What Are Two Key Ingredients To Natural Selection
The engine driving the evolution of life on Earth, natural selection, isn't a mysterious force but a logical consequence of simple biological realities. Understanding its core mechanics is crucial for comprehending the diversity of life, from bacteria to blue whales.
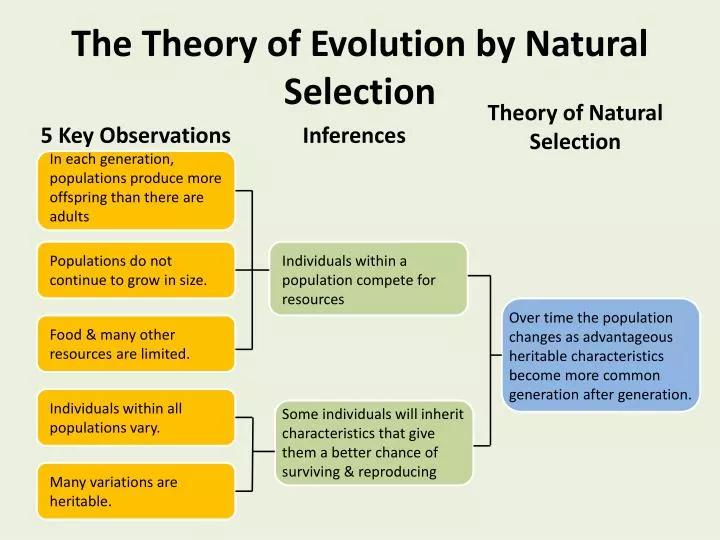
At the heart of natural selection lie two indispensable ingredients: variation within a population and differential reproduction based on that variation. Without these, the evolutionary process grinds to a halt. This article explores these key components, highlighting their importance and impact on the ongoing story of life.
Variation: The Raw Material of Evolution
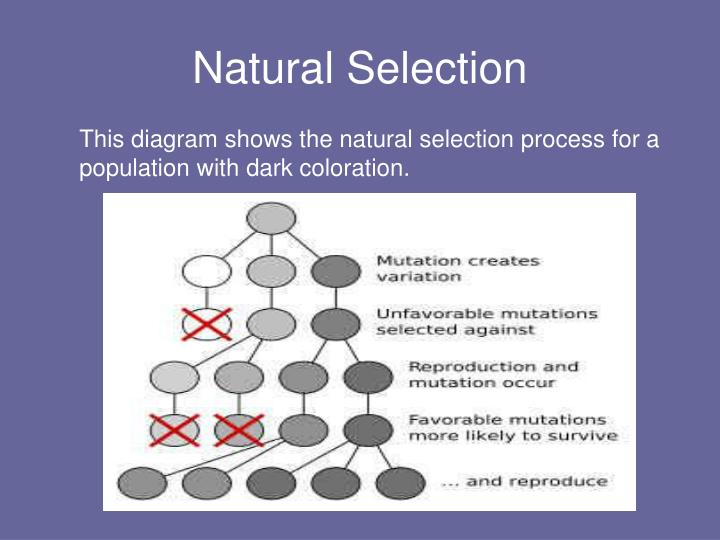
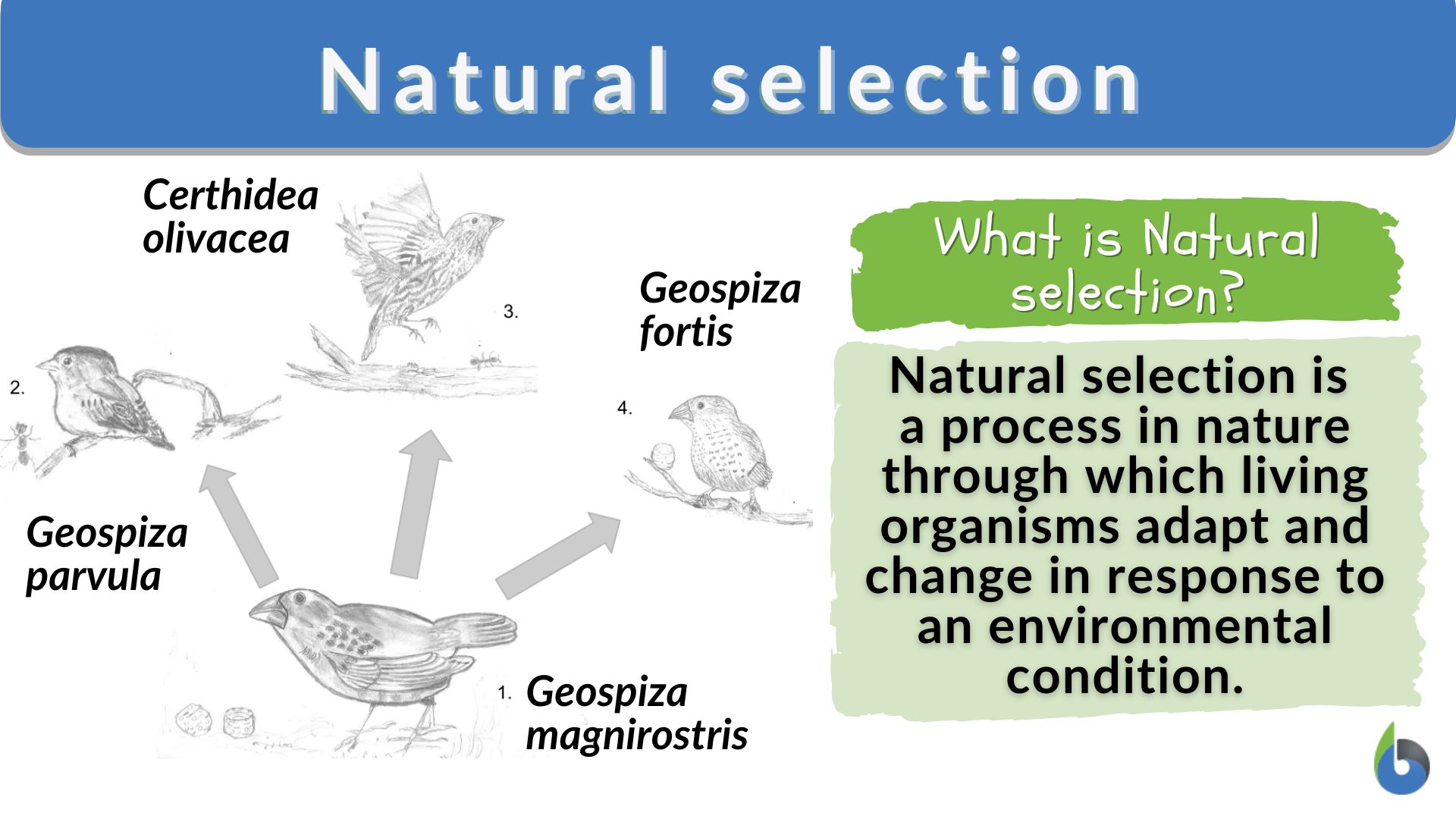
Variation refers to the differences in traits among individuals within a population. These traits can range from subtle variations in size or color to significant differences in behavior or physiological function. This inherent variability provides the raw material upon which natural selection acts.
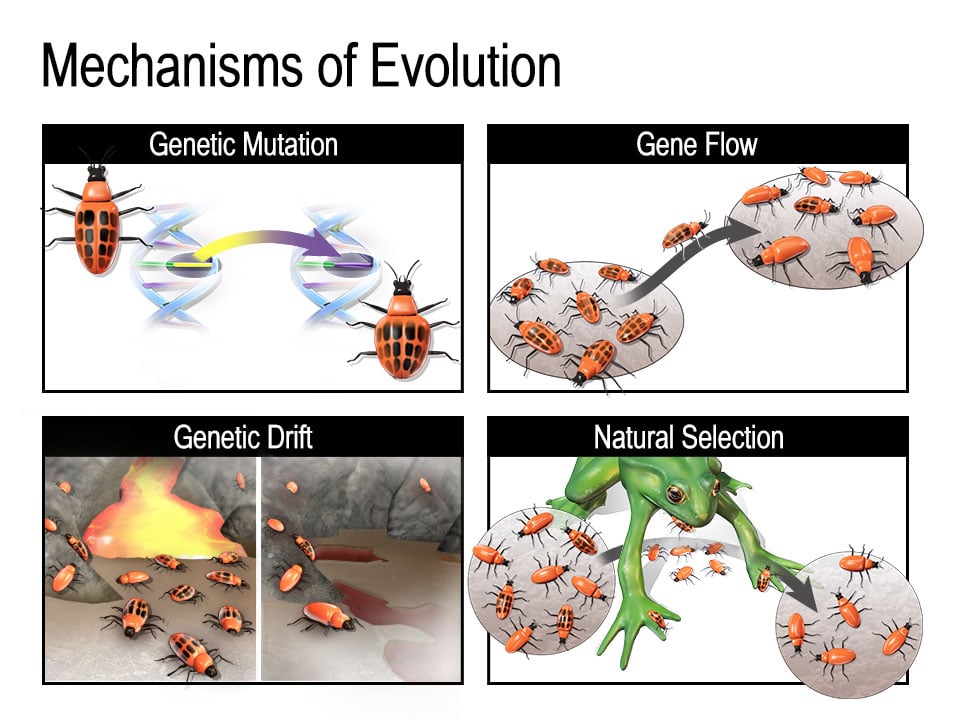
Sources of variation are diverse. Genetic mutations, random changes in the DNA sequence, are a primary source. These mutations can be beneficial, harmful, or neutral.
Another significant source of variation is genetic recombination, which occurs during sexual reproduction. The shuffling and reassortment of genes from both parents create offspring with unique combinations of traits.
Without variation, all individuals would be identical. Natural selection would have no basis to favor some over others.
The Importance of Heritability
For variation to be relevant to natural selection, traits must be heritable. This means that offspring tend to resemble their parents in terms of these traits. If a trait is not passed down through generations, then its impact on survival and reproduction will not lead to evolutionary change.
Heritability is often determined by the genes an organism inherits. However, environmental factors can also influence the expression of genes, leading to complex interactions between heredity and environment.
Only heritable traits can be acted upon by natural selection, leading to changes in the genetic makeup of a population over time. This ensures that beneficial traits that aid survival and reproduction are passed onto future generations.
Differential Reproduction: Survival of the Fittest (or Luckiest)
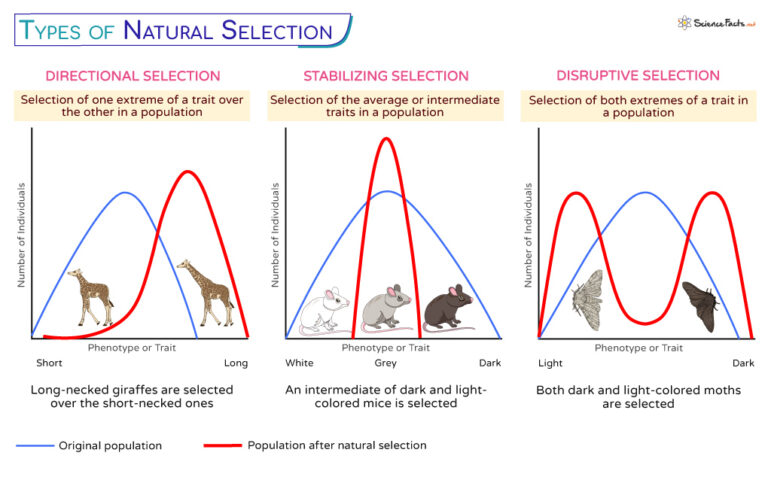
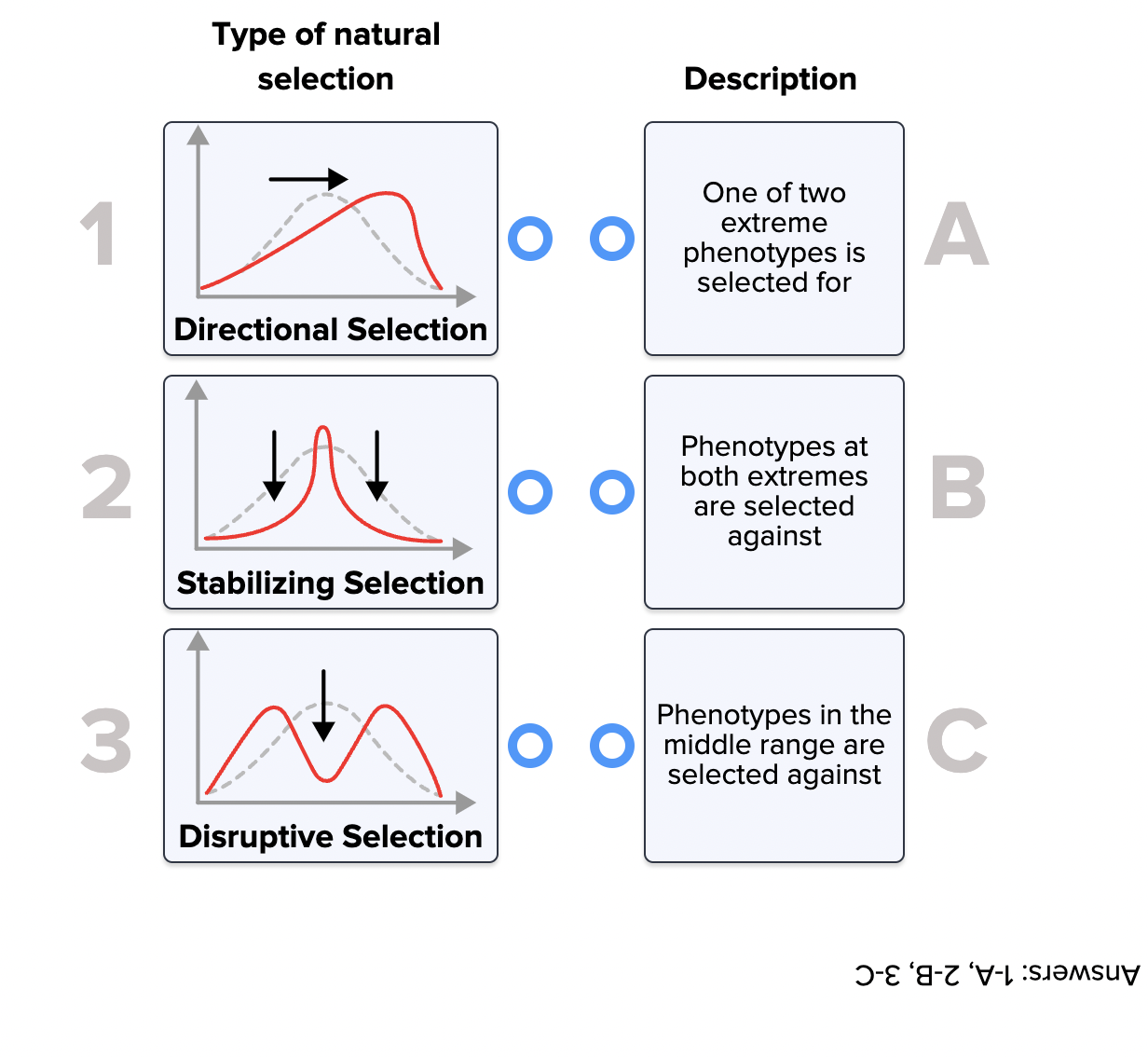
The second critical ingredient is differential reproduction. This refers to the fact that some individuals within a population leave more offspring than others. It’s not necessarily about being “fittest” in a Darwinian sense of brute strength, but rather about possessing traits that increase the likelihood of survival and reproduction in a given environment.
Differential reproduction arises from a variety of factors. Some individuals might be better at acquiring resources, like food or water. Others might be more adept at avoiding predators or resisting diseases.
Still others might be more successful at attracting mates and producing viable offspring. All of these factors contribute to differences in reproductive success.
The Role of Environmental Pressures
Environmental pressures are the selective forces that drive differential reproduction. These pressures can be biotic (e.g., competition, predation, parasitism) or abiotic (e.g., climate, resource availability, natural disasters).
Organisms with traits that are well-suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on those advantageous traits to their offspring. Conversely, organisms with less favorable traits are less likely to survive and reproduce, leading to a decrease in the frequency of those traits in the population.
Over time, these environmental pressures can lead to significant evolutionary changes, as populations become better adapted to their surroundings.
An Ongoing Process
Natural selection is not a one-time event, but an ongoing process. As environments change, so too do the selective pressures acting on populations. This constant interplay between variation and differential reproduction drives the continuous evolution of life on Earth.
Understanding these two key ingredients – variation and differential reproduction – provides a powerful framework for comprehending the remarkable diversity and adaptability of life. It highlights the elegance and efficiency of natural processes in shaping the living world around us.
By studying these fundamental principles, we can gain insights into everything from the evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria to the development of new crop varieties that are better adapted to a changing climate. The study of natural selection continues to be of vital importance.