Veeam Reverse Incremental Vs Incremental
Data backup and recovery are cornerstones of modern IT infrastructure. Organizations face a crucial decision when choosing backup strategies: incremental versus reverse incremental. Understanding the nuances of each approach is paramount for ensuring data integrity and efficient recovery.
The debate between incremental and reverse incremental backups revolves around how data changes are captured and stored, influencing recovery time objectives (RTOs) and storage requirements. Both strategies aim to optimize backup speed and storage space compared to full backups. But they differ significantly in their implementation and impact.
Incremental Backups: Building on the Foundation
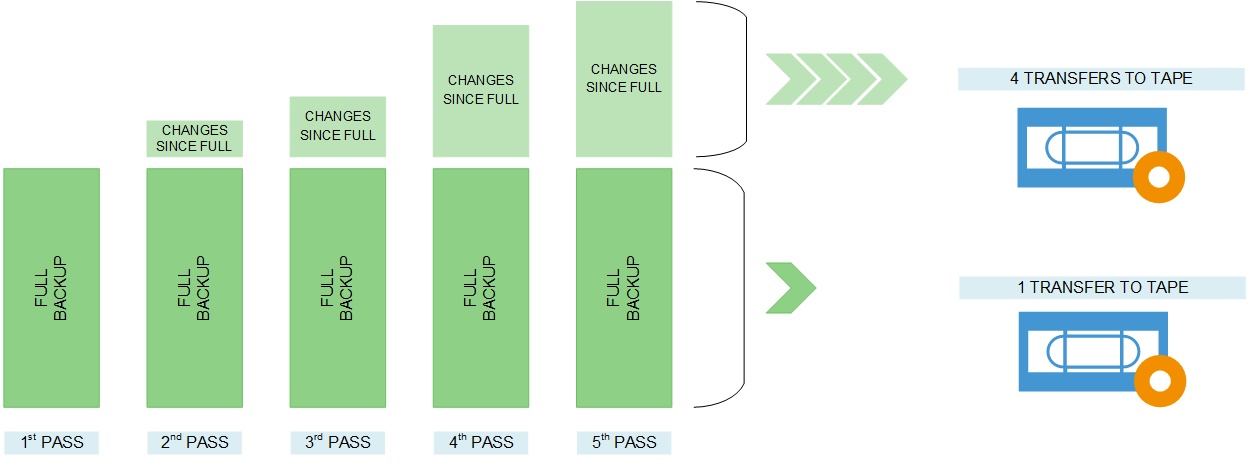
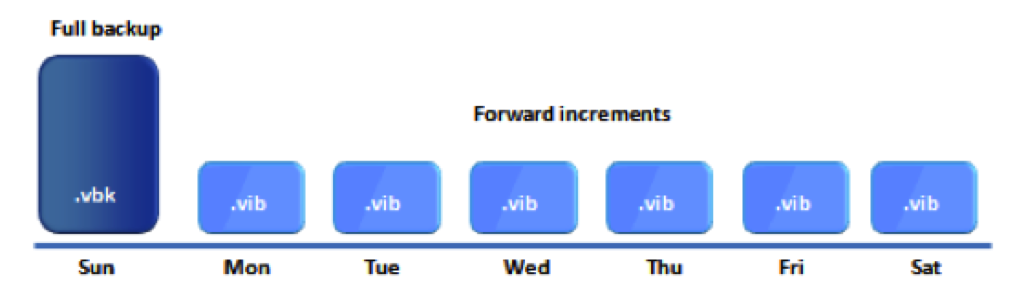
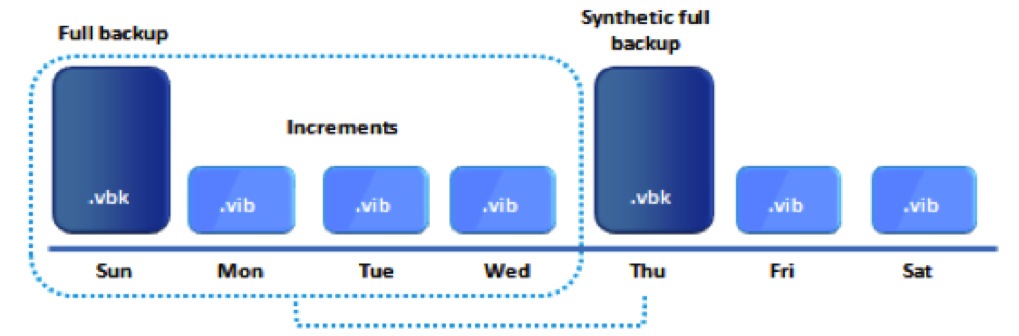
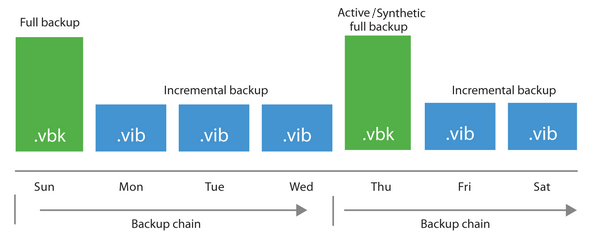
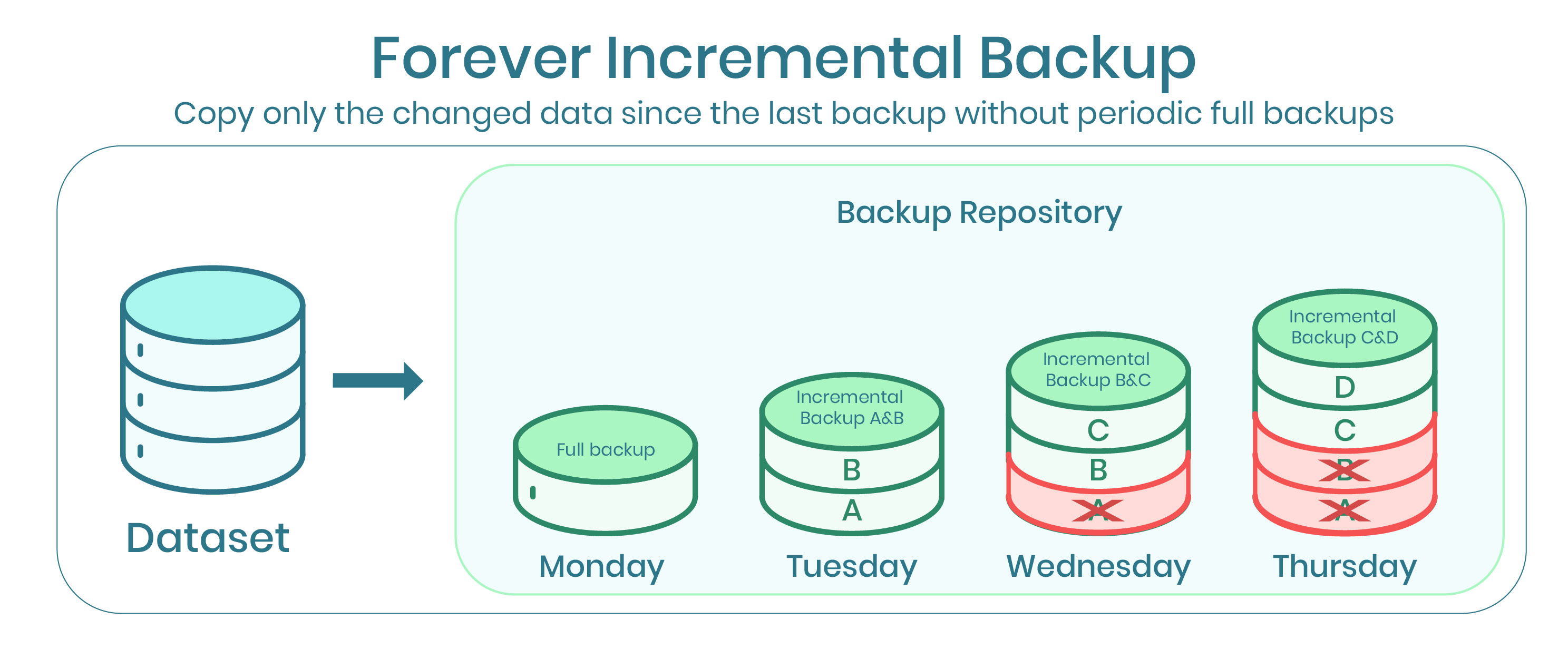
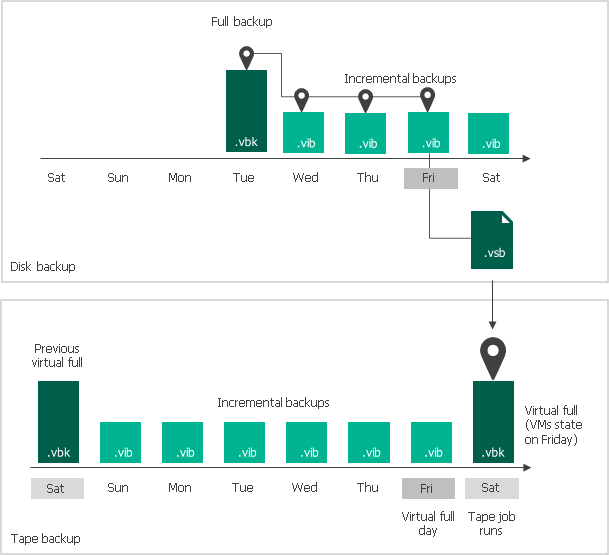
Incremental backups capture only the data that has changed since the last backup, regardless of whether it was a full or another incremental backup. This method significantly reduces the backup window and storage consumption for each backup job after the initial full backup.
The initial full backup serves as the foundation, and subsequent incremental backups record the changes made since the previous backup. To restore data to a specific point in time, the entire chain of backups – the full backup plus all relevant incrementals – must be processed.
The Challenge of Restore Speed
The primary disadvantage of incremental backups is the potential for longer restore times. Because each incremental backup depends on the previous one, a failure in any backup within the chain can compromise the entire restore process.
Additionally, retrieving data requires sequentially reading through multiple backup files, adding to the overall restoration time. This can become a bottleneck in scenarios demanding rapid recovery.
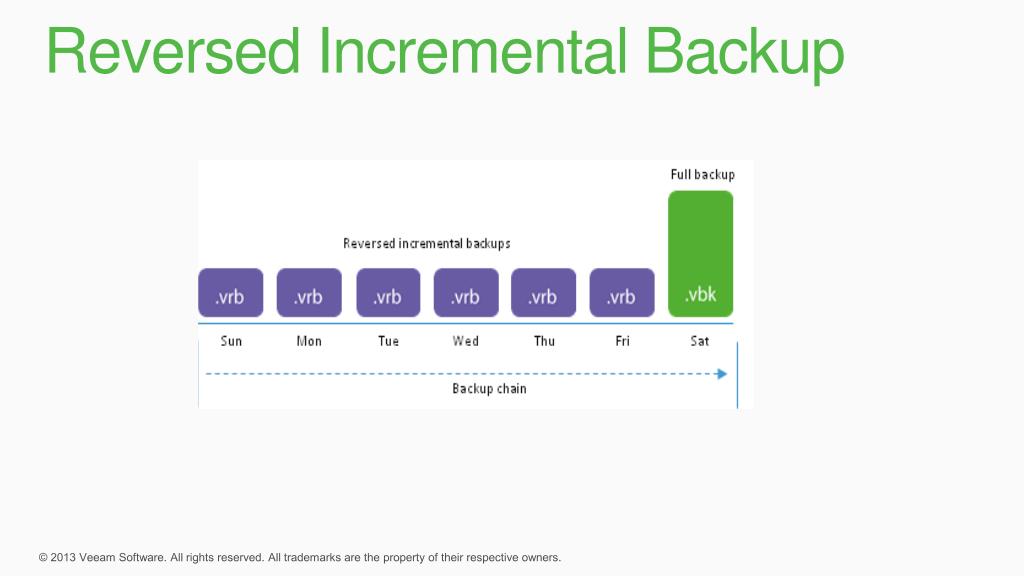
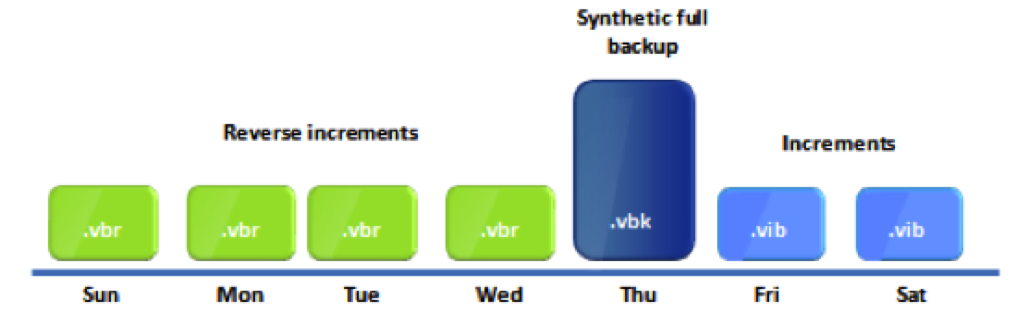
Reverse Incremental Backups: A Modern Approach
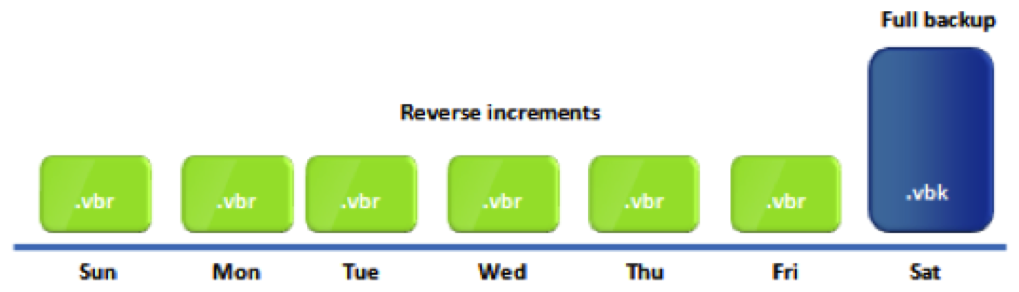
Reverse incremental backups also capture data changes, but they work by injecting the changes *into* the initial full backup. Each incremental backup is merged with the existing full backup, creating a perpetually updated full backup image.
This approach eliminates the dependency on a chain of incremental backups. The latest version of the data is always readily available in the consolidated full backup file.
Faster Restores, Simplified Management
The most significant benefit of reverse incremental backups is the rapid restore time. Since the full backup image is always up-to-date, recovering data only involves accessing a single file, significantly reducing RTOs.
Furthermore, managing backups becomes simpler because there’s no complex chain of dependencies to maintain. This reduces the risk of restore failures due to corrupted or missing incremental backups.
Veeam's Implementation and Impact
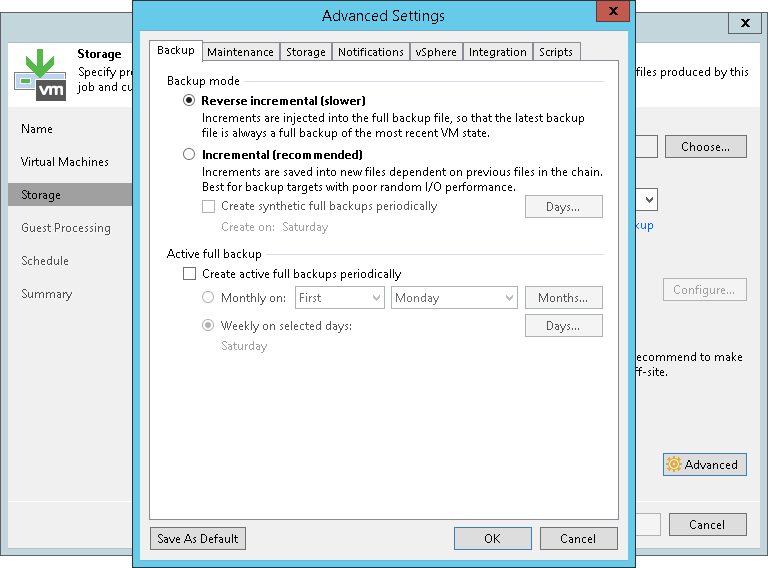
Veeam, a prominent provider of backup, recovery, and data management solutions, incorporates both incremental and reverse incremental backup methods into its platform. Veeam's solutions are widely used across different sectors, which makes the choice of a suitable backup strategy significantly important.
Veeam's users can select the backup method that best aligns with their specific requirements and infrastructure. Organizations can optimize their backup strategy based on factors such as RTO requirements, storage capacity, and network bandwidth.
According to Veeam documentation, reverse incremental backups are often recommended for environments where fast restores are critical. For example, in scenarios involving critical production systems or demanding service level agreements (SLAs).
Choosing the Right Approach
The optimal backup strategy ultimately depends on the specific needs of the organization. Consider the impact of downtime, the available resources, and the complexity of the IT infrastructure when making a decision.
While incremental backups can be cost-effective in terms of storage, the potential for longer restore times should be carefully considered. Reverse incremental backups offer faster restores and simplified management, but they may require more processing power during the backup process.
Organizations should evaluate their specific requirements and conduct thorough testing to determine the backup method that best meets their needs. Regular monitoring and maintenance are also crucial for ensuring the effectiveness of any backup strategy.