What Does It Take To Become An Attorney

The path to becoming an attorney is a rigorous and demanding one, requiring years of dedicated study, financial investment, and a commitment to upholding the principles of justice. Understanding the specific steps involved is crucial for anyone considering a career in law.
This article outlines the key requirements and stages involved in becoming a qualified attorney in the United States, from undergraduate education to passing the bar exam and maintaining professional standards. It aims to provide a clear and objective overview for prospective law students and those interested in the legal profession.
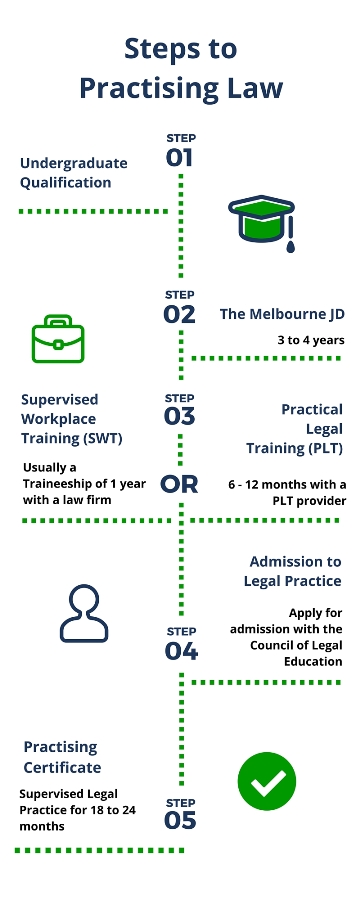
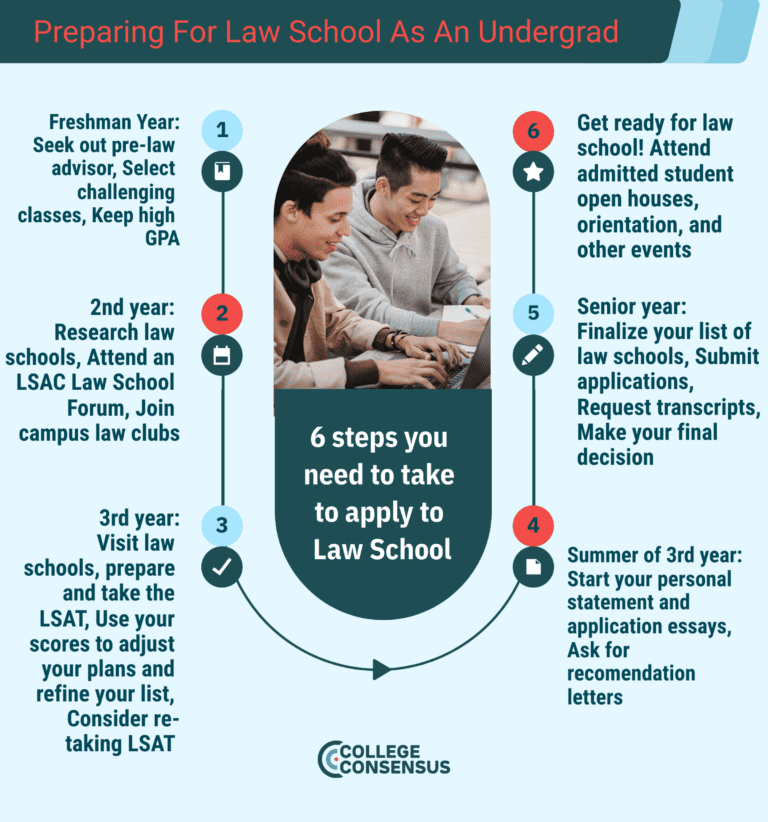
The Foundation: Undergraduate Education
While there isn't a specific pre-law major, a bachelor's degree is the first necessary step. Law schools generally seek students with strong analytical, critical thinking, and communication skills.
Common undergraduate majors for aspiring lawyers include political science, history, English, and economics. According to the Law School Admission Council (LSAC), a solid foundation in these areas can be beneficial for law school success.
LSAT and Law School Application
The Law School Admission Test (LSAT) is a standardized exam designed to assess reading comprehension, logical reasoning, and analytical reasoning skills. A high LSAT score is crucial for gaining admission to a competitive law school.
Law school applications typically require LSAT scores, transcripts, personal essays, and letters of recommendation. The application process is highly competitive, with admission rates varying significantly depending on the law school's ranking and reputation.
The Law School Experience: Three Years of Intensive Study
Law school is a full-time commitment, typically lasting three years. The curriculum focuses on legal theory, case law, statutory law, and practical legal skills.
First-year courses generally include foundational subjects such as contracts, torts, civil procedure, and criminal law. Upper-level courses offer opportunities to specialize in areas of interest, such as corporate law, environmental law, or family law.
Beyond coursework, law students often participate in moot court competitions, law review, and clinical programs to gain practical experience and enhance their legal skills.
The Bar Exam: The Final Hurdle
After graduating from law school, aspiring attorneys must pass the bar exam in the state where they intend to practice law. The bar exam is a comprehensive test covering a wide range of legal subjects.
The format and content of the bar exam vary by state, but most exams include multiple-choice questions, essay questions, and performance tests. Bar exam pass rates vary, and many graduates enroll in bar review courses to prepare.
Passing the bar exam is not the end of the road, it's merely the beginning of a lawyer's professional journey.
Character and Fitness Review
In addition to passing the bar exam, applicants must also undergo a character and fitness review. This review assesses an applicant's moral character and fitness to practice law.
The character and fitness review typically involves a thorough background check, interviews, and the submission of personal affidavits. Any past misconduct or ethical concerns can potentially delay or prevent admission to the bar.
Admission to the Bar and Continuing Legal Education
Once an applicant has passed the bar exam and completed the character and fitness review, they can be admitted to the bar. Admission to the bar grants the attorney the license to practice law in that jurisdiction.
Most states require attorneys to complete continuing legal education (CLE) courses throughout their careers to stay up-to-date on legal developments and maintain their professional competence. These courses cover changes in the law, ethics, and legal practice management.
The Ethical Obligations of an Attorney
Attorneys are bound by a strict code of ethics and professional responsibility. These rules govern attorney-client relationships, confidentiality, conflicts of interest, and other aspects of legal practice.
Failure to comply with ethical obligations can result in disciplinary action, including suspension or disbarment. The American Bar Association (ABA) provides resources and guidance on ethical standards for attorneys.
"The practice of law is not merely a profession; it is a calling that demands integrity, diligence, and a commitment to serving the interests of justice,"according to a statement from a former president of the ABA.
The Impact and Significance
Becoming an attorney is a significant accomplishment that requires years of dedication and hard work. Attorneys play a vital role in society by providing legal representation, upholding the rule of law, and advocating for justice.
The journey is challenging but rewarding for those passionate about law and committed to making a difference. For many, it’s a gateway to shaping policy and influencing lives.






.webp)