Why Is My Wifi Cutting In And Out
Imagine this: You're finally in the zone, crafting that perfect email, streaming the climax of your favorite show, or video conferencing with family across the miles. Suddenly, the spinning wheel of doom appears. The video freezes, the email stalls, and you're left staring blankly at a screen, wondering what gremlin has invaded your Wi-Fi again.
The frustratingly common experience of intermittent Wi-Fi connectivity plagues homes and offices worldwide. But why does this happen? Understanding the root causes, from simple interference to complex network configurations, can empower you to troubleshoot and reclaim a stable internet connection.
Understanding the Basics of Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi, short for Wireless Fidelity, allows devices to connect to the internet without physical cables. It uses radio waves to transmit data between your devices (laptops, phones, tablets) and a router, which is connected to your internet service provider (ISP). The router then relays this data to and from the internet.
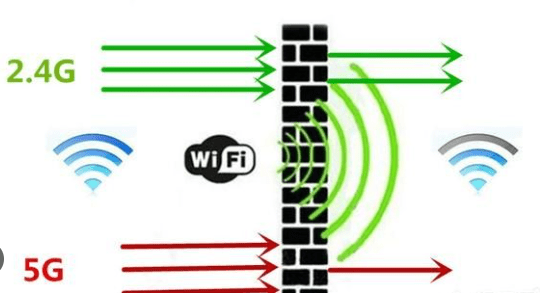
These radio waves operate on specific frequencies, usually 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Each frequency has its advantages and disadvantages; 2.4 GHz offers a longer range but is more susceptible to interference, while 5 GHz provides faster speeds but a shorter range.
Common Culprits Behind Dropped Connections
1. Interference: The Invisible Enemy
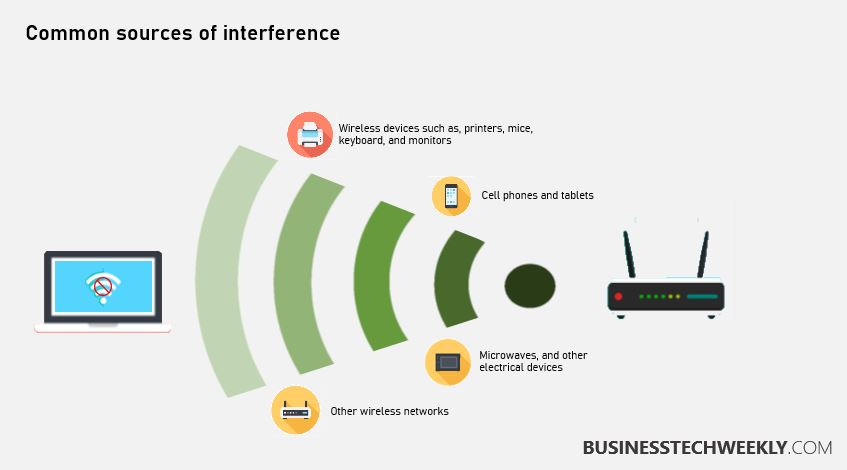
One of the most common causes of Wi-Fi instability is interference. Many devices in our homes emit radio waves that can disrupt Wi-Fi signals. Think microwave ovens, Bluetooth speakers, cordless phones, and even neighboring Wi-Fi networks.
According to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), the 2.4 GHz band, in particular, is heavily congested, leading to more interference. This crowding can cause your Wi-Fi signal to weaken or drop out completely.
2. Router Placement: Location, Location, Location
Where you place your router significantly impacts its performance. Obstacles like walls, metal objects, and even large bodies of water can weaken or block Wi-Fi signals.
A router tucked away in a closet or hidden behind a metal cabinet won't perform as well as one placed in a central, open location. Elevation also plays a role; placing your router on a higher shelf can improve signal distribution.
3. Router Age and Firmware: Keeping Up with the Times
Like any electronic device, routers age and become less efficient over time. Older routers may not support the latest Wi-Fi standards or have the processing power to handle multiple connected devices.
Outdated firmware can also cause connectivity issues. Firmware is the software that controls the router's functions, and updates often include bug fixes, security patches, and performance improvements. Check your router manufacturer's website for available updates. Regular firmware updates are crucial for optimal performance.
4. Too Many Connected Devices: Overcrowding the Network
Every router has a limit to the number of devices it can efficiently support simultaneously. When too many devices are connected and actively using the internet, the router can become overwhelmed, leading to slowdowns and dropped connections.
Consider the bandwidth demands of each device. Streaming video, playing online games, and downloading large files require significant bandwidth, putting a strain on your router.
5. ISP Issues: Blame the Source
Sometimes, the problem isn't within your home network but with your internet service provider. Outages, maintenance, or network congestion on the ISP's end can all cause intermittent internet connectivity.
Check your ISP's website or social media for reported outages in your area. You can also contact their customer support to inquire about potential issues. It's always good to rule out external factors before diving into troubleshooting your own network.
Troubleshooting Tips and Tricks
1. The Classic Reboot: Turn It Off and On Again
The simplest solution is often the most effective. Rebooting your router can resolve many minor glitches and clear temporary memory issues.
Unplug your router from the power outlet, wait 30 seconds, and then plug it back in. Allow a few minutes for the router to fully restart and reconnect to the internet.
2. Optimize Router Placement: Find the Sweet Spot
Experiment with different router locations to find the optimal spot for signal coverage. Keep it away from walls, metal objects, and other sources of interference.
Consider using a Wi-Fi analyzer app on your smartphone to measure signal strength in different areas of your home. These apps can help you identify dead zones and find the best location for your router.
3. Upgrade Your Router: A Worthwhile Investment
If your router is several years old, upgrading to a newer model can significantly improve your Wi-Fi performance. Look for routers that support the latest Wi-Fi standards (e.g., Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E) for faster speeds and improved range.
Mesh Wi-Fi systems are also a great option for larger homes or areas with thick walls. These systems use multiple nodes placed throughout your home to create a seamless Wi-Fi network.
4. Manage Connected Devices: Prioritize Bandwidth
Identify devices that are consuming the most bandwidth and limit their usage during peak hours. Some routers allow you to prioritize bandwidth for specific devices, ensuring that your most important devices have a stable connection.
Consider using a wired connection for devices that require a consistently stable connection, such as gaming consoles or desktop computers.
5. Change Wi-Fi Channel: Find a Clear Path
Routers broadcast Wi-Fi signals on specific channels within the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. If multiple routers in your area are using the same channel, it can cause interference.
Use a Wi-Fi analyzer app to identify the least congested channel and change your router's channel settings accordingly. Most routers allow you to change the channel through their web interface.
6. Contact Your ISP: When All Else Fails
If you've tried all the troubleshooting steps and your Wi-Fi is still cutting in and out, it's time to contact your ISP. They can run diagnostics on your connection and identify any issues on their end.
They may also be able to provide you with a new modem or router if your current equipment is faulty.
The Future of Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi technology continues to evolve, with new standards like Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E offering significant improvements in speed, range, and capacity. These advancements promise to alleviate many of the common Wi-Fi issues we face today.
As our homes become increasingly connected, a stable and reliable Wi-Fi connection is more important than ever. By understanding the factors that can cause Wi-Fi to cut in and out and taking proactive steps to optimize your network, you can enjoy a seamless online experience. According to a Statista report, the number of connected devices is expected to reach 75 billion worldwide by 2025. This makes managing your home network even more important.
Conclusion: Reclaiming Your Connection
Wi-Fi woes can be incredibly frustrating, but armed with the right knowledge and troubleshooting techniques, you can often resolve these issues yourself. From addressing simple interference to upgrading your router, there are many steps you can take to improve your Wi-Fi stability.
So, next time your Wi-Fi starts acting up, don't despair. Take a deep breath, follow these tips, and reclaim your connection. A stable and reliable Wi-Fi network is within your reach, enabling you to stay connected, productive, and entertained in today's digital world.
![Why Is My Wifi Cutting In And Out How to Fix a Laptop that Won’t Connect to WiFi [2024 Guide]](https://www.cgdirector.com/wp-content/uploads/media/2023/02/Wi-Fi-Connectivity-Issues-In-A-Laptop.jpg)



![Why Is My Wifi Cutting In And Out WiFi Not Showing Up WINDOWS 11 [2025] BEST FIX](https://www.thecpuguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/WIFI-Manage-Know-Networks-1024x640.jpg)
![Why Is My Wifi Cutting In And Out Why Does my WiFi Keep Disconnecting? [Solved on Windows 10 PC]](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/content/images/size/w2000/2021/11/wifi.png)