Which Of The Following Describes A Speculative Risk

The financial landscape is riddled with risks, some unavoidable, others actively embraced for potential gain. But distinguishing between inherent dangers and calculated gambles is crucial for individuals, businesses, and the stability of the global economy. Understanding the nuances of risk – particularly the difference between speculative and pure risk – is essential for informed decision-making and effective risk management.
This article aims to clarify speculative risk, a concept often misunderstood and conflated with other forms of risk. We will explore its defining characteristics, differentiate it from pure risk, and examine real-world examples to illustrate its impact on various sectors. By understanding the nature of speculative risk, readers can better navigate the complexities of investment, business ventures, and personal finance.
Defining Speculative Risk
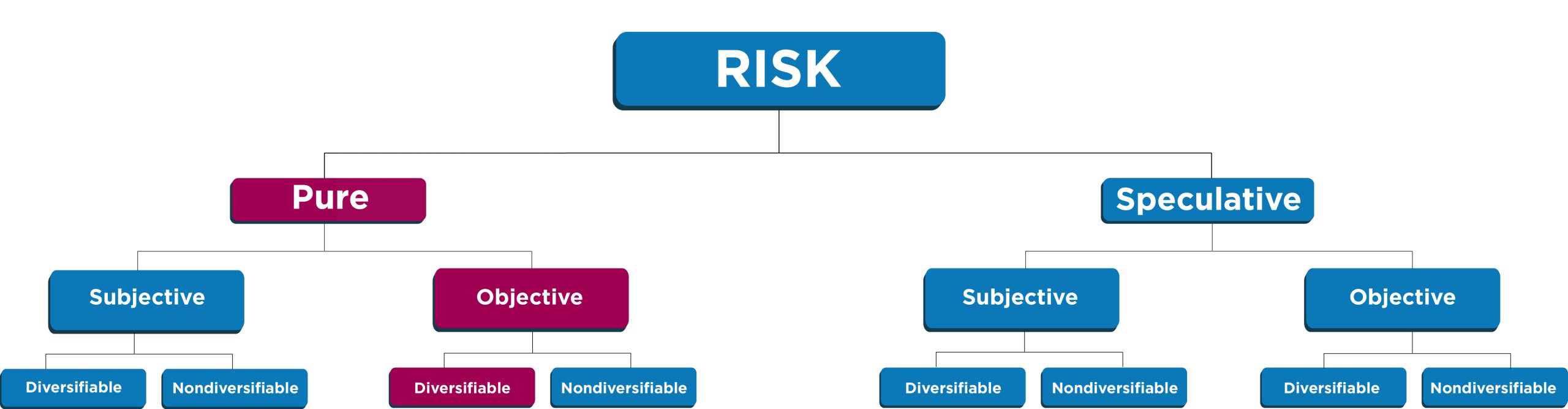
Speculative risk involves situations where the outcome can be either a gain or a loss. This is unlike pure risk, where the only possibilities are loss or no loss. The defining characteristic of speculative risk is the potential for profit, making it a conscious and often deliberate undertaking.
Examples of speculative risk abound in the financial world. Investing in the stock market, launching a new business, or engaging in real estate development all involve the possibility of both financial gains and losses.
Speculative Risk vs. Pure Risk
The key differentiator between speculative and pure risk lies in the outcome. Pure risk, such as the risk of fire or natural disaster, offers only the potential for loss or no change. There is no possibility of profit from a pure risk event.
Speculative risk, however, presents a binary outcome: gain or loss. This potential for reward is what makes it a calculated decision, rather than an unavoidable circumstance.
Insurance companies typically cover pure risks, such as damage to property, as these are insurable against potential losses. Speculative risks, on the other hand, are generally uninsurable due to the potential for intentional manipulation and the difficulty in quantifying potential gains.
Examples of Speculative Risk
Investing in the Stock Market: Buying stocks represents a speculative risk. An investor hopes for the price to increase, resulting in a profit, but there is always the possibility that the price will decrease, leading to a loss.
Launching a New Business: Starting a company is inherently a speculative venture. The entrepreneur anticipates success and profit, but faces the risk of failure and financial losses.
Real Estate Development: Developing property involves significant financial investment with the expectation of a profitable return. However, factors like market fluctuations, construction delays, and unforeseen expenses can lead to substantial losses.
Gambling: Perhaps the most obvious example, gambling is a purely speculative risk. The gambler wagers money with the hope of winning more, but faces the very real possibility of losing their stake.
Foreign Exchange Trading (Forex): Buying and selling currencies in the Forex market is a highly speculative activity. Traders aim to profit from fluctuations in exchange rates, but these rates are volatile and unpredictable, leading to potential losses.
Managing Speculative Risk
While speculative risk cannot be entirely eliminated, it can be managed through various strategies. These strategies aim to minimize potential losses and maximize the chances of achieving desired gains.
Diversification: Spreading investments across different asset classes can reduce the impact of losses in any single investment. This is a common strategy in stock market investing.
Thorough Research and Due Diligence: Before undertaking any speculative venture, conducting thorough research and due diligence is crucial. This involves analyzing market trends, assessing potential risks, and developing a comprehensive business plan.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Identifying potential risks and developing strategies to mitigate them is essential for effective risk management. This includes contingency planning, insurance coverage for insurable risks, and setting realistic expectations.
Setting Stop-Loss Orders: In trading and investing, stop-loss orders automatically sell an asset when it reaches a certain price, limiting potential losses. This is a common risk management tool used in the stock market and Forex trading.
Proper Capital Allocation: Allocating an appropriate amount of capital to speculative ventures is crucial. Avoid risking more than you can afford to lose, and ensure that your overall financial stability is not jeopardized.
The Broader Impact of Speculative Risk
Speculative risk plays a vital role in driving innovation and economic growth. Entrepreneurs and investors who are willing to take calculated risks are often the ones who create new businesses, develop new technologies, and generate wealth.
However, excessive or poorly managed speculative risk can also lead to financial instability and economic crises. The 2008 financial crisis, for example, was partly triggered by excessive speculation in the housing market.
Therefore, a balance is needed between encouraging risk-taking and ensuring responsible risk management. Regulatory oversight, financial education, and prudent lending practices can all contribute to a more stable and sustainable economic environment.
The Future of Speculative Risk
As the global economy becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, the nature of speculative risk is constantly evolving. New technologies, emerging markets, and changing consumer preferences are creating both new opportunities and new challenges for risk-takers.
The rise of cryptocurrencies, for example, represents a new frontier for speculative investment. While cryptocurrencies offer the potential for high returns, they are also highly volatile and subject to regulatory uncertainty.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are also transforming the way speculative risk is assessed and managed. These technologies can be used to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and predict potential outcomes, helping investors and businesses make more informed decisions.
Ultimately, the successful navigation of speculative risk requires a combination of knowledge, skill, and discipline. By understanding the nature of speculative risk, developing effective risk management strategies, and staying informed about market trends, individuals and businesses can increase their chances of achieving their financial goals while minimizing potential losses. The willingness to take calculated risks is essential for progress, but it must be tempered with prudence and a clear understanding of the potential consequences.