What Do Glasses Do As A Result Of Condensation

Vision across the globe is being hampered. Condensation on eyeglasses renders them temporarily useless, impacting daily life and posing safety risks.
This widespread phenomenon, impacting millions who rely on corrective lenses, demands immediate attention. Understanding the mechanics behind this moisture buildup is crucial for mitigating its effects and ensuring clear vision in fluctuating environmental conditions.
The Science of Spectacle Steam: Unveiling the Condensation Culprit
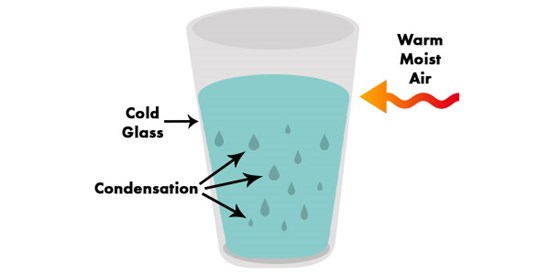
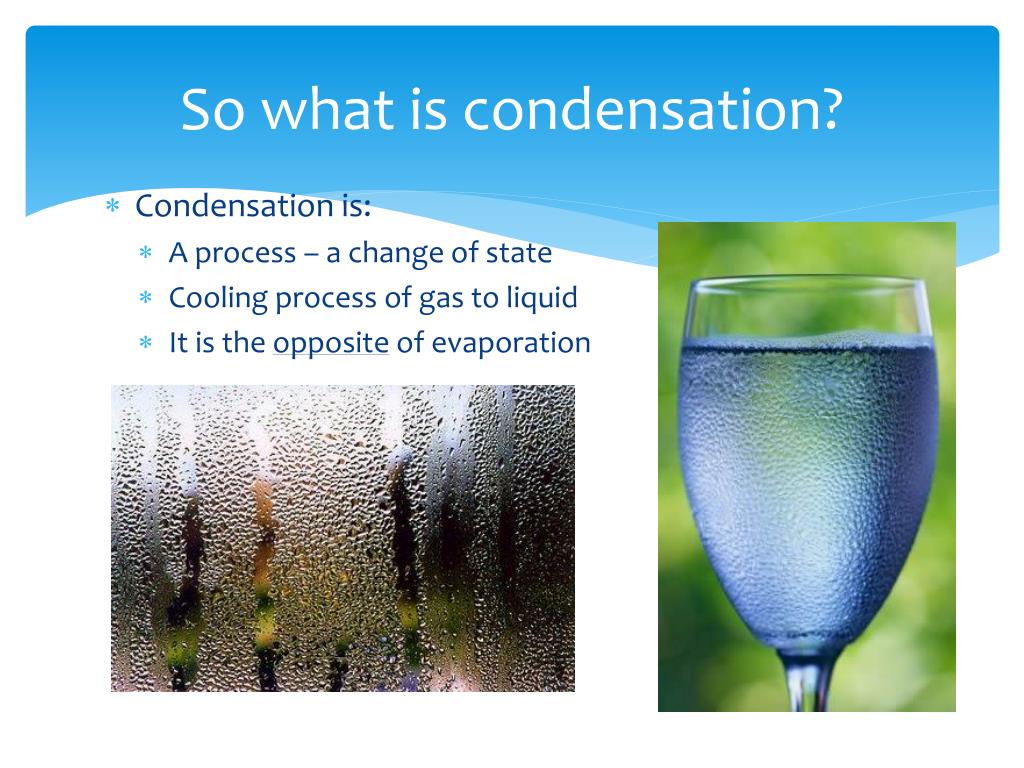
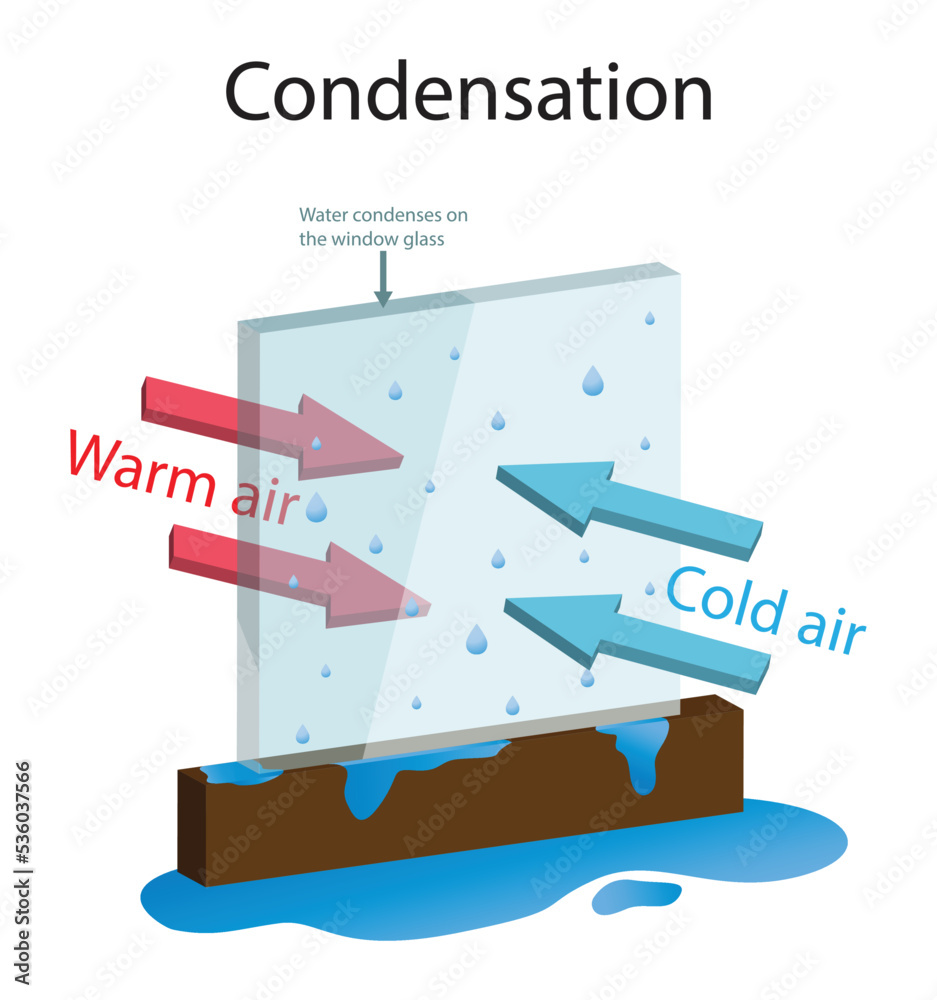
Condensation forms when warm, moist air encounters a cooler surface. Specifically, the water vapor in the air comes into contact with the colder lenses of the glasses. The air cools, causing the water vapor to change into liquid water, forming a film of tiny droplets.
This process is accelerated by significant temperature differences. Think stepping from a cold outdoors into a warm building, or exercising indoors with air conditioning.
The Impact on Daily Life: More Than Just an Inconvenience
The consequences of foggy glasses extend beyond mere annoyance. Drivers, for example, experience reduced visibility, posing a serious safety hazard. Similarly, factory workers operating machinery may face increased risks due to impaired vision.
Even simple tasks like reading or navigating stairs become challenging. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has no specific reports, but anecdotal evidence suggests vision impairment is a common safety issue.
Furthermore, in medical settings, doctors and nurses find their glasses fogging up while wearing masks. According to a study published in the Journal of Hospital Infection, this can hinder their ability to provide timely and accurate care.
Combating Condensation: Current Solutions and Their Limitations
Several solutions aim to prevent or quickly eliminate condensation. Anti-fog sprays and wipes are readily available, creating a temporary barrier between the lens surface and water vapor.
These products work by reducing the surface tension of water. This causes water to spread out in a thin, transparent layer instead of forming droplets. However, their effectiveness is often limited, requiring frequent reapplication.
Another approach involves using cloths made from special microfibers. These cloths are designed to absorb moisture quickly without leaving streaks. While helpful for quick fixes, they don't prevent condensation from forming.
The Quest for Permanent Solutions: Exploring Advanced Technologies
Researchers are exploring more permanent solutions for preventing lens fogging. Hydrophilic coatings are being developed to attract and spread water evenly across the lens surface.
Other technologies include electrically heated lenses. These lenses maintain a consistent temperature above the dew point. However, these advancements are typically more expensive and less accessible to the average consumer.
Current lens materials such as polycarbonate and Trivex have no specific feature that naturally resists condensation. The application of a special coating is a must.
Real-World Examples: Situations Where Condensation Poses the Greatest Risk
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the problem of fogging glasses. Mask-wearing exacerbated the issue, as exhaled breath was redirected upwards toward the lenses. This creates a concentrated stream of warm, moist air.
In sports, athletes often encounter condensation while participating in activities in humid or cold conditions. Skiers, for example, struggle with fogging goggles, impacting their visibility and performance.
Chefs and food service workers are constantly exposed to steam and temperature fluctuations. This creates a perpetual challenge in maintaining clear vision.
Looking Ahead: Research, Innovation, and Public Awareness
Ongoing research is focused on developing more effective and durable anti-fog coatings. Innovations in nanotechnology hold promise for creating lenses that are inherently resistant to condensation.
Raising public awareness about the causes and solutions for fogging glasses is also crucial. Simple strategies, like adjusting mask fit or using readily available anti-fog products, can significantly improve the daily lives of glasses wearers.
Further investigation is needed to quantify the impact of fogging glasses on accidents and injuries. Public health organizations and safety regulators may need to develop guidelines.