Microbiological Contaminants Are Best Described As

The invisible world of microorganisms plays a vital role in our lives, but it also presents a significant challenge: microbiological contamination. This complex issue affects food safety, water quality, healthcare, and numerous other industries, demanding a comprehensive understanding of what these contaminants are and how they spread.
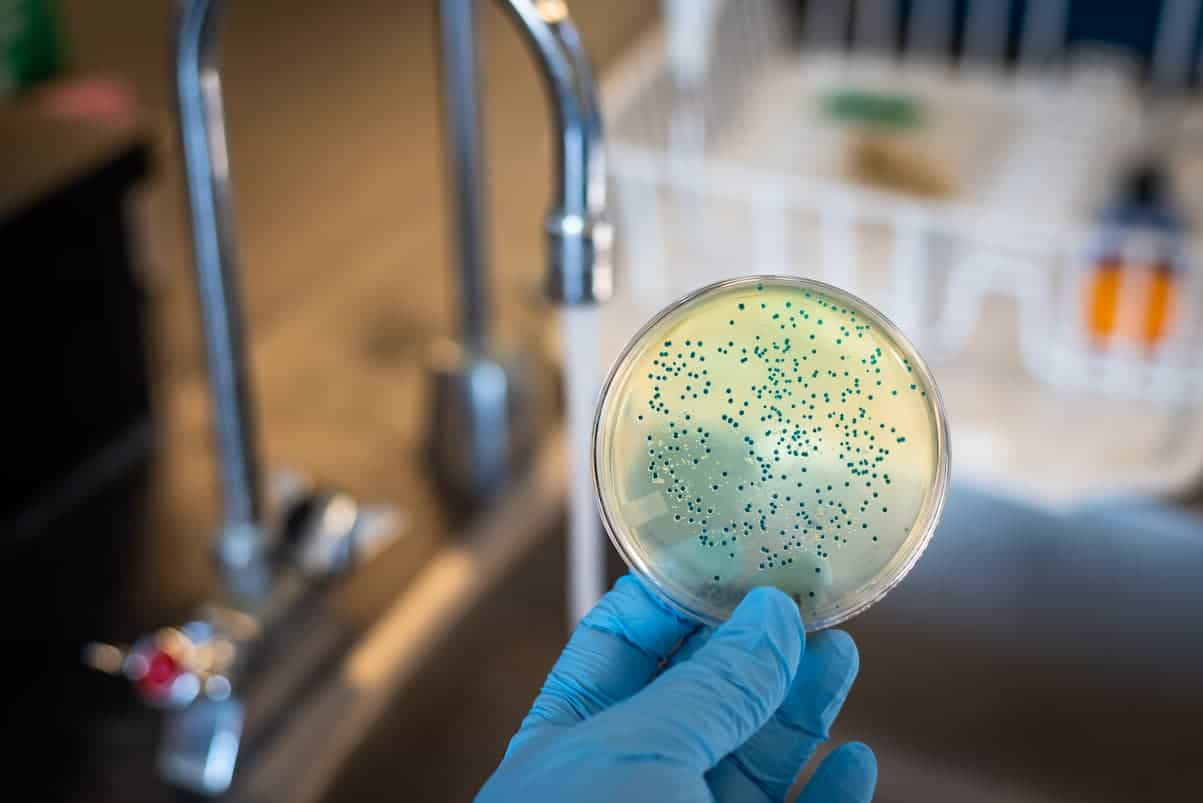
At its core, microbiological contamination refers to the unwanted introduction of harmful microorganisms – bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites – into an environment or substance. Understanding the specifics of microbiological contaminants is crucial for effective prevention, control, and mitigation strategies.
Defining Microbiological Contaminants
Microbiological contaminants are best described as any microorganism present in an environment or substance where it is not desired. This definition is broad, encompassing a wide range of organisms and contexts, from a single bacterium in sterile medical equipment to a complex community of fungi in contaminated food.
The key aspect is the undesirable presence of these microbes, leading to potential harm or disruption. This definition highlights the context-dependent nature of contamination: a microbe that is harmless or even beneficial in one environment can be a significant contaminant in another.
Types of Microbiological Contaminants
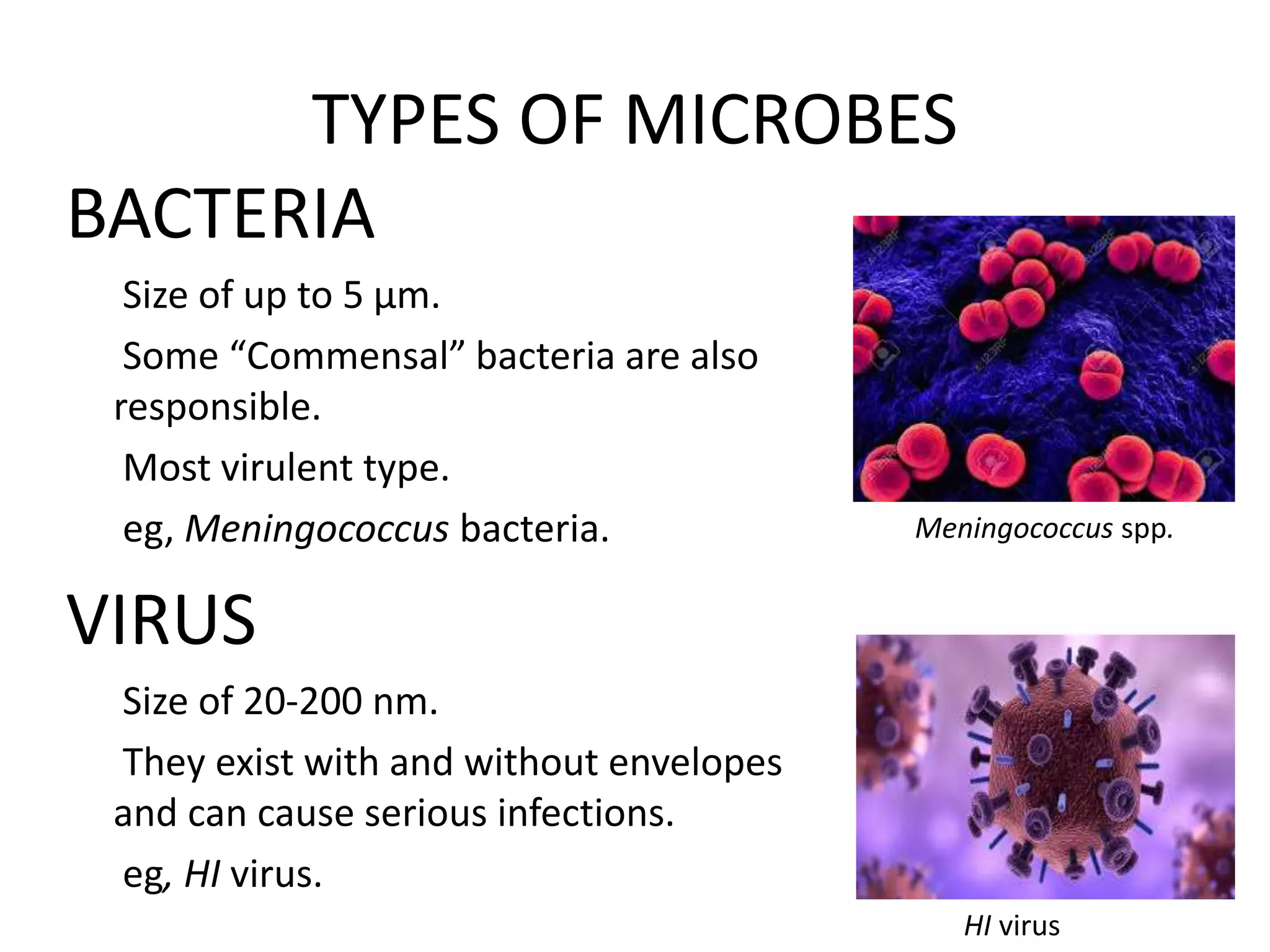
Bacteria: These single-celled organisms are ubiquitous and diverse, some are beneficial for human health, but others, like Salmonella and E. coli, cause severe foodborne illnesses.
Viruses: These infectious agents require a host cell to replicate. Norovirus, a common cause of gastroenteritis, and Hepatitis A, which affects the liver, are significant viral contaminants.
Fungi: This group includes molds and yeasts. They can contaminate food, water, and indoor environments, leading to allergic reactions, respiratory problems, and mycotoxin production.
Parasites: These organisms live on or in a host organism, obtaining nutrients at the host's expense. Giardia and Cryptosporidium are waterborne parasites that can cause diarrheal illnesses.
Sources and Pathways of Contamination
Microbiological contamination can originate from various sources, including human activity, animal waste, environmental factors, and manufacturing processes. Understanding these sources and pathways is crucial for implementing effective control measures.
Foodborne contamination often occurs during food production, processing, storage, or preparation. Improper handling, inadequate sanitation, and cross-contamination are common causes.
Waterborne contamination can result from sewage leaks, agricultural runoff, or inadequate water treatment. Drinking water, recreational waters, and even irrigation systems can be affected.
Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) are a significant concern in hospitals and other healthcare facilities. Contamination can occur through medical devices, surfaces, and even healthcare workers.
Impact on Human Health and Society
The impact of microbiological contamination can be far-reaching, affecting human health, the economy, and public safety. Foodborne illnesses alone cause millions of cases of sickness and thousands of deaths each year.
Waterborne diseases are a major public health concern, particularly in developing countries. HAIs increase healthcare costs and contribute to patient morbidity and mortality.
"Microbiological contamination poses a significant threat to global public health and requires a multidisciplinary approach to address effectively." - World Health Organization (WHO)
Prevention and Control Strategies
Combating microbiological contamination requires a multifaceted approach, including strict hygiene practices, effective sanitation measures, and advanced technologies. Food safety regulations, water treatment processes, and infection control protocols play a vital role.
Food safety measures include proper handwashing, cooking food to safe temperatures, preventing cross-contamination, and storing food properly. These simple steps can significantly reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Water treatment involves a series of processes to remove or kill microorganisms and other contaminants from water sources. Filtration, disinfection, and monitoring are essential components of water treatment systems.
Infection control in healthcare settings includes hand hygiene, environmental cleaning, sterilization of medical devices, and isolation of infected patients. These practices help to prevent the spread of HAIs.
Emerging Challenges and Future Directions
The fight against microbiological contamination is an ongoing challenge, with new threats emerging constantly. Antimicrobial resistance, climate change, and globalization are factors that complicate the issue.
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microorganisms develop resistance to antimicrobial drugs, making infections more difficult to treat. The overuse and misuse of antibiotics contribute to the rise of AMR.
Climate change can alter the distribution and abundance of microorganisms, potentially increasing the risk of contamination. Extreme weather events, such as floods and droughts, can also compromise water quality and sanitation systems.
Globalization facilitates the rapid spread of microorganisms across borders, posing a challenge to public health officials. International collaboration and surveillance are essential for detecting and responding to emerging threats.
Conclusion
Microbiological contaminants are a pervasive and multifaceted challenge that requires a comprehensive understanding and a collaborative approach to address effectively. By focusing on prevention, control, and mitigation strategies, we can protect human health, safeguard our environment, and ensure a safer future for all.