The Primary Source Of Fuel For The Body Is
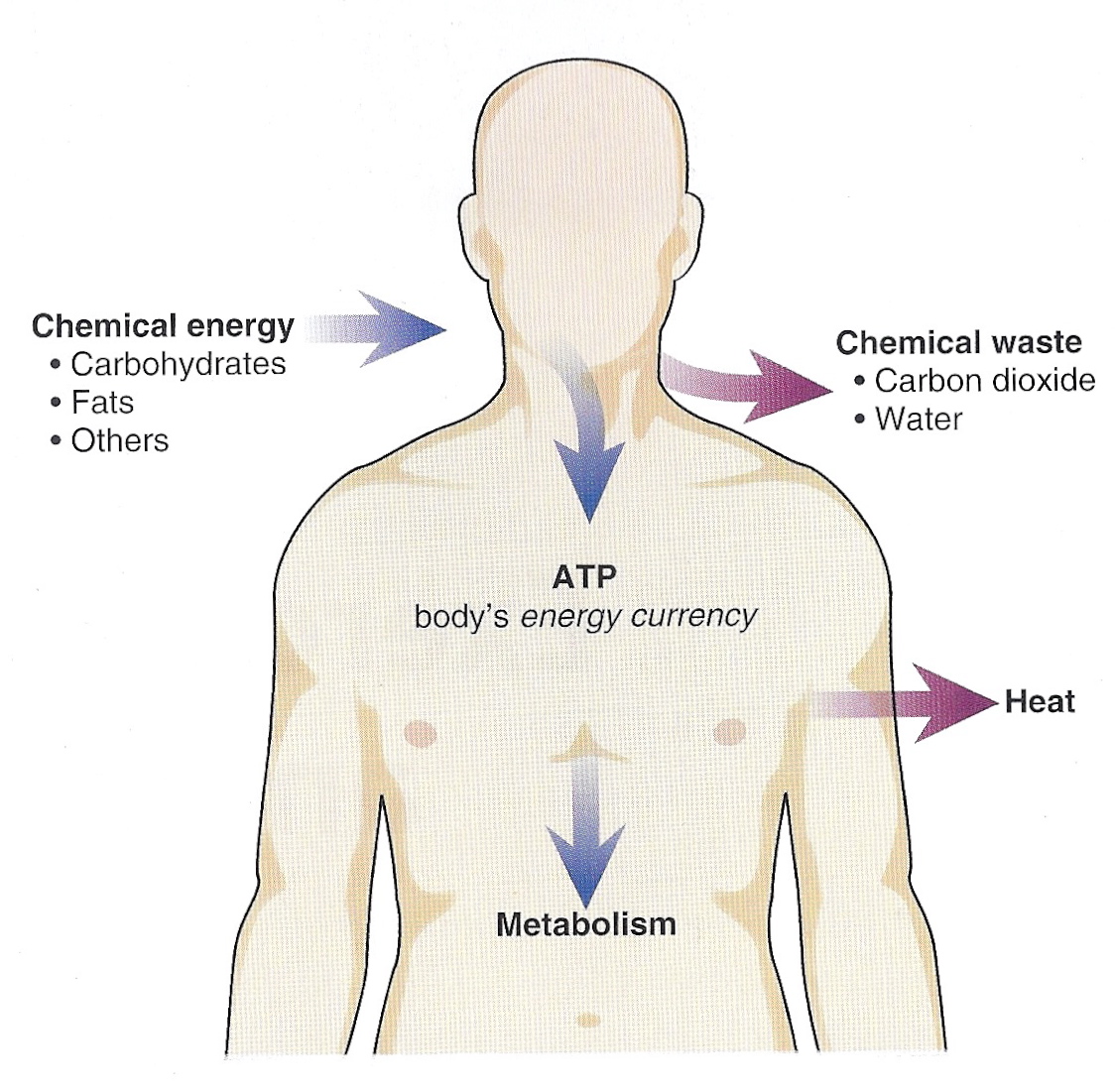
The human body, a marvel of biological engineering, operates on a complex energy system. Misunderstandings about its primary fuel source can lead to ineffective diets, diminished athletic performance, and even chronic health problems.
At the heart of this energy equation lies a fundamental question: What single substance powers our cells, fuels our muscles, and sustains life itself?
This article delves into the science behind the body’s preferred fuel, examining the biochemical pathways, expert opinions, and the implications for overall health.
The Nut Graf: Glucose, the Body's Champion Fuel
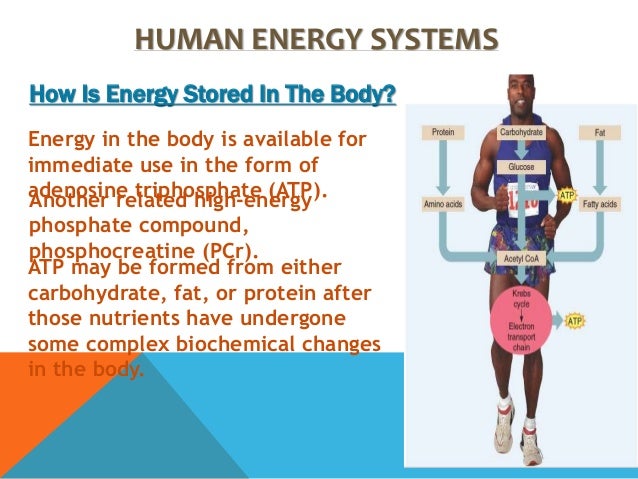
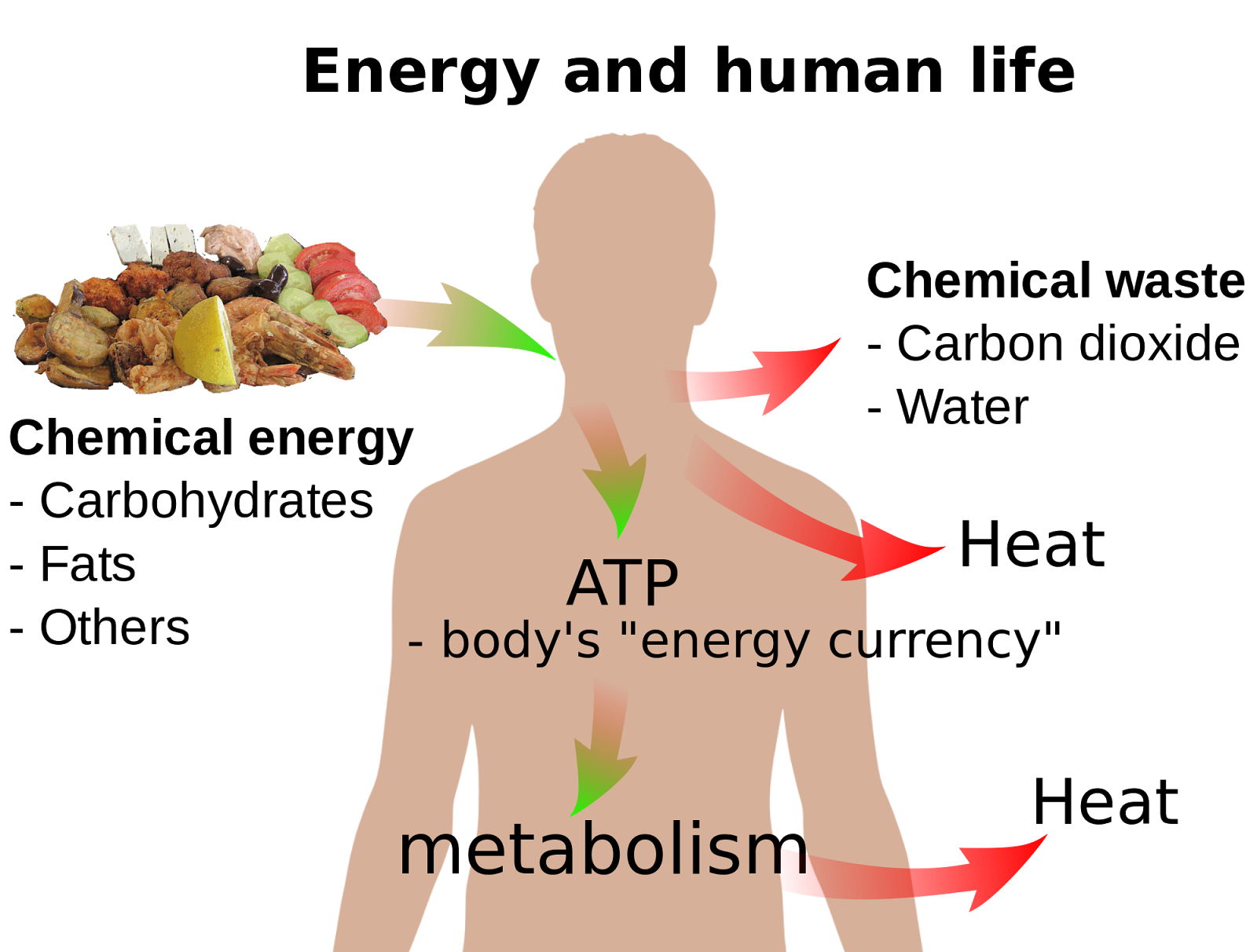
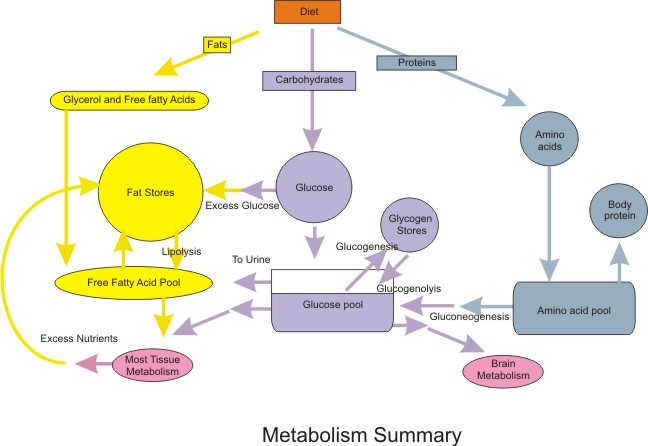
While the body can utilize fats and proteins for energy, the primary and preferred source of fuel is glucose, a simple sugar derived from carbohydrates. This isn't merely an opinion, but a scientifically backed fact supported by decades of research in biochemistry and physiology.
Glucose powers our brains, fuels muscle contractions, and keeps vital organs functioning smoothly. Understanding this fundamental principle is crucial for optimizing health and well-being.
Carbohydrates: The Source of Glucose
Carbohydrates, found in a wide variety of foods, are the primary dietary source of glucose. These include grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
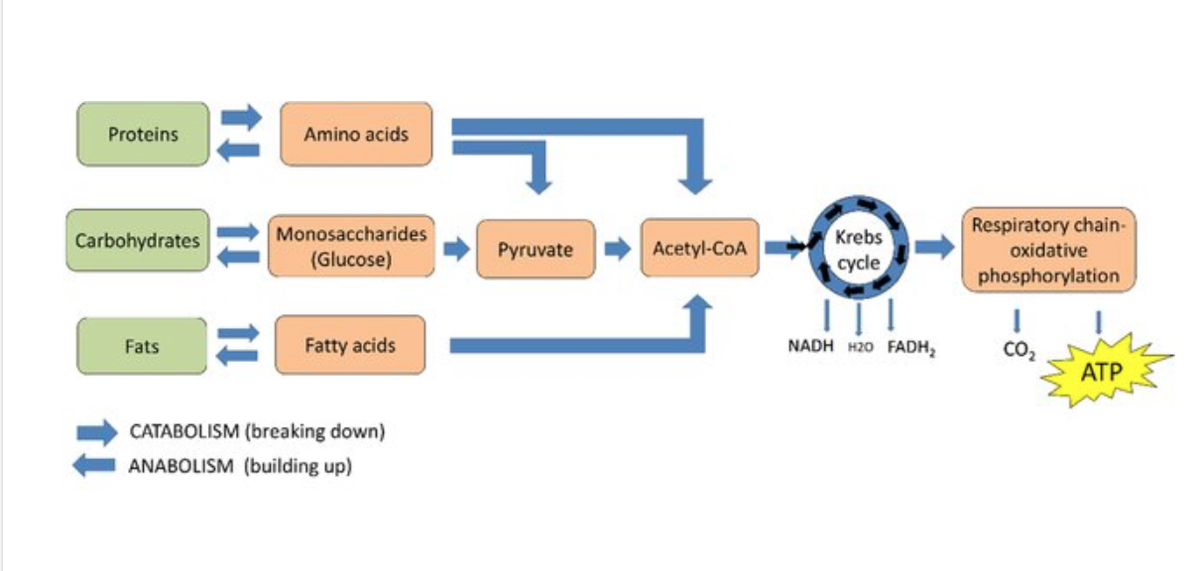
When we consume carbohydrates, our digestive system breaks them down into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. This process is crucial for supplying energy to our cells.
The Role of Insulin
The hormone insulin, produced by the pancreas, plays a vital role in regulating blood glucose levels. Insulin acts like a key, unlocking cells to allow glucose to enter and be used for energy or stored for later use.
When insulin is insufficient or the body becomes resistant to its effects, glucose levels can rise, leading to conditions like type 2 diabetes. This highlights the critical importance of carbohydrate metabolism in maintaining overall health.
The Brain's Dependence on Glucose
The brain, our body's control center, is particularly dependent on a constant supply of glucose. Unlike other tissues, the brain cannot efficiently utilize fatty acids as an energy source, except under specific conditions of prolonged starvation or a ketogenic diet.
This reliance on glucose underscores its importance for cognitive function, concentration, and overall mental performance. Low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia) can lead to impaired brain function, causing confusion, dizziness, and even loss of consciousness.
Muscles and Glucose: Fueling Movement
Muscles also rely heavily on glucose for energy, especially during physical activity. During exercise, muscles rapidly deplete their glucose stores, requiring a constant supply from the bloodstream.
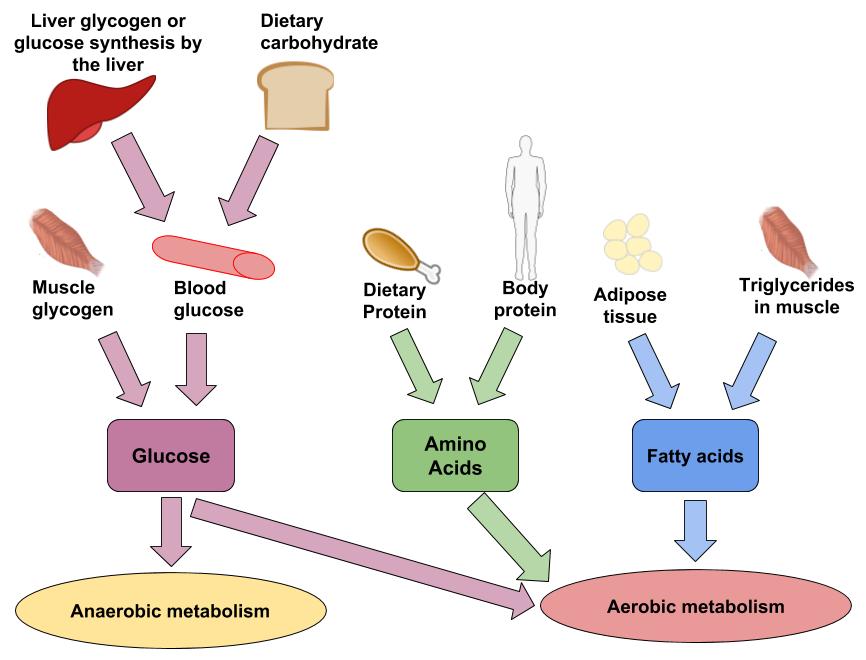
Glycogen, the stored form of glucose in muscles and the liver, serves as a readily available energy reserve. This stored glucose is crucial for sustained physical performance.
Fats and Proteins: Alternative Fuel Sources
While glucose is the body’s preferred fuel, fats and proteins can also be used for energy. However, this process is less efficient and may have metabolic consequences.
During periods of carbohydrate restriction, such as during a ketogenic diet, the body shifts to utilizing fat as a primary fuel source, producing ketones. While this can be beneficial for some, it's not the body's preferred or most efficient mode of operation.
The Role of Ketones
Ketones can serve as an alternative fuel source for the brain when glucose is scarce. However, the long-term effects and suitability of ketogenic diets for everyone remain a subject of ongoing research.
Protein can also be broken down into glucose through a process called gluconeogenesis, but this is generally reserved for situations where carbohydrate and fat intake are insufficient.
Misconceptions and Controversies
Despite the scientific consensus, misconceptions about the body's primary fuel source persist. Some popular diets advocate for restricting carbohydrates, emphasizing fat and protein intake instead.
While these diets can be effective for weight loss in the short term, they may not be optimal for long-term health and performance. A balanced approach that prioritizes complex carbohydrates, alongside healthy fats and lean protein, is generally recommended.
Dr. Emily Carter, a leading endocrinologist at the National Institutes of Health, emphasizes the importance of a balanced diet. "Carbohydrates are not the enemy," she states. "They are the body's preferred source of energy, especially for the brain and muscles."
She further adds, "The key is to choose complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, over refined sugars and processed foods."
Implications for Health and Performance
Understanding that glucose is the body’s primary fuel has significant implications for health and athletic performance. Ensuring an adequate intake of complex carbohydrates can improve energy levels, cognitive function, and physical endurance.
Athletes, in particular, need to pay close attention to their carbohydrate intake to fuel their workouts and replenish glycogen stores. Insufficient carbohydrate intake can lead to fatigue, decreased performance, and increased risk of injury.
The Future of Fuel Research
Research into the body's energy metabolism is ongoing, with scientists constantly seeking to better understand the intricacies of glucose utilization. Emerging areas of interest include the role of the gut microbiome in carbohydrate metabolism and the development of personalized nutrition strategies based on individual metabolic profiles.
Advancements in technology, such as continuous glucose monitoring, are also providing valuable insights into how our bodies respond to different foods and activities. This data can be used to optimize dietary choices and improve overall health.
Conclusion: A Balanced Approach to Fueling the Body
The evidence overwhelmingly supports the conclusion that glucose, derived from carbohydrates, is the body’s primary and preferred fuel source. While fats and proteins can be used as alternative fuels, they are not as efficient or readily available as glucose.
A balanced diet that includes adequate amounts of complex carbohydrates, alongside healthy fats and lean protein, is essential for optimal health and performance. By understanding the body's fundamental energy needs, we can make informed dietary choices that support our physical and mental well-being.
Ignoring this fundamental principle can lead to suboptimal health outcomes and prevent us from reaching our full potential. Fueling our bodies correctly is an investment in our long-term health and vitality.