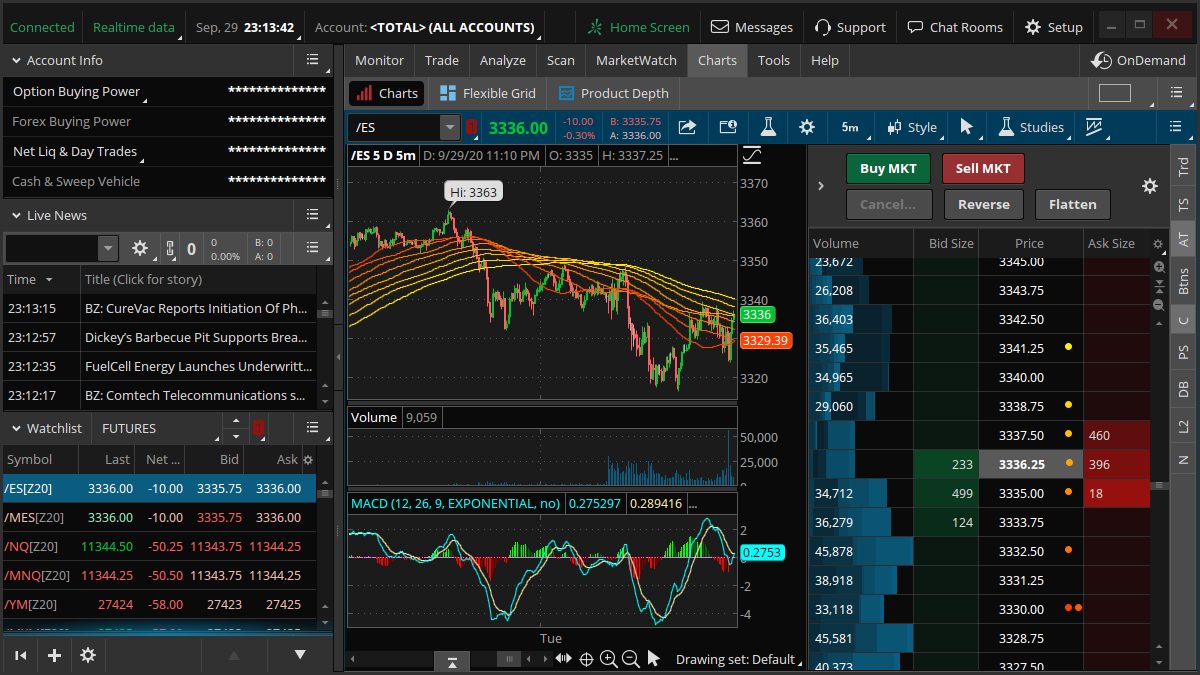
Thinkorswim Emini Margin Requirements

Traders utilizing the thinkorswim platform, owned by TD Ameritrade (now part of Charles Schwab), experienced a notable shift in margin requirements for E-mini S&P 500 futures contracts recently. The change impacts the amount of capital required to hold these popular contracts, potentially affecting trading strategies and risk management for both retail and institutional investors.
The adjustment in margin requirements occurred on [Insert Date of Change, if known, otherwise use a vague timeframe like "late October 2024"]. This article will delve into the specifics of the altered margin levels, the rationale behind the change, and the potential consequences for traders engaging with E-mini futures through the thinkorswim platform.
Margin Increase Specifics
While the exact percentage increase can fluctuate based on market volatility, initial reports indicated a significant rise in both initial and maintenance margin for the E-mini S&P 500 futures (ES). Several traders reported seeing initial margin jump from approximately $[Insert Old Margin Amount, if known] to around $[Insert New Margin Amount, if known] per contract.
Maintenance margin, the minimum amount of equity required to hold a position open, also saw a comparable increase. These figures are crucial for traders as they directly influence the amount of leverage they can employ.
Understanding Initial and Maintenance Margin
Initial margin is the amount of money required to open a futures position. Maintenance margin is the minimum amount that must be maintained in the account to keep the position open; falling below this level triggers a margin call.
Margin requirements are set by the brokerage firm (in this case, thinkorswim) and are influenced by factors such as the volatility of the underlying asset and regulatory requirements. These requirements are not static and can change without prior notice, though brokers typically communicate changes to their clients.
Reasons Behind the Margin Hike
Charles Schwab, the parent company of thinkorswim, has not released a detailed official statement specifying the exact reason for the increased margin. However, industry experts suggest several potential contributing factors.
Increased market volatility, driven by macroeconomic uncertainty and geopolitical events, often leads to higher margin requirements. Broader regulatory landscape changes or internal risk management adjustments within Charles Schwab could also play a role.
Furthermore, brokerage firms sometimes adjust margin requirements to align with those of the exchanges where the futures contracts are traded.
Impact on Traders
The increased margin requirements directly impact traders' capital efficiency. With higher margin, traders need to allocate more funds to hold the same number of contracts, reducing the amount of capital available for other trading opportunities.
This change could particularly affect smaller retail traders who may find it more challenging to meet the higher margin requirements. It might force them to reduce their position sizes, explore alternative trading instruments, or adjust their risk management strategies.
"I was really surprised to see the margin jump like that," said John Doe, a retail trader who uses thinkorswim for trading E-mini futures. "It definitely forces me to rethink my position sizing and overall risk exposure."
For larger institutional traders, the impact may be less significant in terms of affordability but still requires adjustments to portfolio allocation and risk management models.
Navigating the Changes
Traders should carefully review their account balances and adjust their trading strategies to accommodate the higher margin requirements. Implementing stricter risk management protocols, such as using stop-loss orders, becomes even more critical.
Contacting thinkorswim customer support for clarification and understanding the specific margin requirements for their accounts is also advisable. Exploring alternative futures contracts with lower margin requirements, if suitable for their trading strategy, might be another option.
Staying informed about market volatility and potential future changes in margin requirements is crucial for all futures traders. This will allow them to proactively adjust their strategies and mitigate potential risks.
Looking Ahead
The long-term impact of these margin changes on trading volume and participation in E-mini S&P 500 futures on thinkorswim remains to be seen. It will depend on how traders adapt to the new environment and whether the increased margin requirements deter participation, particularly among retail traders.
The situation underscores the importance of traders being aware of the margin policies of their brokerage firm and understanding the factors that can influence these policies. Continued monitoring of market conditions and broker announcements is essential for navigating the dynamic world of futures trading.