue from software subscriptions.
A manufacturing company calculates material costs, labor costs, and overhead against the revenue from selling finished products. Even non-profit organizations must manage their expenses against incoming donations to ensure financial stability.
Nuances in Cost Accounting
While the basic equation is simple, the details of cost accounting can be complex. Different costing methods, such as activity-based costing (ABC) and standard costing, can yield varying results.
Depreciation, amortization, and inventory valuation all contribute to the overall cost picture. Accurately tracking and allocating these costs is critical for making informed decisions regarding pricing and resource allocation.
Direct vs. Indirect Costs
Distinguishing between direct and indirect costs is crucial for accurate profit assessment. Direct costs, such as raw materials and direct labor, are easily traceable to a specific product or service.
Indirect costs, such as rent and utilities, are more challenging to allocate. Assigning indirect costs fairly is essential for properly pricing products and assessing the profitability of different business segments.
Impact on Investment Decisions
Investors rely heavily on profit data when evaluating companies. Profit margins, return on equity (ROE), and earnings per share (EPS) are key metrics used to assess financial performance.
A company consistently demonstrating strong profitability is more likely to attract investment. Conversely, declining profits can signal financial distress and lead to a decrease in share price.
Influence on Economic Trends
Aggregate profit data provides valuable insights into the overall health of the economy. Increasing corporate profits can signal economic expansion and lead to increased investment and job creation.
Conversely, declining profits can indicate a recessionary trend. Governments and central banks closely monitor profit data to inform economic policies.
Human-Interest Angle: Small Business Survival
For small business owners, understanding the profit equation is not just about numbers; it's about survival. Accurately tracking revenue and expenses allows them to make informed decisions about pricing, inventory management, and hiring.
Many small businesses fail due to poor financial management, underlining the critical importance of this fundamental calculation. A local bakery, for instance, must carefully manage the cost of ingredients, labor, and rent to ensure it remains profitable and can continue serving its community.
Conclusion: A Foundational Principle
The simple equation of deducting costs from revenue is a fundamental principle that underpins all business activity. From multinational corporations to small local businesses, understanding and managing costs relative to revenue is essential for long-term sustainability.
By mastering this basic calculation, businesses can make informed decisions that drive profitability, attract investment, and contribute to a healthy economy.
/dotdash_inv-gross-profit-operating-profit-and-net-income-july-2021-01-48310634db4240ba9a78ef19456430af.jpg)









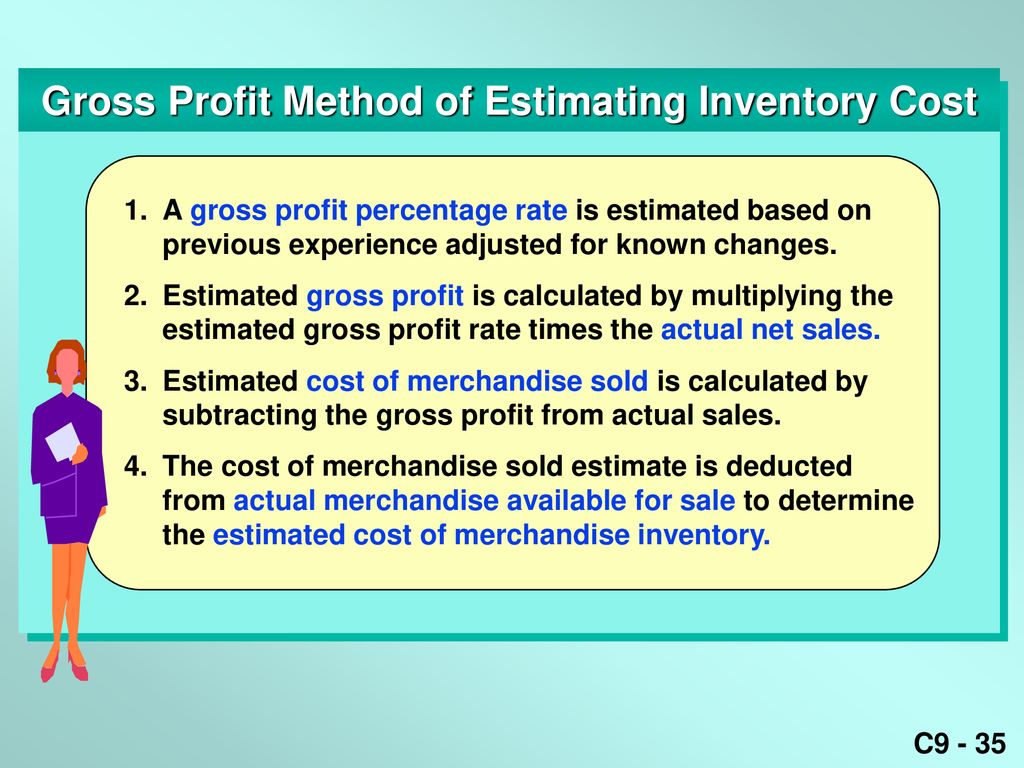


+from+the+cost+of+goods+available+for+sale+(beginning+inventory+plus+purchases+during+the+period)..jpg)