This Technology Could Be Worth $80 Trillion By 2030.

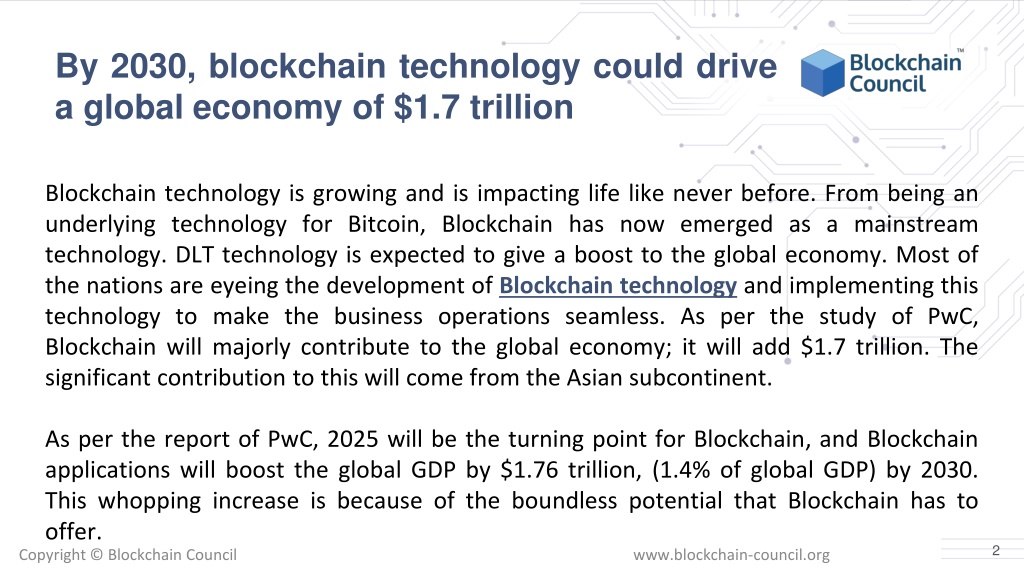
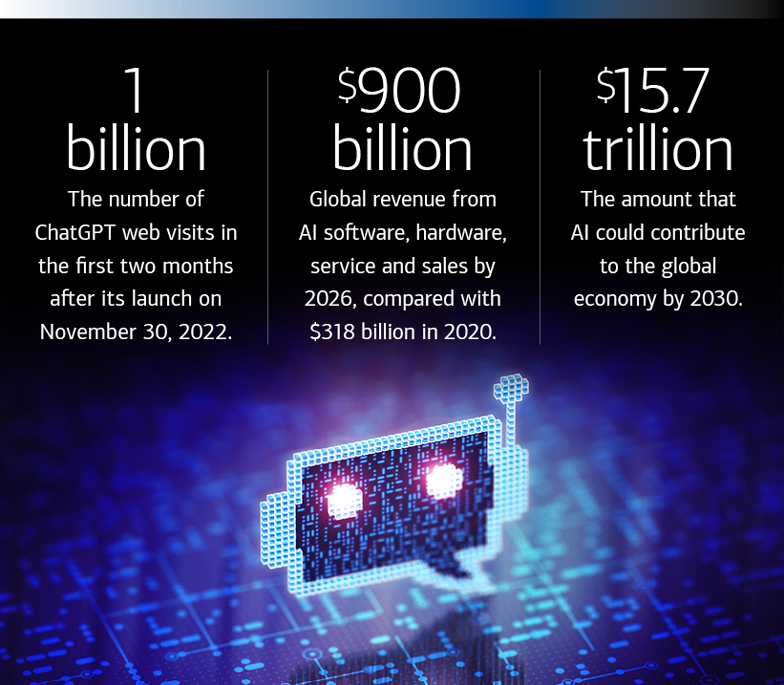
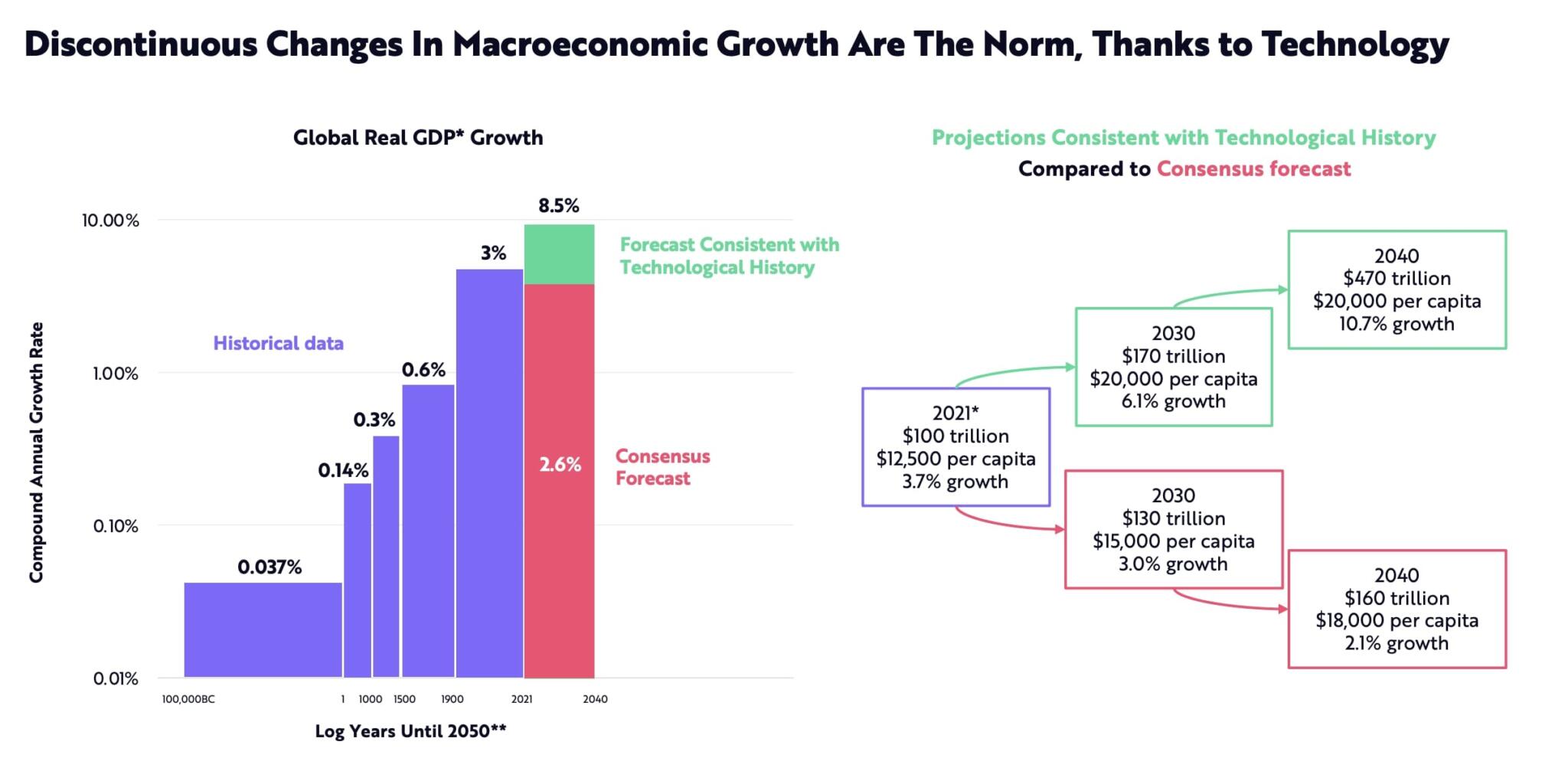
The convergence of physical, digital, and biological spheres, often dubbed the "bioeconomy," is poised for unprecedented growth, with some analysts predicting a market valuation of $80 trillion by 2030. This projection has ignited discussions across industries, governments, and research institutions, prompting a reassessment of investment strategies and policy frameworks. The potential impact on global economies and individual lives could be transformative, though realizing this potential requires careful navigation of ethical considerations and technological challenges.
This figure, while substantial, represents the anticipated value generated by products, services, and research stemming from biotechnological advancements. It encompasses diverse sectors, including agriculture, healthcare, manufacturing, and energy. The forecasted growth underscores the increasing reliance on biological processes and materials to address global challenges like food security, disease, and climate change.
Defining the Bioeconomy
The bioeconomy is not a singular industry, but rather a multifaceted ecosystem. It leverages biological resources and processes to create sustainable solutions across multiple sectors. OECD (The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) defines bioeconomy as comprising those parts of the economy that use renewable biological resources from land and sea – such as crops, forests, animals and micro-organisms – to produce food, materials and energy.
This includes the production of biofuels from algae, the development of gene therapies for inherited diseases, and the creation of biodegradable plastics from plant-based materials. Advances in biotechnology, coupled with advancements in data analytics and artificial intelligence, are accelerating the bioeconomy's expansion.
Key Drivers of Growth
Several factors are fueling the projected surge in the bioeconomy's value. A growing global population is driving the demand for sustainable food production methods and novel disease treatments. Concerns about climate change and resource depletion are pushing industries to adopt bio-based alternatives to fossil fuels and traditional manufacturing processes.
Increased investment in research and development is fostering innovation and accelerating the development of new bio-based products and technologies. Furthermore, supportive government policies and regulatory frameworks are creating a more favorable environment for bioeconomy companies to thrive.
Sector-Specific Opportunities
The $80 trillion valuation is distributed across various sectors within the bioeconomy. In agriculture, developments like genetically modified crops and precision farming techniques are increasing crop yields and reducing reliance on pesticides.
Healthcare is witnessing breakthroughs in personalized medicine, gene editing, and the development of new diagnostic tools and therapies. The manufacturing sector is embracing bio-based materials and processes to create sustainable packaging, textiles, and construction materials.
The energy sector is exploring biofuels, biogas, and other renewable energy sources derived from biomass. These trends point to a future where biological processes play a central role in addressing critical societal needs.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
The rapid advancement of the bioeconomy also raises significant ethical and regulatory concerns. The development and deployment of new technologies, such as gene editing and synthetic biology, require careful consideration of potential risks to human health and the environment.
Issues related to intellectual property, data privacy, and equitable access to bio-based products and services must also be addressed. Governments and international organizations are working to develop regulatory frameworks that promote innovation while safeguarding public safety and environmental sustainability.
Challenges and Obstacles
Despite its immense potential, the bioeconomy faces several challenges that could hinder its growth. The high cost of research and development, the lack of skilled workforce, and the complexity of regulatory approval processes are significant obstacles.
Public acceptance of bio-based products and technologies is also crucial. Overcoming misinformation and addressing concerns about safety and environmental impact will be essential for gaining public trust. Investing in education and public outreach is important.
The Role of Investment
Realizing the $80 trillion potential will require substantial investment from both public and private sectors. Governments need to provide funding for research and development, infrastructure development, and workforce training.
Venture capitalists and private equity firms play a critical role in supporting innovative bioeconomy companies. Attracting investment requires clear policy frameworks, stable regulatory environments, and a supportive ecosystem for entrepreneurship.
A Human Perspective
Beyond the economic figures, the bioeconomy holds the promise of improving lives in tangible ways. Imagine a future where diseases are cured with gene therapies, food is produced sustainably, and pollution is a thing of the past.
This potential is driving researchers, entrepreneurs, and policymakers to work together to unlock the bioeconomy's full potential. While the journey will undoubtedly be complex and challenging, the potential rewards are too significant to ignore.
Conclusion
The projected $80 trillion valuation of the bioeconomy by 2030 is not merely an economic forecast, but a call to action. It underscores the urgent need to embrace innovation, address ethical concerns, and invest in the future of biological technologies. Whether this ambitious projection is fully realized remains to be seen, but the trajectory is clear: the bioeconomy is poised to reshape our world in profound ways, offering solutions to some of humanity's most pressing challenges. Its success hinges on a collective effort to foster innovation, ensure responsible development, and unlock the vast potential of biology.