Which Of The Following Is Not An Epithelial Membrane
Imagine a world where our bodies lacked the protective barriers they so diligently maintain. Picture the delicate inner workings of our lungs exposed directly to the harsh elements, or the constant friction within our joints causing relentless pain. These are the vital roles played by epithelial membranes, intricate layers of tissue that safeguard and facilitate countless functions within us.
The question "Which of the following is not an epithelial membrane?" might seem straightforward, yet it unlocks a deeper understanding of our anatomy and the crucial differences between various tissue types. This article will explore the fascinating world of epithelial membranes, differentiating them from other structures to help you identify the imposter.
Understanding Epithelial Membranes
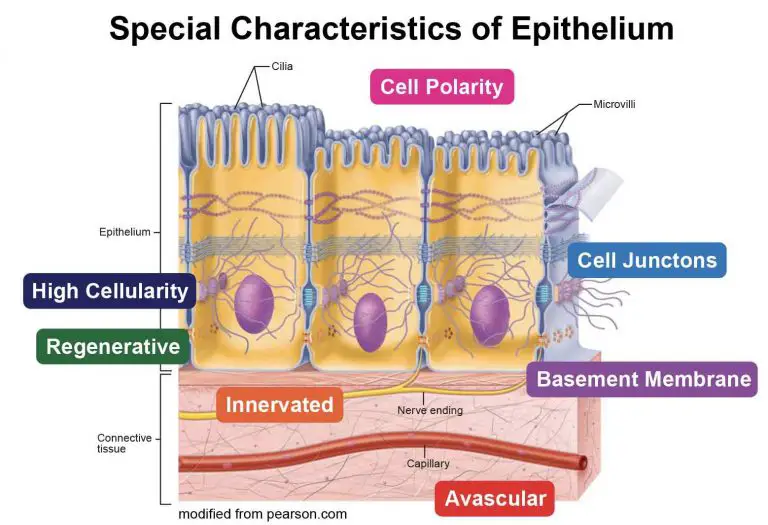
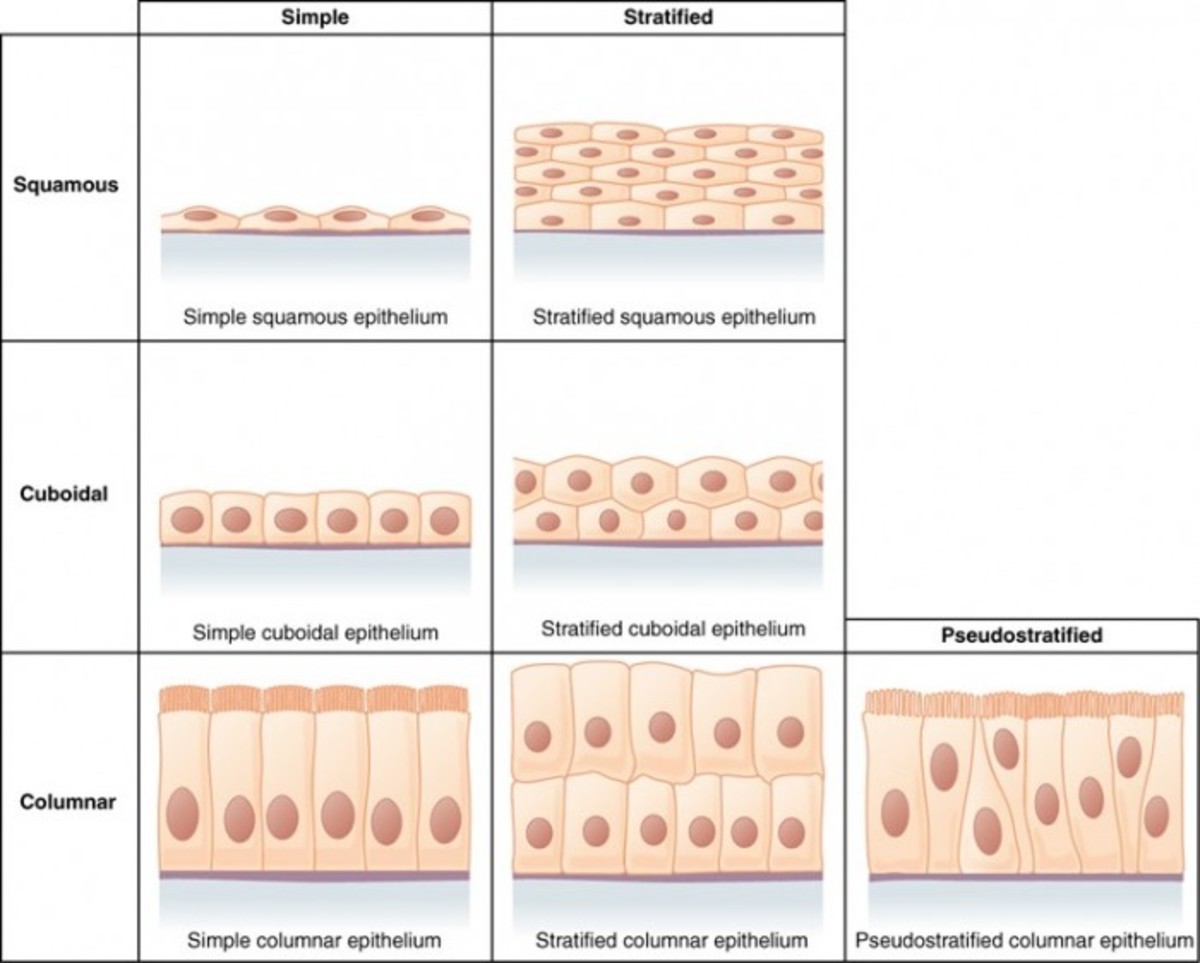
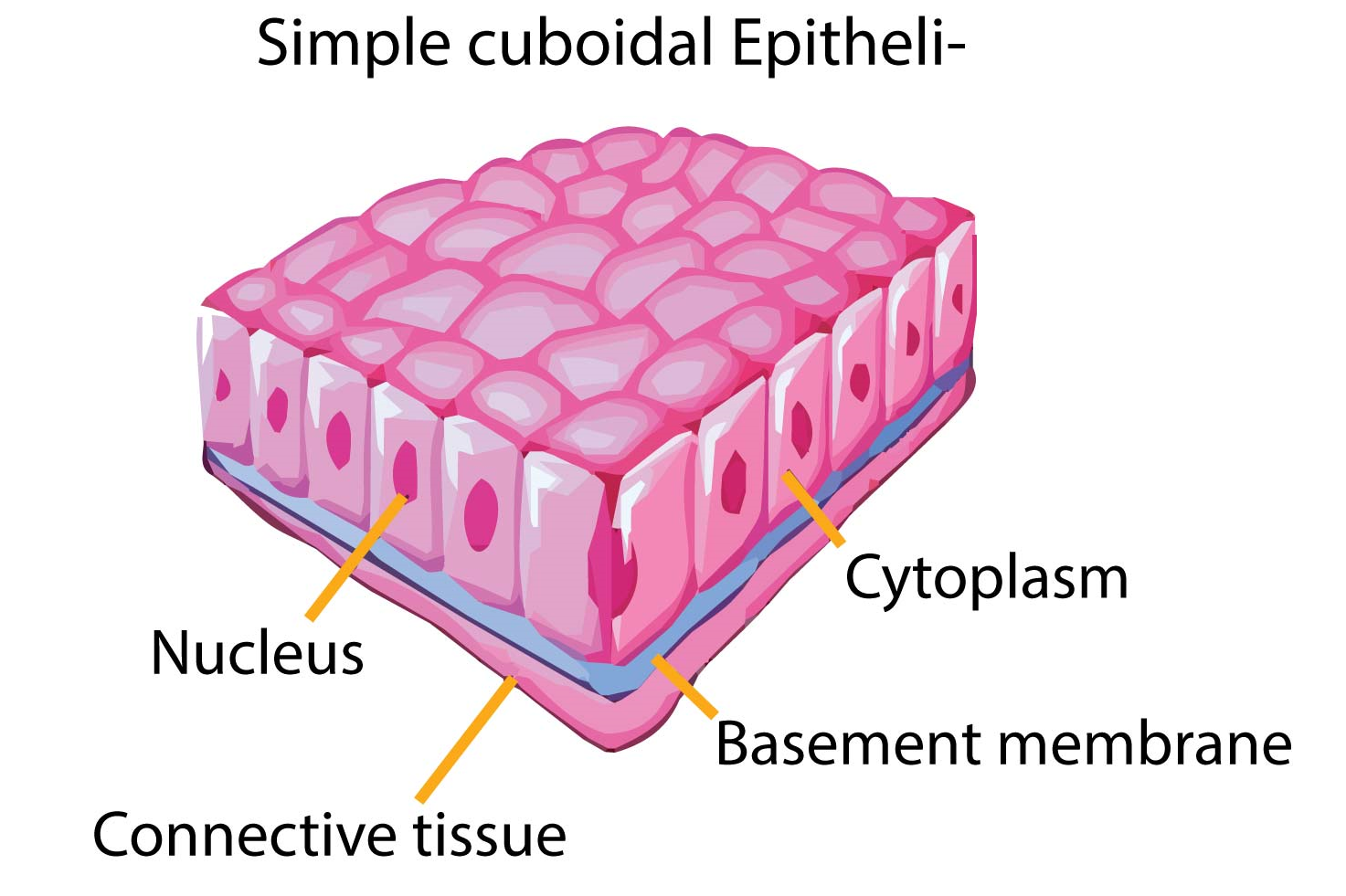
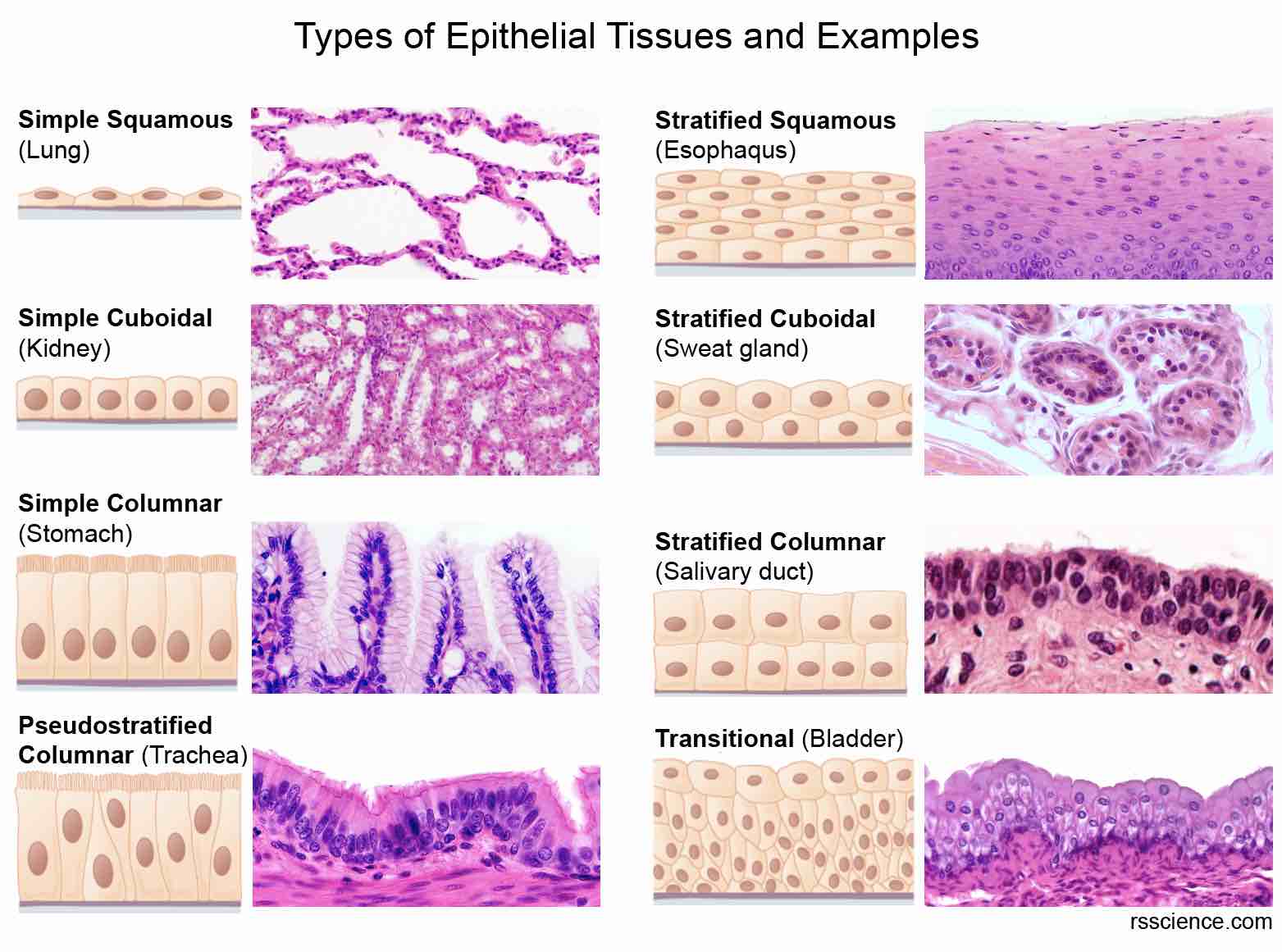
Epithelial membranes, also known as covering and lining membranes, are composite tissues comprised of an epithelial layer bound to an underlying layer of connective tissue. These membranes serve multiple functions, including protection, absorption, filtration, and secretion, depending on their location within the body.
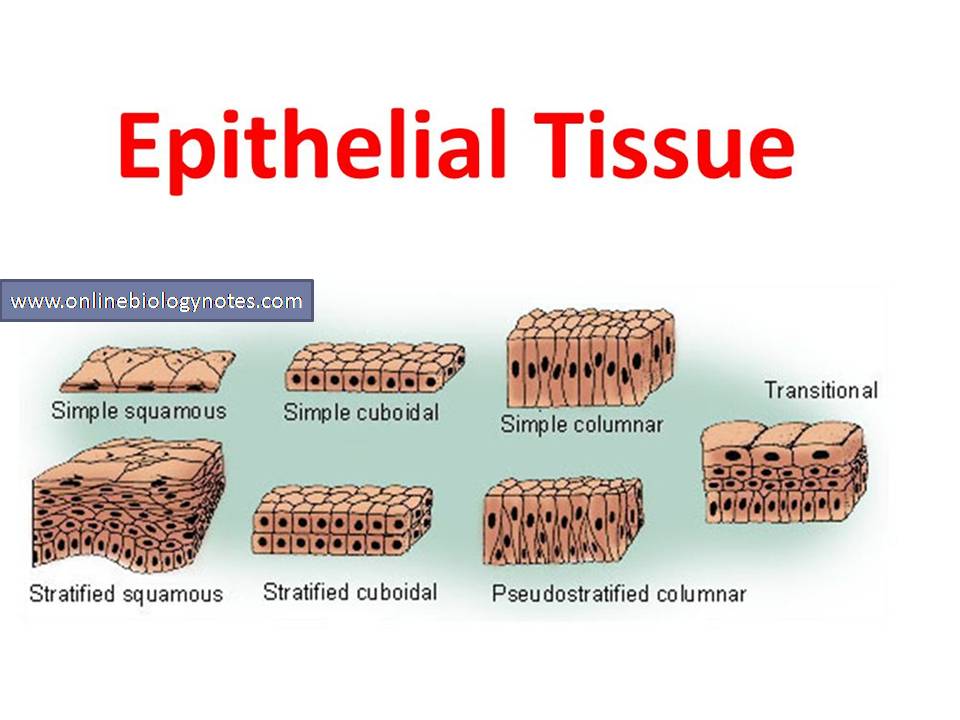
There are several types of epithelial membranes, each uniquely structured for its specific role. Let's examine some key examples:
Mucous Membranes
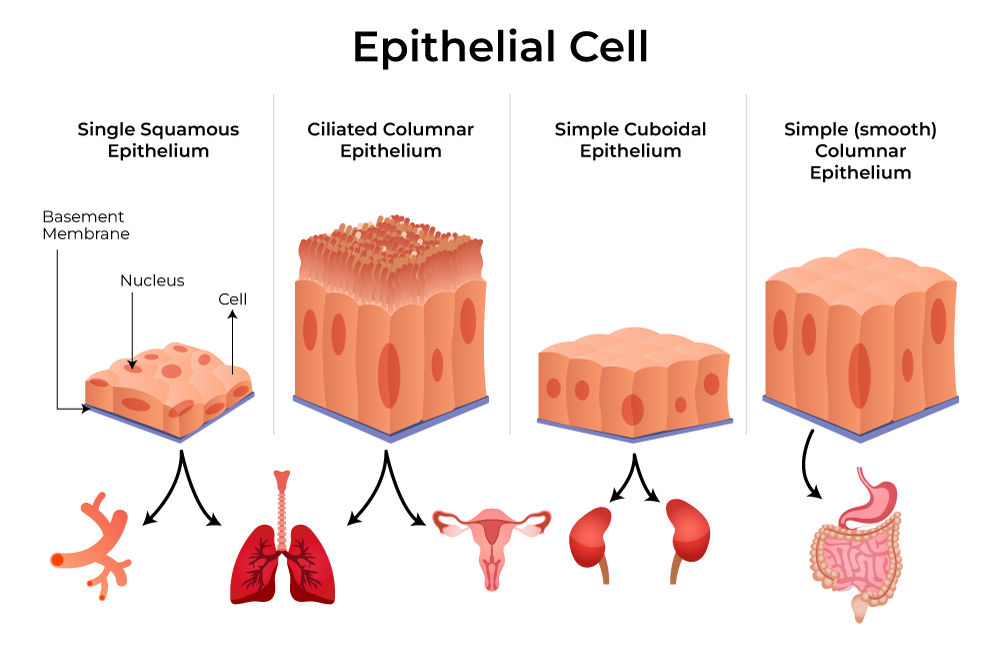
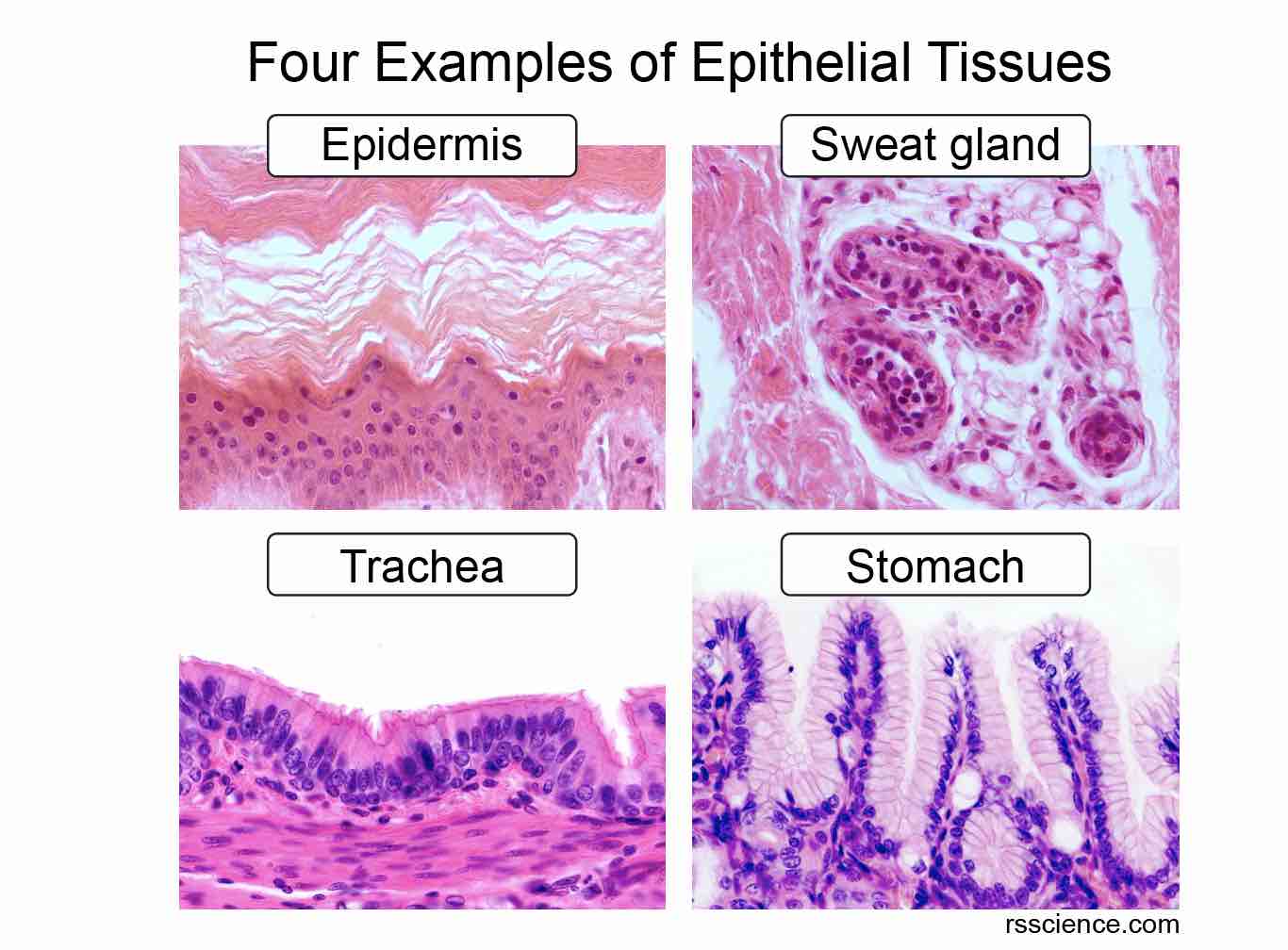
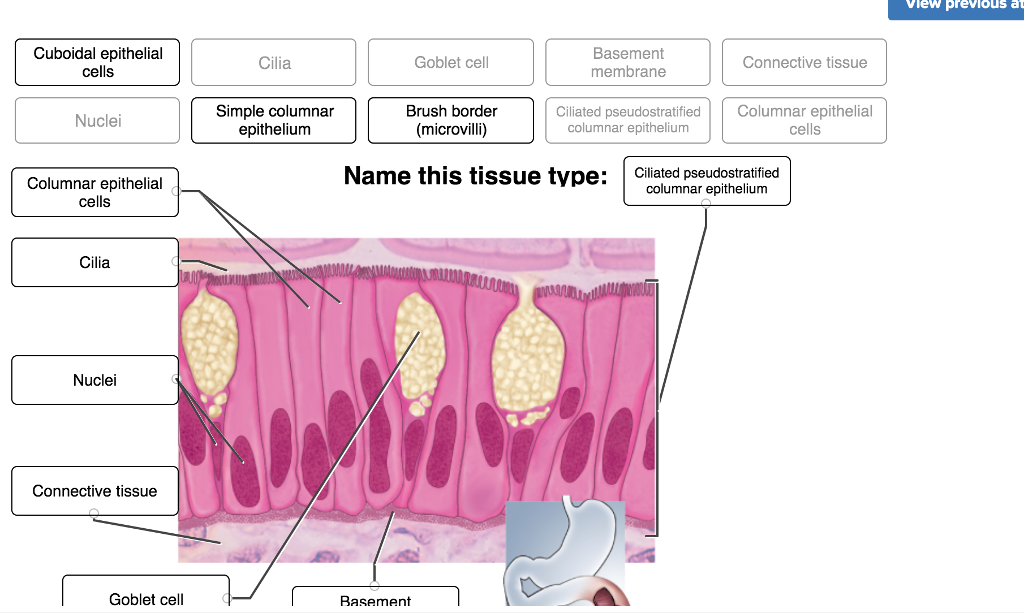
Mucous membranes, or mucosae, line body cavities that open to the exterior, such as the respiratory, digestive, and urogenital tracts. These membranes are typically moist and lubricated by mucus produced by goblet cells, which are specialized epithelial cells.
The mucus traps debris and pathogens, preventing them from entering the body. The epithelial layer in mucous membranes can vary, ranging from simple columnar epithelium in the stomach to pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium in the trachea.
Serous Membranes
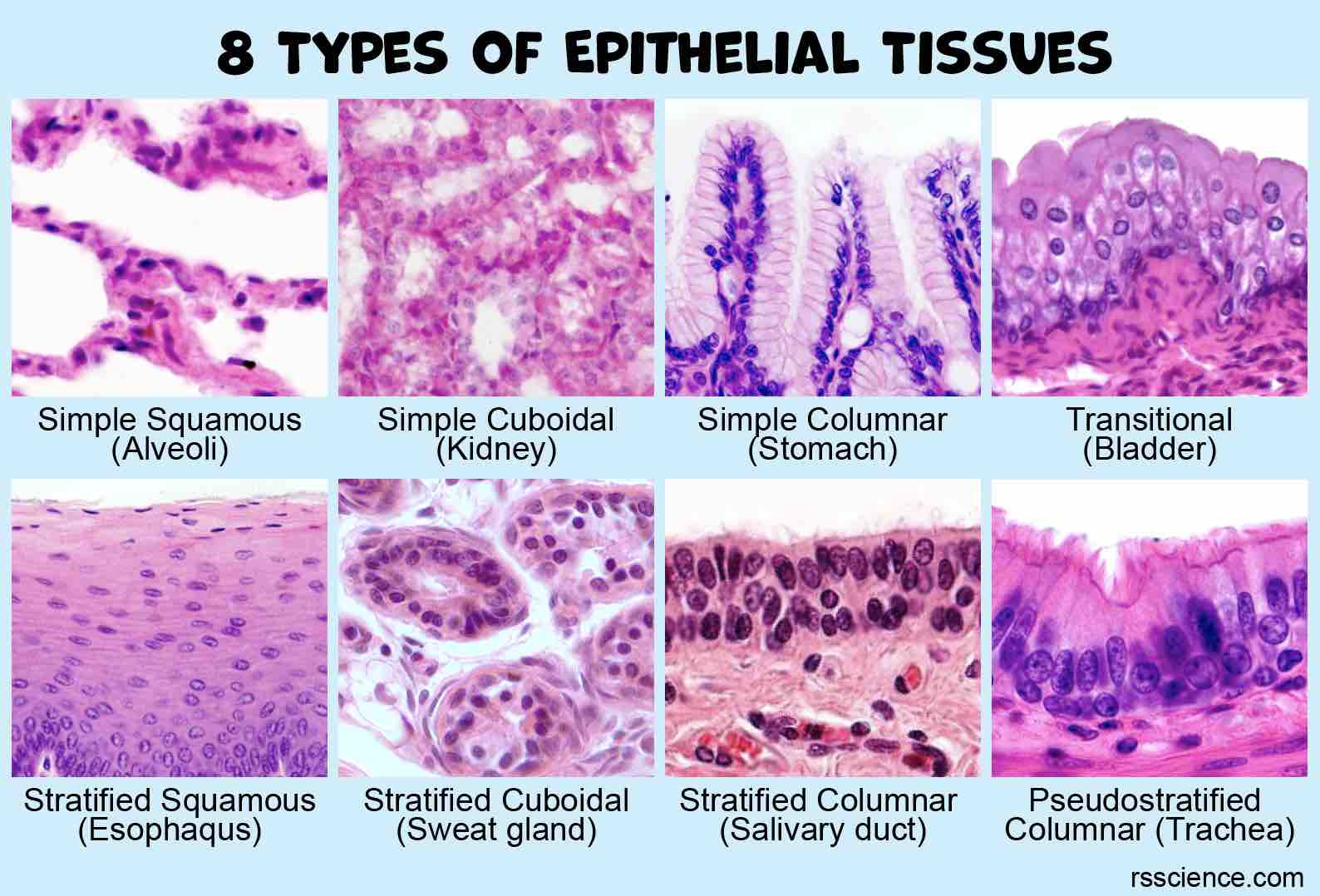
Serous membranes, or serosae, line body cavities that are closed to the exterior, like the peritoneal, pleural, and pericardial cavities. They are composed of a layer of simple squamous epithelium resting on a thin layer of areolar connective tissue.
Serous membranes secrete a thin, watery fluid called serous fluid, which lubricates the membrane surfaces and reduces friction between organs. This fluid is essential for smooth organ movement within the body.
Cutaneous Membrane
The cutaneous membrane, or skin, is our outermost protective layer. It’s composed of a keratinized stratified squamous epithelium (epidermis) attached to a thick layer of dense irregular connective tissue (dermis).
Unlike mucous and serous membranes, the cutaneous membrane is exposed to the air and is a dry membrane. The keratinized epidermis provides a tough, waterproof barrier that protects the body from abrasion, dehydration, and infection.
Identifying Non-Epithelial Structures
To answer the question of what isn't an epithelial membrane, it's essential to understand the basic components of these membranes. Remember, they always involve an epithelial layer attached to connective tissue.
Structures like synovial membranes, which line joint cavities, might appear similar but lack a true epithelial layer. Instead, they consist of specialized connective tissue cells called synoviocytes.
Synovial membranes secrete synovial fluid, which lubricates the joint and reduces friction between the bones. This fluid contains hyaluronic acid, which gives it a viscous consistency.
Synovial Membranes: A Closer Look
The critical difference lies in the cellular composition. While epithelial membranes consist of tightly packed epithelial cells forming a barrier, synovial membranes are made up of connective tissue.
Synovial membraneslack the distinct epithelial layer that is the defining characteristic of epithelial membranes.
Synovial membranes are crucial for joint function, ensuring smooth and painless movement. Damage to these membranes can lead to conditions like arthritis, highlighting their importance in maintaining musculoskeletal health.
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), synovial membrane inflammation is a hallmark of many joint disorders. Research focuses on understanding the complex interplay of cells and molecules within the synovial membrane to develop effective treatments for these conditions.
The Significance of Distinguishing Membranes
Understanding the difference between epithelial and non-epithelial membranes is critical in various fields, from medicine to biology. It is essential for accurately diagnosing diseases and developing targeted therapies.
For example, understanding the epithelial nature of the respiratory mucosa helps researchers develop effective drug delivery systems for treating lung conditions. Similarly, knowing that synovial membranes are connective tissue informs the development of treatments for arthritis and other joint disorders.
Furthermore, this knowledge is fundamental for medical students and healthcare professionals. It supports their ability to understand how different tissues respond to injury and disease.
Looking Ahead
As our understanding of tissue biology deepens, so does our ability to treat and prevent diseases. Advances in fields like tissue engineering and regenerative medicine hold immense promise for repairing damaged membranes and restoring their function.
For instance, researchers are exploring the possibility of creating artificial epithelial membranes to treat severe burns or to create bioartificial organs. These innovations could revolutionize healthcare and significantly improve patient outcomes.
The question "Which of the following is not an epithelial membrane?" is more than just a trivia question. It represents a gateway to understanding the complexity and beauty of our bodies. Synovial membranes, with their unique structure and function, stand as a crucial example of how diverse tissues work together to maintain our health and well-being.

![Which Of The Following Is Not An Epithelial Membrane [GET ANSWER] 1: Histology us Figure 4.11: Distinguishing Between](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/27dc7d3b11854ee9b99707067aa2224d.jpg)