What Does Gmo Strain Stand For

Confusion and misinformation surrounding GMO terminology continue to plague public discourse. The term "GMO strain" itself is largely inaccurate, highlighting a critical misunderstanding of genetic modification and its application.
Understanding the correct terminology and the science behind genetic modification is paramount. This article aims to clarify what the term "GMO strain" implies, why it's often misused, and the accurate language to describe genetically modified organisms.
What Does GMO Really Mean?
GMO stands for Genetically Modified Organism. It refers to an organism whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques. These techniques involve introducing specific genes into an organism to confer desired traits.
These traits can include resistance to pests, tolerance to herbicides, or enhanced nutritional content. The key point is that GMO refers to the organism itself, not necessarily a specific "strain."
The Misuse of "GMO Strain"
The phrase "GMO strain" is often used incorrectly. The term "strain" typically refers to a specific genetic variant within a species that possesses unique characteristics. When applied to GMOs, it creates a misconception.
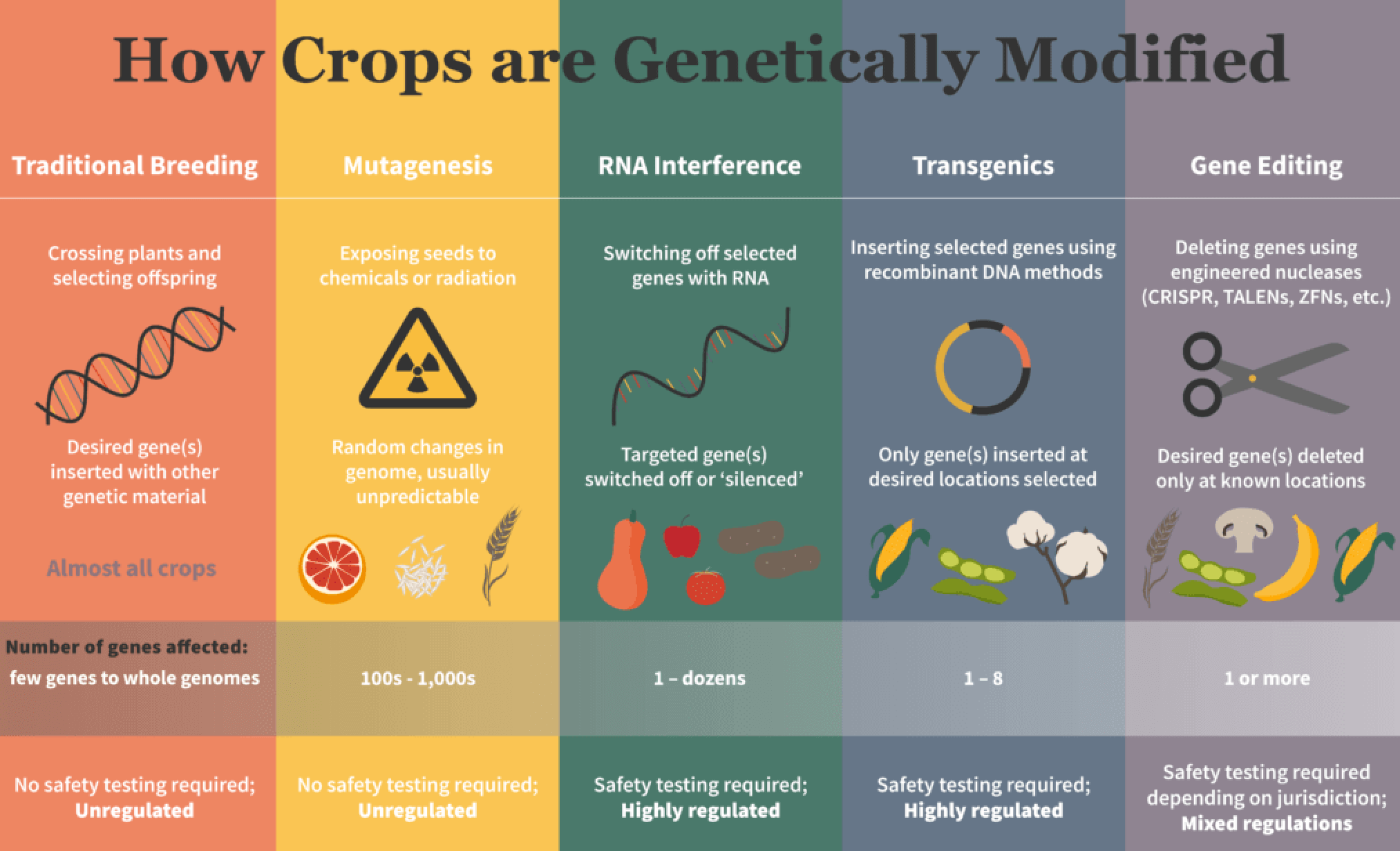
Genetic modification usually involves a single or a few specific gene insertions or modifications. It doesn't necessarily create a new "strain" in the traditional biological sense. Instead, it creates a modified version of an existing organism.
Accurate Terminology: Genetically Modified Varieties or Lines
Instead of "GMO strain," more accurate terms include "genetically modified variety" or "genetically modified line." These terms better reflect the nature of genetic modification. They acknowledge that the organism is a variation of an existing species.
For example, instead of saying "a GMO strain of corn," it's more precise to say "a genetically modified variety of corn" or "a genetically modified line of corn." This conveys that the corn has been altered but remains within the corn species.
Examples of Genetically Modified Crops
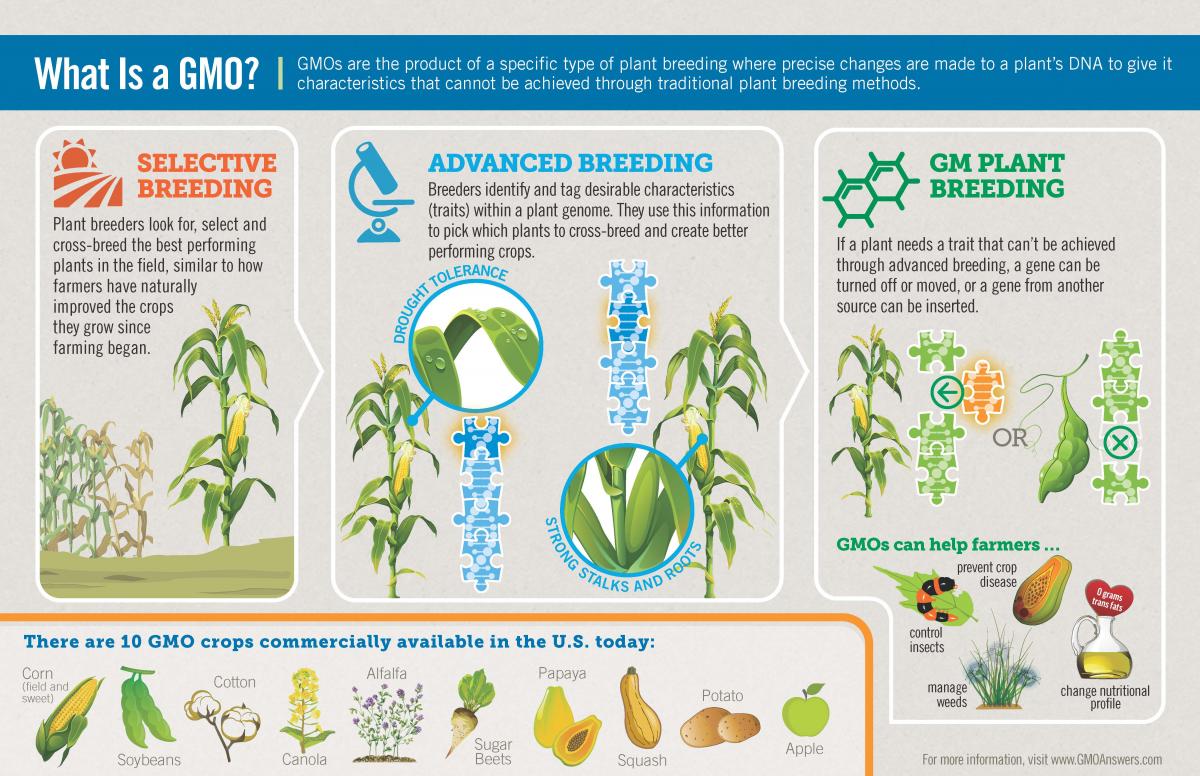
Several crops are commonly genetically modified for various purposes. Bt corn is a genetically modified variety of corn that produces its own insecticide. It reduces the need for external pesticide applications.
Roundup Ready soybeans are another example. They are genetically modified to tolerate the herbicide glyphosate, commonly known as Roundup. This allows farmers to control weeds without harming the soybean crop.
How Genetic Modification Works
Genetic modification involves several steps. Scientists first identify a gene with a desired trait. This gene is then isolated and inserted into the target organism's genome.
The process often involves using vectors, such as bacteria or viruses, to carry the gene into the organism's cells. Once the gene is integrated, the organism expresses the desired trait.
Regulation and Labeling of GMOs
GMOs are subject to strict regulations in many countries. Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA in the United States, assess the safety of GMOs before they are allowed on the market.
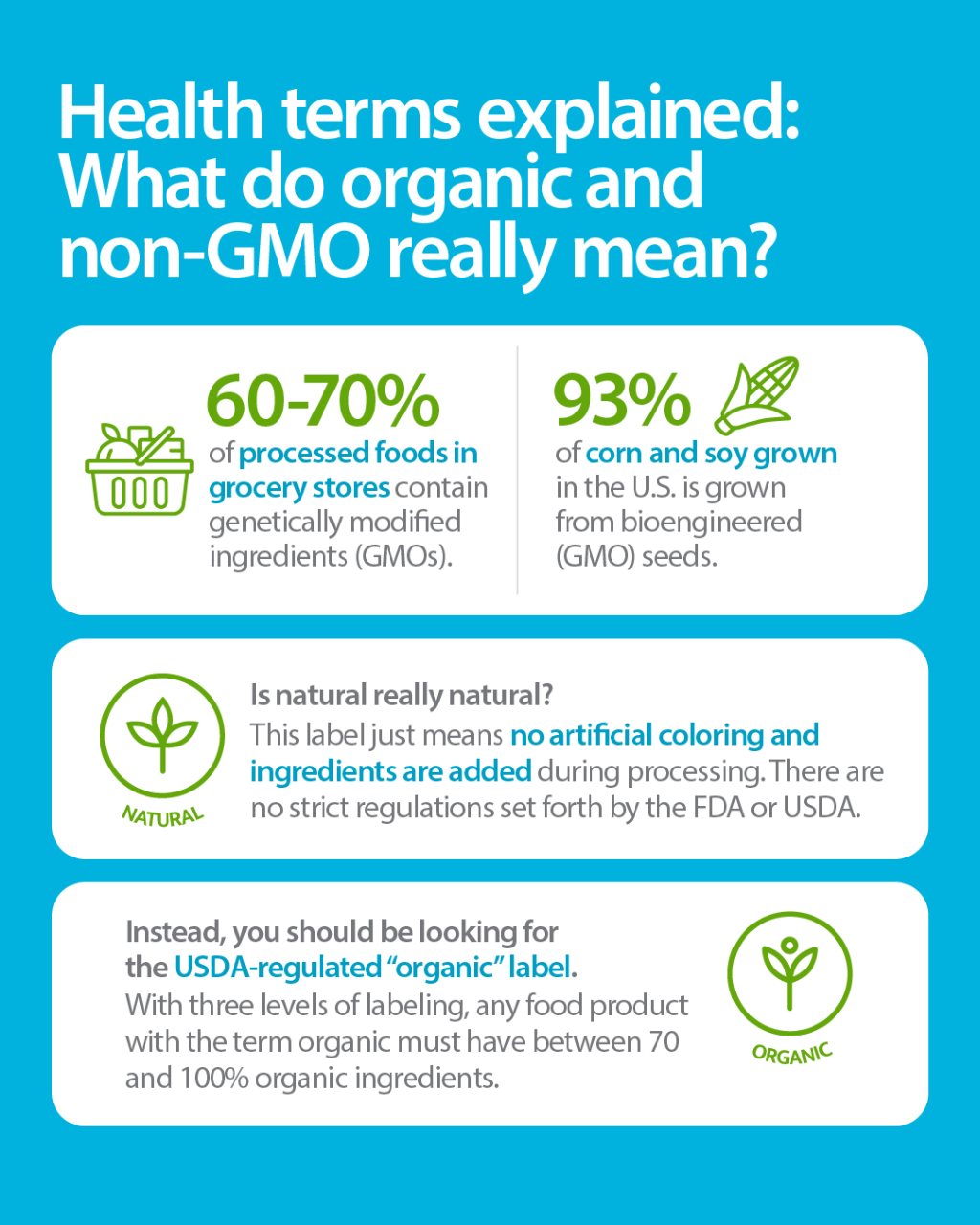
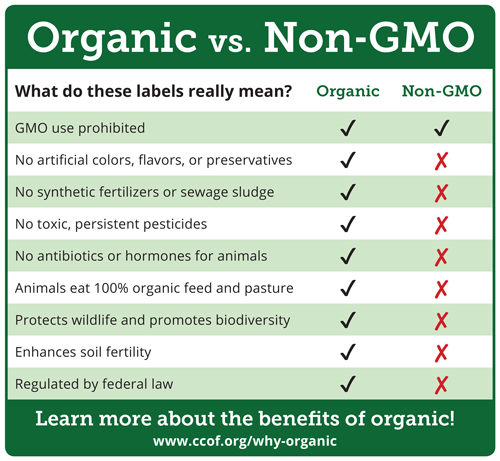
Labeling requirements for GMOs vary by country. Some countries require mandatory labeling of GMO foods. Others rely on voluntary labeling initiatives. The debate over GMO labeling continues to evolve.
The Ongoing Debate Surrounding GMOs
The use of GMOs remains a controversial topic. Proponents argue that GMOs can increase crop yields, reduce pesticide use, and enhance nutritional content.
Opponents raise concerns about potential environmental impacts. Concerns also exist about the effects on human health, and the control of the food supply by large corporations. Scientific consensus, however, supports the safety of currently available GMOs.
Moving Forward: Accurate Communication is Key
Using precise language is crucial for informed discussions about genetic modification. Avoiding the term "GMO strain" and instead using "genetically modified variety" or "genetically modified line" promotes accuracy.
Continued education and transparent communication are essential. Public understanding of the science behind GMOs will lead to more productive conversations about their role in agriculture and food production.