Is Lead Sulfate Soluble In Water

The question of whether lead sulfate (PbSO4) dissolves in water is not merely a matter of academic curiosity. It has profound implications for public health, environmental safety, and industrial processes.
Minute amounts of lead, even those deemed "insoluble," can leach into water systems, posing significant risks. This article dives deep into the solubility of lead sulfate, exploring scientific data, regulatory perspectives, and potential consequences of its presence in water resources.
Understanding Lead Sulfate Solubility: The Nut Graf
While often described as "insoluble," lead sulfate possesses a very low, but measurable, solubility in water. This seemingly minor solubility is critical, as it dictates the extent to which lead ions can contaminate water sources.
Factors like temperature, pH, and the presence of other ions can influence this solubility, creating complex environmental scenarios. This article will examine these factors and their impact on lead contamination levels.
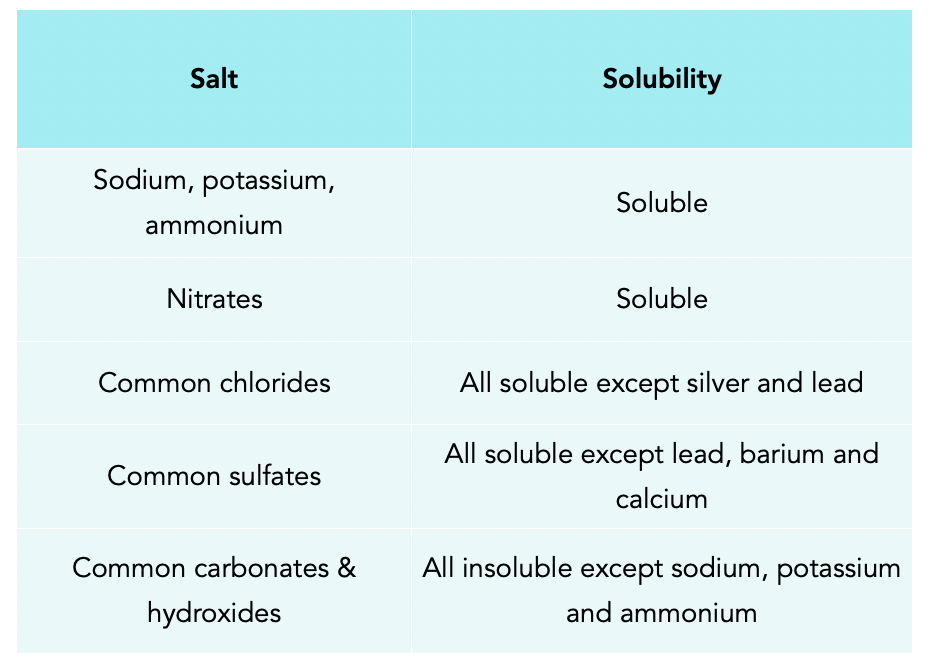
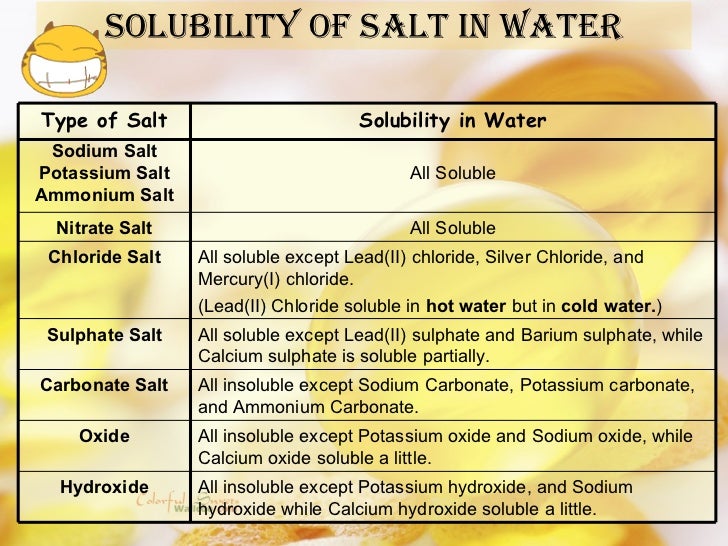
Defining "Insoluble": A Matter of Scale
The term "insoluble" is often used loosely. In chemistry, it usually signifies a substance that dissolves in water to a very limited extent.
Lead sulfate falls into this category. It doesn't completely dissolve like table salt, but a small quantity of lead ions can still break free and enter the water.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets stringent limits for lead in drinking water. This highlights that even trace amounts are concerning.
The Science Behind Lead Sulfate's Dissolution
The dissolution of lead sulfate involves the breaking of ionic bonds between lead and sulfate ions.
Water molecules can disrupt these bonds, freeing individual lead (Pb2+) and sulfate (SO42-) ions into the solution.
This process is governed by the solubility product constant (Ksp), a value that indicates the extent to which a compound will dissolve at a given temperature.
The Solubility Product (Ksp) Value
The Ksp for lead sulfate is a very small number, typically around 1.6 x 10-8 at 25°C. This reflects its low solubility.
However, even this small value translates to a concentration of lead ions in water that can exceed regulatory limits.
Changes in temperature affect the Ksp. Generally, solubility increases slightly with increasing temperature, though the effect is not dramatic for lead sulfate.
Factors Influencing Lead Sulfate Solubility
The pH of water plays a significant role. Lower pH (acidic conditions) tends to increase the solubility of lead sulfate.
This is because acidic conditions can protonate sulfate ions, disrupting the equilibrium and favoring the dissolution of the salt.
The presence of other ions, such as chloride or sulfate, can also influence solubility through the common ion effect, which can either increase or decrease solubility depending on the specific ions involved.
Lead Sulfate in Real-World Scenarios
Lead sulfate is a common component of lead-acid batteries. Improper disposal of these batteries can lead to environmental contamination.
Mining activities, particularly those involving lead ores, can also release lead sulfate into the environment.
Paint, historically containing lead, can degrade over time, forming lead sulfate as a byproduct, contributing to soil and water contamination.
Health and Environmental Impacts
Lead is a neurotoxin. Even low levels of exposure can cause developmental problems in children and cardiovascular issues in adults.
Exposure to lead through contaminated water can have severe and long-lasting health consequences.
The persistence of lead sulfate in the environment makes it a long-term pollution concern, requiring careful monitoring and remediation efforts.
Regulatory Perspectives and Remediation Strategies
The EPA has established a maximum contaminant level goal (MCLG) of zero for lead in drinking water, and an action level of 15 parts per billion (ppb).
Water treatment plants employ various methods to reduce lead levels, including corrosion control and filtration techniques.
Remediation strategies for contaminated sites often involve stabilizing lead sulfate in the soil to prevent it from leaching into groundwater.
Future Directions: Research and Monitoring
Ongoing research focuses on developing more effective and sustainable methods for removing lead from contaminated water and soil.
Advanced analytical techniques are being used to better understand the speciation of lead in different environmental matrices.
Continuous monitoring of water sources is crucial for detecting and addressing potential lead contamination issues promptly, safeguarding public health and the environment.
In conclusion, while lead sulfate is often considered "insoluble," its low solubility is sufficient to pose significant environmental and health risks. Understanding the factors influencing its dissolution, coupled with robust monitoring and remediation efforts, is crucial for minimizing lead exposure and protecting our water resources. The seemingly simple question of solubility, therefore, is a critical component of a much larger and more complex effort to ensure a safe and healthy environment for all.
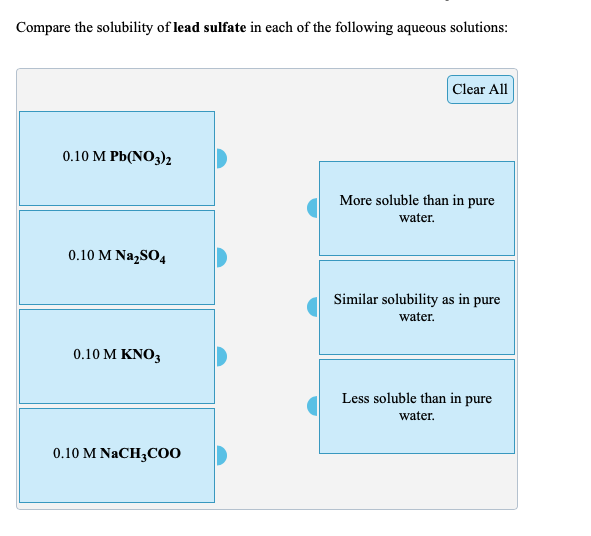
![Is Lead Sulfate Soluble In Water [FREE] A 9 req req Compare the solubility of lead sulfate in each of](https://media.brainly.com/image/rs:fill/w:750/q:75/plain/https://us-static.z-dn.net/files/d9a/853950012bfb3a7ad3fe072946657b35.png)




![Is Lead Sulfate Soluble In Water Lecture 0502 Types of Reactions. 1. Synthesis [composition] elements](https://images.slideplayer.com/27/8985395/slides/slide_9.jpg)

![Is Lead Sulfate Soluble In Water Solved [References] Anglesite (lead sulfate, PBSO4) is a | Chegg.com](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/b71/s700x460/b71b2d12-6049-4b8d-9f86-8c572c5d752c/image.png)

+or+insoluble+(I).jpg)