The Ability To Understand Others And Practice Empathy Is Called

In an increasingly interconnected and often polarized world, the ability to bridge divides and foster understanding is more crucial than ever. This capacity, often referred to as empathy, is now recognized as a fundamental skill for navigating personal relationships, professional collaborations, and societal challenges.
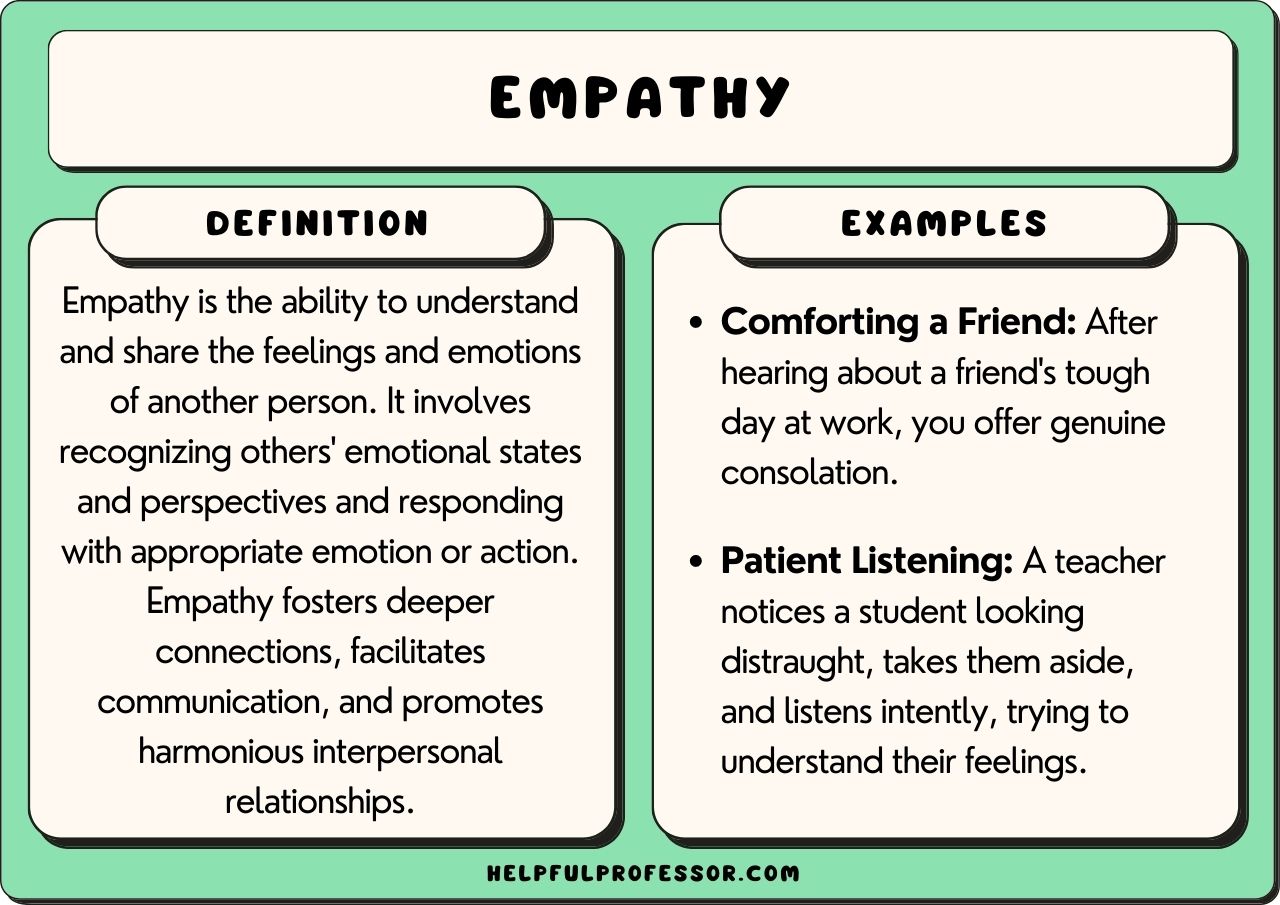
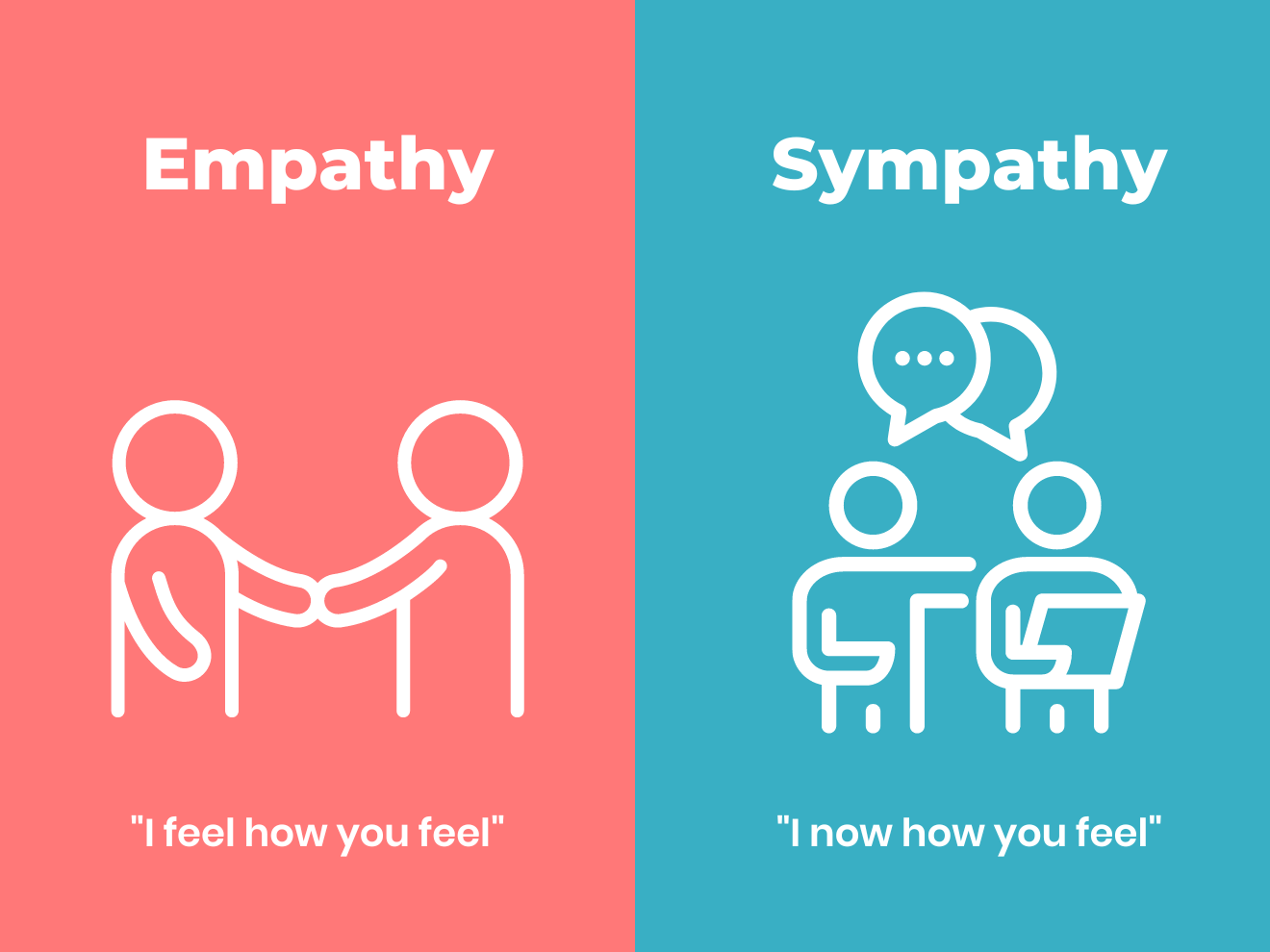
At its core, empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of another. This article will explore the significance of empathy, its core components, and the increasing emphasis being placed on its development across various sectors.
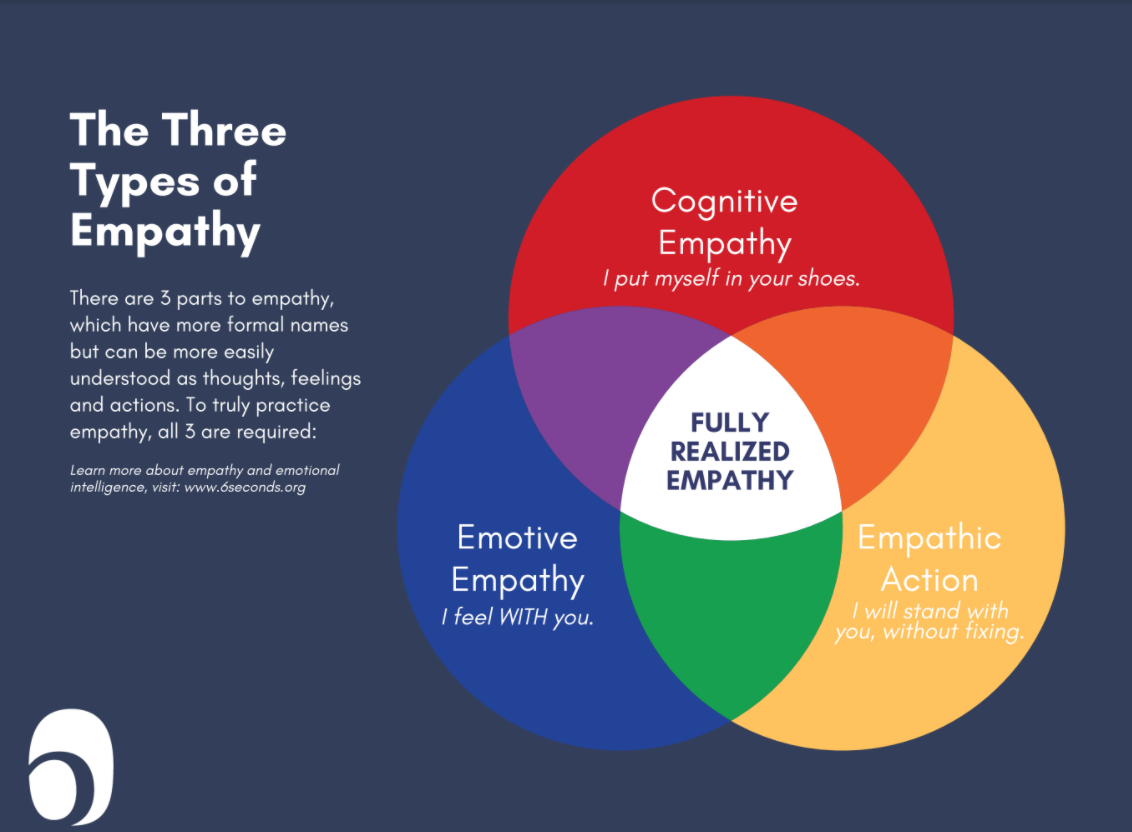
Empathy encompasses both cognitive and affective dimensions. Cognitive empathy involves understanding another person's perspective and thoughts. Affective empathy, on the other hand, refers to the ability to experience and share another's emotions.
Recent research from organizations like the Greater Good Science Center at UC Berkeley highlights the benefits of empathy. These benefits include improved communication, stronger relationships, and increased prosocial behavior.
Beyond interpersonal relationships, empathy plays a vital role in leadership and organizational success. Studies published in the Harvard Business Review suggest that empathetic leaders foster more engaged and productive teams.
Empathy in Education
Educators are increasingly recognizing the importance of incorporating empathy training into curricula. Programs designed to cultivate emotional intelligence are being implemented at various levels, from primary schools to universities.
These programs often involve activities that encourage students to consider different perspectives. Role-playing exercises and discussions about social issues are common features.
Empathy in Healthcare
The healthcare sector is also prioritizing empathy training for medical professionals. Studies have shown that empathetic doctors build stronger relationships with their patients. This leads to improved health outcomes and increased patient satisfaction.
"Empathy is not simply feeling sorry for someone," explains Dr. Sarah Chen, a leading researcher in the field. "It's about truly understanding their experience and responding with compassion."
Challenges to Empathy
Despite its recognized benefits, cultivating empathy can be challenging. Factors such as personal biases, societal prejudices, and exposure to violence can hinder the development of empathy.
Social media can also present a double-edged sword. While it can connect people across geographical boundaries, it can also contribute to echo chambers and online aggression, thereby diminishing empathy.
Cultivating Empathy
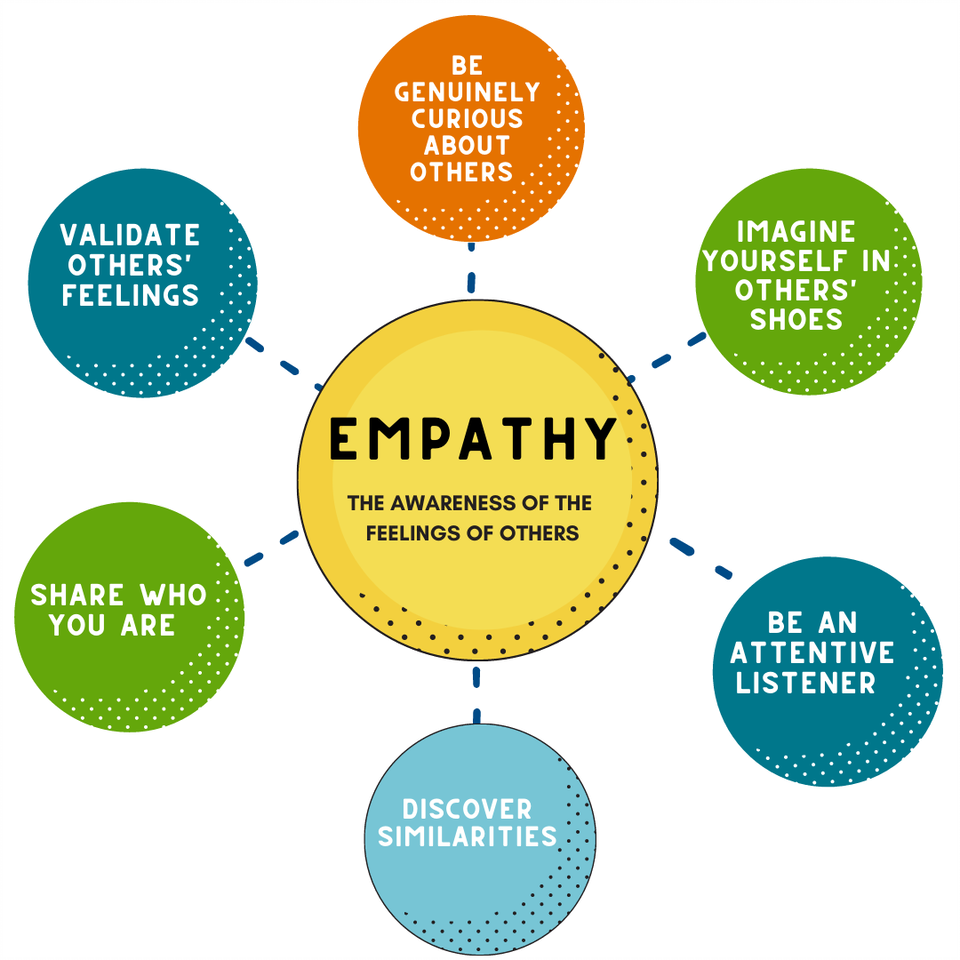
Fortunately, empathy is a skill that can be developed and strengthened. Active listening, perspective-taking exercises, and exposure to diverse cultures and viewpoints can all contribute to fostering empathy.
Individuals can also practice self-compassion, which involves treating oneself with kindness and understanding. Research suggests that self-compassion is linked to increased empathy towards others.
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) presents both opportunities and challenges for empathy. While AI can be used to analyze emotions and provide personalized feedback, it also raises concerns about the potential for dehumanization and manipulation.
Moving forward, fostering empathy will require a concerted effort from individuals, educators, policymakers, and technology developers. By prioritizing empathy, we can build more inclusive and compassionate societies.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-empathy-2795562_source_file-1102e99b63214d12ad63732278597497.png)